Genetic Defect Linked to Pediatric Liver Disease
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 04 Mar 2019
Biliary atresia (BA) is the most common cause of end‐stage liver disease in children and the primary indication for pediatric liver transplantation, yet underlying etiologies remain unknown.Posted on 04 Mar 2019
Approximately 10% of infants affected by BA exhibit various laterality defects (heterotaxy) including splenic abnormalities and complex cardiac malformations, a distinctive subgroup commonly referred to as the biliary atresia splenic malformation (BASM) syndrome.
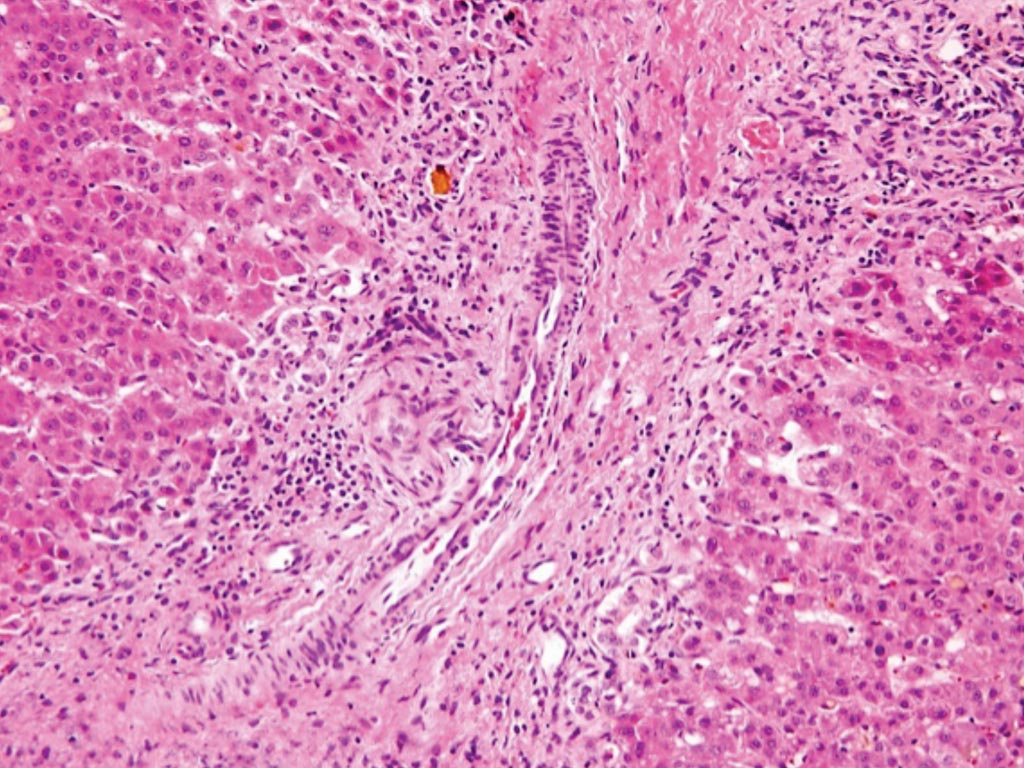
Image: A histopathology of the bile duct of a patient with biliary atresia: loss of bile ducts, brisk ductular reaction, and bile plugs (Photo courtesy of Hopkins GI Pathology).
A large team of medical scientists at the University of Colorado Anschutz (Aurora, CO, USA) sequenced DNA specimens from 67 subjects with BASM, including 58 patient-parent trios. They looked at 2,016 genes, a subset of the full genome that was associated with proteins that were candidates to cause a disease like BA. Candidate gene variants derived from the pre‐specified set of 2,016 genes associated with ciliary dysgenesis and/or dysfunction or cholestasis were prioritized according to pathogenicity, population frequency, and mode of inheritance.
The team found five BASM subjects harbored rare and potentially deleterious bi‐allelic variants in polycystin 1‐like 1, (PKD1L1), a gene associated with ciliary calcium signaling and embryonic laterality determination. Heterozygous PKD1L1 variants were found in three additional subjects. Immunohistochemical analysis of liver from the one BASM subject available revealed decreased PKD1L1 expression in bile duct epithelium when compared to normal livers and livers affected by other non‐cholestatic diseases.
Ronald Sokol, MD, a pediatric gastroenterologist and co-author of the study, said, “We don't know the cause of biliary atresia, which interferes with our ability to treat affected children. The importance of this is that scientists have never identified a gene, when mutated that causes BA. This is the first time it has been found.”
The authors concluded that whole exome sequencing identified bi‐allelic and heterozygous PKD1L1 variants of interest in eight BASM subjects from the ChiLDReN dataset. The dual roles for PKD1L1 in laterality determination and ciliary function suggest that PKD1L1 is a new, biologically plausible, cholangiocyte‐expressed candidate gene for the BASM syndrome. The study was published on January 21, 2019, in the journal Hepatology.
Related Links:
University of Colorado Anschutz