Blood Test Shows Promise for Predicting Cancer
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 14 May 2020
Early detection of most cancers is an elusive and daunting task; nevertheless, it has remained a top priority for the cancer research community. Detecting cancer early has manifold advantages: it can increase a patient’s chances of successful treatment, prolong their survival, and substantially improve their quality of life.Posted on 14 May 2020
Developing a blood-based test that is sensitive and specific enough to ensure an accurate diagnosis of cancer before it manifests clinically has many challenges. Liquid biopsy-based tests often utilize analysis of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), DNA from cancer cells circulating in the blood, to look for the presence of DNA alterations in the cancer cells.
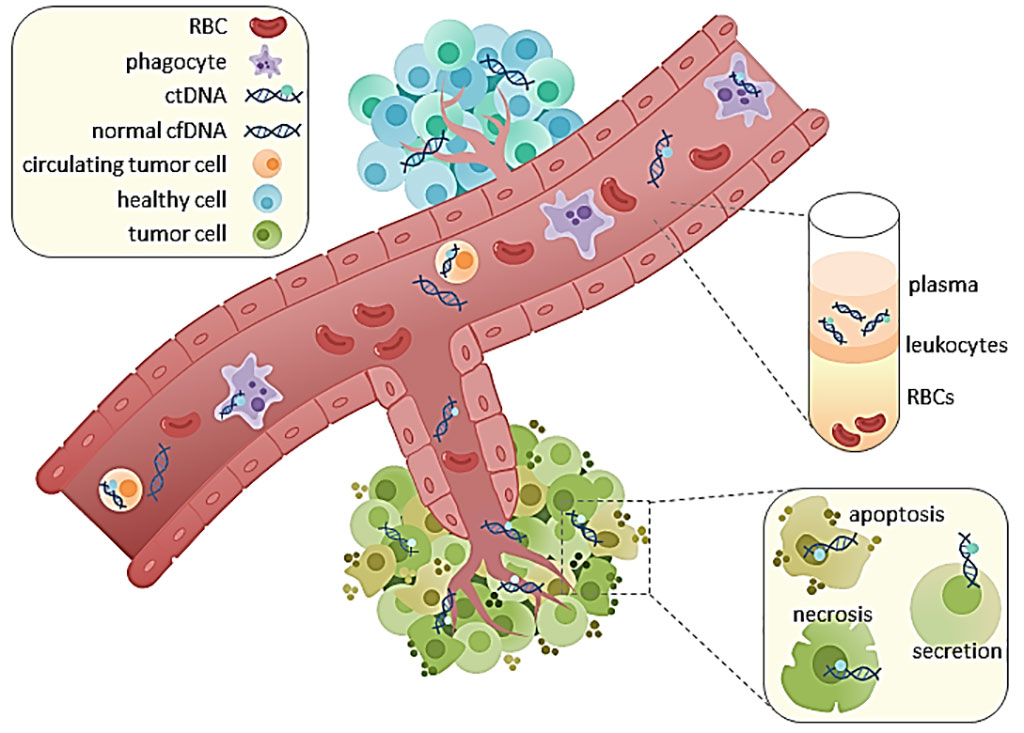
Image: Schematic diagram of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) which is found in serum and plasma fractions from blood. The mechanism of ctDNA release is unknown, though apoptosis, necrosis, and active secretion from tumor cells have been hypothesized. Once ctDNA is isolated, it can be sequenced for mutational analysis (Photo courtesy of Rachel June Wong).
A team of scientists from the Mayo Clinic (Jacksonville, Florida) and their colleagues developed a multicancer detection test through a prospective, longitudinal, case-control study of samples collected from 15,254 individuals from 142 sites in North America, of whom 8,584 had cancer and 6,670 who did not. This test is intended to be used along with guideline-recommended screening and not replace it. They had previously reported that the targeting methylation assay made by GRAIL Inc (Menlo Park, CA, USA) detected and localized more than 20 cancers types with greater than 99% specificity among individuals with cancer in the study.
The team reported on the assessment of the utility of the test in a subset of 303 individuals with a high clinical suspicion (HCS) of cancer through clinical and/or radiological assessments, but without a confirmed pathology-based diagnosis at the time of enrollment. Subsequent pathological analysis showed that in the training set of 213 subjects, 164 had clinically confirmed cancer; in the validation set of 90 subjects, 75 of them had clinically confirmed cancer.
The sensitivity of the test, or the ability of the test to detect any cancer of stages 1 to 4 in clinically confirmed cancer patients, was 40.2% and 46.7% in the training and validation sets, respectively. Excluding samples of kidney cancer, which has a low tumor fraction in the blood, improved the sensitivity of the test. The test could predict the tissue of origin in 93.9% and 100% of the cases in the training and validation sets, respectively. This prediction was accurate in 85.5% and 97.1% in the training and validation sets, respectively.
David D. Thiel, MD, a physician and lead author of the study, said, “Many cancers are detected too late. A simple and noninvasive multicancer early detection test could potentially decrease cancer-related mortality.” The study was presented at the virtual annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting held April 27 - 28, 2020.
Related Links:
Mayo Clinic
GRAIL Inc














