Smartphone Device Created Performs Blood Tests
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 03 Apr 2014 |
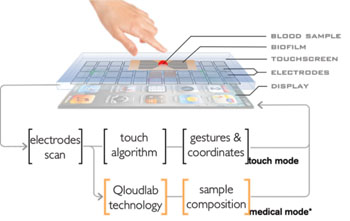
Image: Schematics of the Qloudlab smartphone device (Photo courtesy of Alain Herzog).
A smartphone device has been created that can perform blood tests—an innovation that could improve the quality of life for people undergoing treatment for the prevention of blood clots.
The formation of blood clots in the arteries and veins can increase the risk of heart attack and stroke, and individuals at high risk of blood clots are often treated with anticoagulants drugs that thin the blood and prevent the clotting process.
Bioengineers at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL; Switzerland) microengineering laboratory have created a device that could allow patients undergoing anticoagulant therapy to self-monitor. The gadget consists of a small single-use film that is attached to the screen of a smartphone. The film is made of a microstructured plastic layer that is a few micrometers thick.
When blood enters the film through capillary action, the device can detect a molecule present in blood that initiates coagulation, the process by which blood forms clots. The phone is then able to interpret the results by analyzing interferences in the electric field on the surface of the smartphone's screen. This is a process similar to what happens when a finger comes into contact with the screen of a smartphone. The results are then sent to a specific smartphone application, created by Qloudlab (Lausanne, Switzerland), the start-up company based at EPFL. This data can then be sent directly to a physician, who can assess whether a patient’s treatment needs to be modified.
Qloudlab has recently applied for a patent for the device, and the creators have recently received funding from Venture Kick (St. Gallen, Switzerland) that has allowed them to recruit a biochemist. The team hopes that by the end of next year, they will have shown that the device is as reliable as a laboratory test and can progress toward commercialization. Arther Queval, MSc, the founder of Qloudlab, said, “Such a test will significantly improve the quality of life for people undergoing this kind of treatment."
Related Links:
École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne
Qloudlab
Venture Kick
The formation of blood clots in the arteries and veins can increase the risk of heart attack and stroke, and individuals at high risk of blood clots are often treated with anticoagulants drugs that thin the blood and prevent the clotting process.
Bioengineers at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL; Switzerland) microengineering laboratory have created a device that could allow patients undergoing anticoagulant therapy to self-monitor. The gadget consists of a small single-use film that is attached to the screen of a smartphone. The film is made of a microstructured plastic layer that is a few micrometers thick.
When blood enters the film through capillary action, the device can detect a molecule present in blood that initiates coagulation, the process by which blood forms clots. The phone is then able to interpret the results by analyzing interferences in the electric field on the surface of the smartphone's screen. This is a process similar to what happens when a finger comes into contact with the screen of a smartphone. The results are then sent to a specific smartphone application, created by Qloudlab (Lausanne, Switzerland), the start-up company based at EPFL. This data can then be sent directly to a physician, who can assess whether a patient’s treatment needs to be modified.
Qloudlab has recently applied for a patent for the device, and the creators have recently received funding from Venture Kick (St. Gallen, Switzerland) that has allowed them to recruit a biochemist. The team hopes that by the end of next year, they will have shown that the device is as reliable as a laboratory test and can progress toward commercialization. Arther Queval, MSc, the founder of Qloudlab, said, “Such a test will significantly improve the quality of life for people undergoing this kind of treatment."
Related Links:
École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne
Qloudlab
Venture Kick
Latest Hematology News
- Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
- New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
- Automated Hemostasis System Helps Labs of All Sizes Optimize Workflow
- Fast and Easy Test Could Revolutionize Blood Transfusions
- High-Sensitivity Blood Test Improves Assessment of Clotting Risk in Heart Disease Patients
- AI Algorithm Effectively Distinguishes Alpha Thalassemia Subtypes
- MRD Tests Could Predict Survival in Leukemia Patients
- Platelet Activity Blood Test in Middle Age Could Identify Early Alzheimer’s Risk
- Microvesicles Measurement Could Detect Vascular Injury in Sickle Cell Disease Patients
- ADLM’s New Coagulation Testing Guidance to Improve Care for Patients on Blood Thinners
- Viscoelastic Testing Could Improve Treatment of Maternal Hemorrhage
- Pioneering Model Measures Radiation Exposure in Blood for Precise Cancer Treatments
- Platelets Could Improve Early and Minimally Invasive Detection of Cancer
- Portable and Disposable Device Obtains Platelet-Rich Plasma Without Complex Equipment
- Disposable Cartridge-Based Test Delivers Rapid and Accurate CBC Results
- First Point-of-Care Heparin Monitoring Test Provides Results in Under 15 Minutes

Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
AI Sensor Detects Neurological Disorders Using Single Saliva Drop
Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease often develop gradually and present subtle symptoms in their early stages. Because early signs are frequently vague or atypical,... Read moreNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
World’s First Portable POC Test Simultaneously Detects Four Common STIs in One Hour
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) often present with similar symptoms, making accurate diagnosis challenging without laboratory testing. Delays in identifying the exact infection can lead to inappropriate... Read more
Simple One-Hour Saliva Test Detects Common Cancers
Early detection is critical for improving cancer outcomes, yet many diagnostic tests rely on invasive procedures such as blood draws or biopsies. Researchers are exploring simpler approaches that could... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Cancer Mutation ‘Fingerprints’ to Improve Prediction of Immunotherapy Response
Cancer cells accumulate thousands of genetic mutations, but not all mutations affect tumors in the same way. Some make cancer cells more visible to the immune system, while others allow tumors to evade... Read more
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
New Imaging Approach Could Help Predict Dangerous Gut Infection
Clostridioides difficile infections affect roughly half a million people in the United States each year and are a leading cause of infectious diarrhea in healthcare settings. The bacterium can trigger... Read more
Rapid Sequencing Could Transform Tuberculosis Care
Tuberculosis remains the world’s leading cause of death from a single infectious agent, responsible for more than one million deaths each year. Diagnosing and monitoring the disease can be slow because... Read morePathology
view channel
Novel mcPCR Technology to Transform Testing of Clinical Samples
DNA methylation is an important biological marker used in the diagnosis and monitoring of many diseases, including cancer. These chemical modifications to DNA influence gene activity and can reveal early... Read more
Sex Differences in Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Linked to Faster Cognitive Decline
Sex differences in Alzheimer’s disease present ongoing diagnostic challenges, with women often experiencing a disproportionate disease burden even when preclinical amyloid-beta levels are similar to men.... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more




















