HPV Test with Cytology Adds Little Diagnostic Value
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 03 Jan 2018
The main goal of cervical screening programs is to detect and treat precancer before cancer develops. Human papillomavirus (HPV) testing is more sensitive than cytology for detecting precancer.Posted on 03 Jan 2018
Current guidance largely supports inclusion of HPV testing, which is the more sensitive of the two tests for screening for precancers. Guidance documents have varied in their advice on cervical cancer screening, and not all recommend co-testing.
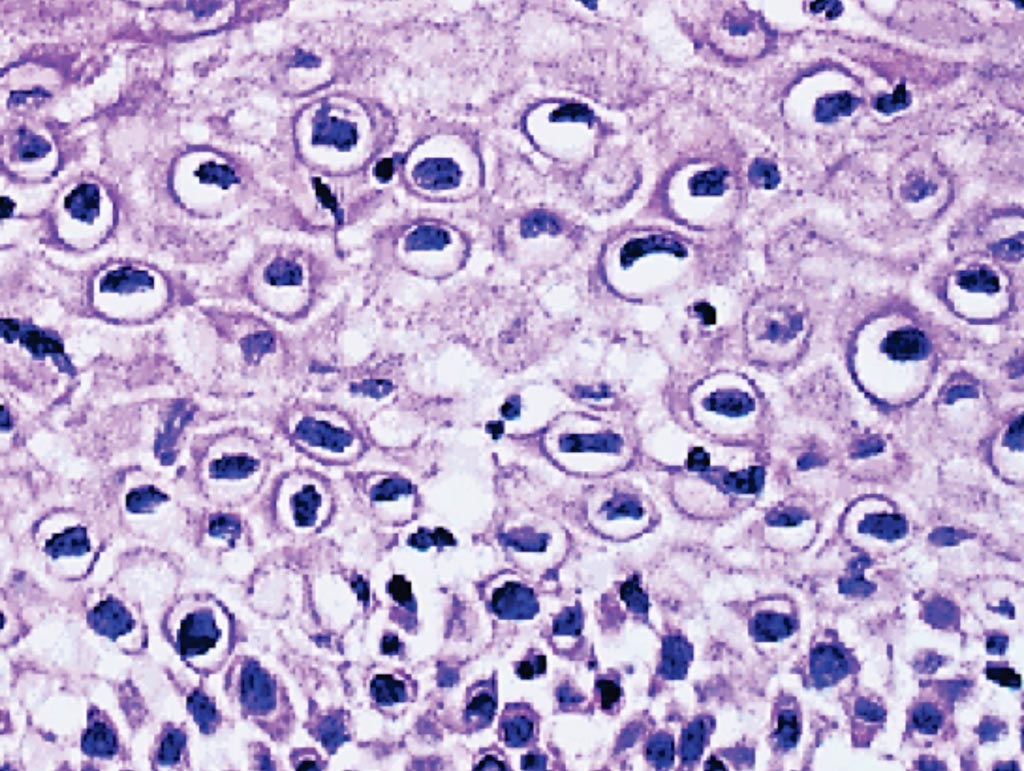
Image: A photomicrograph of a cervical cancer biopsy. Many squamous cells show dark nuclei surrounded by a clear halo. These are koilocytes and indicative of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection (Photo courtesy of Newcastle University).
A team of scientists working with US National Cancer Institute (Rockville, MD, USA) quantified the detection of cervical precancer and cancer by co-testing compared with HPV testing alone at Kaiser Permanente Northern California (KPNC, Oakland, CA, USA), where 1,208,710 women age 30 years and older have undergone triennial cervical co-testing since 2003.They analyzed screening histories of 623 preceding cervical cancers and 5,369 precancers.
The team reported HPV testing identified more women subsequently diagnosed with cancer and precancer than cytology. HPV testing was statistically significantly more likely to be positive for cancer at any time point, except within 12 months. HPV-negative/cytology-positive results preceded only small fractions of cases of precancer (3.5%) and cancer (5.9%). These cancers were more likely to be regional or distant stage with squamous histopathology than other cases.
Given the rarity of cancers among screened women, the contribution of cytology to screening translated to earlier detection of at most five cases per million women per year. Two-thirds (67.9%) of women found to have cancer during 10 years of follow-up at KPNC were detected by the first co-test performed. The added sensitivity of co-testing versus HPV alone for detection of treatable cancer affected extremely few women.
Mark Schiffman, MD, MPH, senior investigator at the National Cancer Institute and the study’s lead author, said, “The molecular test detects the virus before the clone of cells is large enough to be readily detectable as abnormal cytology on an exfoliated cell sampling. In other words, first the HPV test turns positive, and then the cytology test is positive if the infected cells reach a size of lesion large enough to be detected when the cervix is scraped for the Pap test.” The study was published on November 14, 2017, in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Related Links:
US National Cancer Institute
Kaiser Permanente Northern California














