AI Model Identifies Sex-Specific Risks Associated with Brain Tumors
Posted on 10 Oct 2024
For years, cancer researchers have observed that men are more likely than women to develop glioblastoma, a deadly and aggressive form of brain cancer with a median survival of just 15 months after diagnosis. Additionally, these tumors tend to be more aggressive in men. However, identifying specific characteristics that could help predict which tumors will grow faster has remained a challenge. Now, researchers are turning to artificial intelligence (AI) to uncover these risk factors and explore how they differ between men and women.
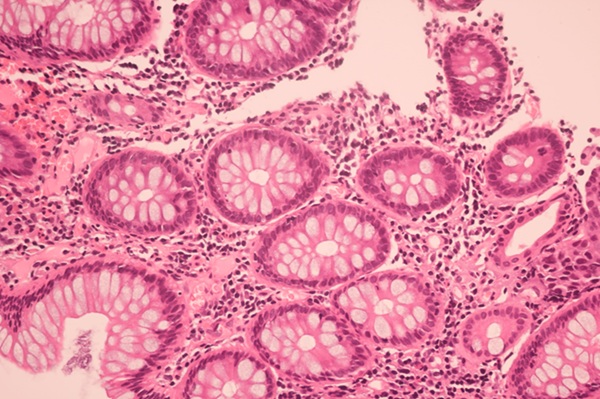
Scientists at the University of Wisconsin–Madison (Madison, WI, USA) are utilizing AI's computational capabilities to analyze large datasets of medical images, aiming to find patterns that could assist oncologists in making more informed decisions for their patients. Their goal is to address the entire range of challenges that cancer patients face, from diagnosis and prognosis to assessing treatment response. In this study, the researchers focused on digital images of pathology slides—thin sections of tumor samples—in an effort to detect patterns that might predict how fast a tumor could grow and, consequently, how long a patient might survive. Accurate prognosis is critical, as it influences treatment decisions and impacts patients’ quality of life after diagnosis.
.jpg)
To tackle this problem, the researchers developed an AI model capable of detecting subtle patterns in pathology slides that might be imperceptible to the human eye. They trained the model using data from over 250 glioblastoma studies, teaching it to recognize distinctive tumor features such as the abundance of certain cell types and the extent of the tumor’s invasion into nearby healthy tissue. Additionally, the model was trained to identify correlations between these features and patients' survival times, while also considering their sex. Through this approach, the team created an AI model that can identify risk factors for more aggressive tumors, with distinct patterns associated with each sex.
For women, higher-risk characteristics identified by the AI model included tumors that were infiltrating into healthy tissue. In men, the presence of pseudopalisading cells—cells that surround dying tissue—was linked to more aggressive tumors. The researchers' initial findings, published in Science Advances, revealed that the model also detected tumor traits associated with poorer prognoses for both sexes. The team is now extending their work to MRI data and has started using AI to analyze other cancers, such as pancreatic and breast cancers, with the goal of improving patient outcomes. This study could pave the way for more personalized treatment approaches for glioblastoma patients.
“There’s a ton of data collected in a cancer patient’s journey,” said radiology and biomedical engineering professor Pallavi Tiwari. “Right now, unfortunately, it’s usually studied in a siloed fashion, and this is where AI has huge potential. By uncovering these unique patterns, we hope to inspire new avenues for personalized treatment and encourage continued inquiry into the underlying biological differences seen in these tumors.”








 (3) (1).png)