Combining Two Diagnostic Tests Drastically Reduces Cancer Miss Rates
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 17 May 2016 |
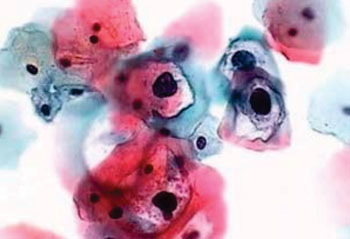
Image: A photomicrograph of an abnormal Pap smear showing changes consistent with Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) and Mild Dysplasia. Note the irregular perinuclear cytoplasmic clearing, which is the key characteristic of identifying HPV visually on a Pap smear (Photo courtesy of Dr. Cynthia D Booth, MD).
The Papanicolaou (Pap) test is recommended for women between 21 and 65 years old as a screening test for cervical cancer. Women 30 and older who are negative on co-testing may wait as long as five years for their next testing, but physicians still recommend annual examinations.
In recent years, high-risk human papillomavirus (hrHPV) testing for triaging atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance and co-testing with cytology have been implemented in clinical practice. However, clinical data for primary screening with human papillomavirus (HPV) testing alone are currently lacking.
Scientists at the Houston Methodist Hospital (Houston, TX, USA) and their colleagues retrospectively reviewed the correlation of cytology, histology, and hrHPV testing through the use of a cytology laboratory quality assurance database with 130,648 Papanicolaou (Pap) tests interpreted at the BioReference Laboratories (Houston, TX, USA) and Houston Methodist Hospital between March 1, 2013, and June 30, 2014. Among the 47,499 patients who had undergone cytology-HPV co-testing, 1,654 underwent follow-up biopsies.
The sensitivities of the hrHPV and Pap tests were 80.8% and 81.2%, respectively, for detecting any type of cervicovaginal dysplasia and 91.3% and 90.9%, respectively, for high-grade cervicovaginal lesions. For the 253 biopsy-confirmed high-grade cervicovaginal lesions (cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2+, adenocarcinoma in situ, or carcinoma), the false-negative rates for hrHPV and Pap tests were 8.7% and 9.1%, respectively. When they combined the tests, the teams found only three of the 253 cases were double negatives for both the Pap and hrHPV test. Therefore the false-negative rate for cytology-hrHPV co-testing was only 1.2%.
Dina Mody, MD, director of cytopathology at Houston Methodist Hospital and co-author of the study said, “We have known that neither test is perfect and misses a certain number of cases, but we did not realize until we analyzed the data just how impactful the combination of these tests would be. The numbers tell me that Obstetrics and Gynecology specialists need to regularly offer co-testing, and woman age 30 or older need to proactively request co-testing.” The study was published in the May 2016 issue of the journal Cancer Cytopathology.
Related Links:
Houston Methodist Hospital
BioReference Laboratories
In recent years, high-risk human papillomavirus (hrHPV) testing for triaging atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance and co-testing with cytology have been implemented in clinical practice. However, clinical data for primary screening with human papillomavirus (HPV) testing alone are currently lacking.
Scientists at the Houston Methodist Hospital (Houston, TX, USA) and their colleagues retrospectively reviewed the correlation of cytology, histology, and hrHPV testing through the use of a cytology laboratory quality assurance database with 130,648 Papanicolaou (Pap) tests interpreted at the BioReference Laboratories (Houston, TX, USA) and Houston Methodist Hospital between March 1, 2013, and June 30, 2014. Among the 47,499 patients who had undergone cytology-HPV co-testing, 1,654 underwent follow-up biopsies.
The sensitivities of the hrHPV and Pap tests were 80.8% and 81.2%, respectively, for detecting any type of cervicovaginal dysplasia and 91.3% and 90.9%, respectively, for high-grade cervicovaginal lesions. For the 253 biopsy-confirmed high-grade cervicovaginal lesions (cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2+, adenocarcinoma in situ, or carcinoma), the false-negative rates for hrHPV and Pap tests were 8.7% and 9.1%, respectively. When they combined the tests, the teams found only three of the 253 cases were double negatives for both the Pap and hrHPV test. Therefore the false-negative rate for cytology-hrHPV co-testing was only 1.2%.
Dina Mody, MD, director of cytopathology at Houston Methodist Hospital and co-author of the study said, “We have known that neither test is perfect and misses a certain number of cases, but we did not realize until we analyzed the data just how impactful the combination of these tests would be. The numbers tell me that Obstetrics and Gynecology specialists need to regularly offer co-testing, and woman age 30 or older need to proactively request co-testing.” The study was published in the May 2016 issue of the journal Cancer Cytopathology.
Related Links:
Houston Methodist Hospital
BioReference Laboratories
Latest Molecular Diagnostics News
- Ultra-Sensitive DNA Test Identifies Relapse Risk in Aggressive Leukemia
- Blood Test Could Help Detect Gallbladder Cancer Earlier
- New Blood Test Score Detects Hidden Alcohol-Related Liver Disease
- New Blood Test Predicts Who Will Most Likely Live Longer
- Genetic Test Predicts Radiation Therapy Risk for Prostate Cancer Patients
- Genetic Test Aids Early Detection and Improved Treatment for Cancers
- New Genome Sequencing Technique Measures Epstein-Barr Virus in Blood
- Blood Test Boosts Early Detection of Brain Cancer
- Molecular Monitoring Approach Helps Bladder Cancer Patients Avoid Surgery
- Genetic Tests to Speed Diagnosis of Lymphatic Disorders
- Changes In Lymphatic Vessels Can Aid Early Identification of Aggressive Oral Cancer
- New Extraction Kit Enables Consistent, Scalable cfDNA Isolation from Multiple Biofluids
- New CSF Liquid Biopsy Assay Reveals Genomic Insights for CNS Tumors
- AI-Powered Liquid Biopsy Classifies Pediatric Brain Tumors with High Accuracy
- Group A Strep Molecular Test Delivers Definitive Results at POC in 15 Minutes
- Rapid Molecular Test Identifies Sepsis Patients Most Likely to Have Positive Blood Cultures
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Ultra-Sensitive DNA Test Identifies Relapse Risk in Aggressive Leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a rare but aggressive blood cancer in which relapse after allogeneic stem cell transplant remains a major clinical challenge, particularly for patients with NPM1-mutated disease.... Read more
Blood Test Could Help Detect Gallbladder Cancer Earlier
Gallbladder cancer is one of the deadliest gastrointestinal cancers because it is often diagnosed at an advanced stage when treatment options are limited. Early symptoms are minimal, and current screening... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Hidden Gut Viruses Linked to Colorectal Cancer Risk
Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains a leading cause of cancer mortality in many Western countries, and existing risk-stratification approaches leave substantial room for improvement. Although age, diet, and... Read more
Three-Test Panel Launched for Detection of Liver Fluke Infections
Parasitic liver fluke infections remain endemic in parts of Asia, where transmission commonly occurs through consumption of raw freshwater fish or aquatic plants. Chronic infection is a well-established... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
More than 7 million Americans live with Alzheimer’s disease, and related health and long-term care costs are projected to reach nearly USD 400 billion in 2025. The disease has no cure, and symptoms often... Read more
AI-Powered Biomarker Predicts Liver Cancer Risk
Liver cancer, or hepatocellular carcinoma, causes more than 800,000 deaths worldwide each year and often goes undetected until late stages. Even after treatment, recurrence rates reach 70% to 80%, contributing... Read more
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more


















