Blood Levels of Specific MicroRNA Predict Likelihood of Metastasis
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 09 Feb 2017
The microRNA (miRNA) that regulates the activity of the ubiquitin ligase enzyme SOCS2 (Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 2) has been linked to the ability of prostate cancer to metastasize.Posted on 09 Feb 2017
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a small noncoding family of 19- to 25-nucleotide RNAs that regulate gene expression by targeting messenger RNAs (mRNAs) in a sequence specific manner, inducing translational repression or mRNA degradation, depending on the degree of complementarity between miRNAs and their targets. Many miRNAs are conserved in sequence between distantly related organisms, suggesting that these molecules participate in essential processes. In fact, miRNAs have been shown to be involved in the regulation of gene expression during development, cell proliferation, apoptosis, glucose metabolism, stress resistance, and cancer.
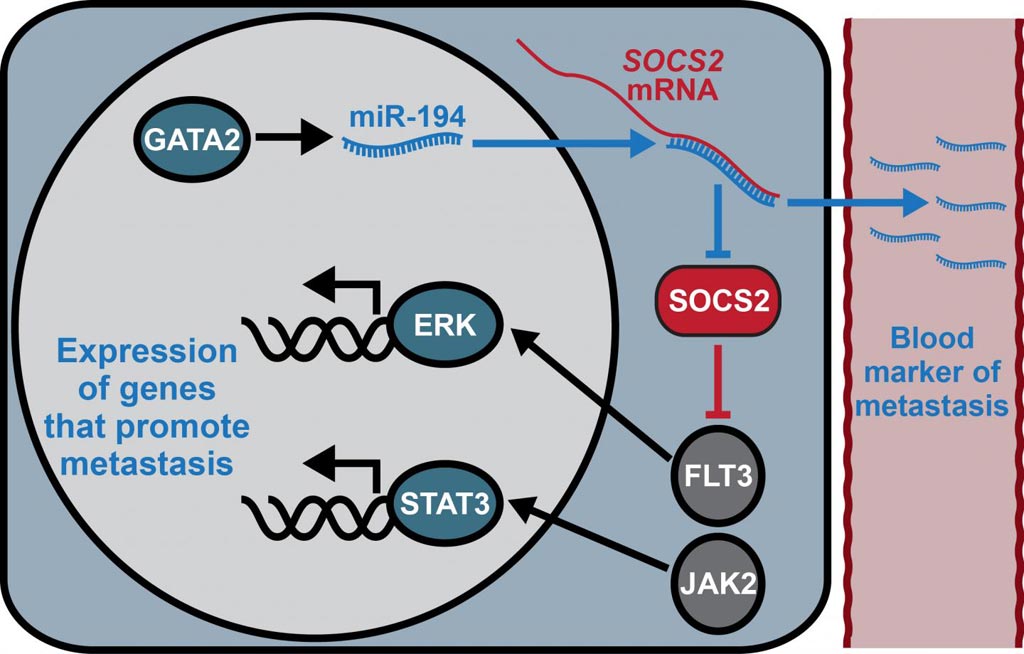
Image: MiR-194 drives prostate cancer metastasis by suppressing SOCS2 activity (Photo courtesy of Dr. Luke Selth, University of Adelaide).
Investigators at the University of Adelaide had demonstrated previously that a high level of the microRNA miR-194 in a patient's blood was associated with rapid relapse of prostate cancer following surgical removal of the tumor.
In the current study, which was published in the December 23, 2016, online edition of the journal Cancer Research, the investigators reported that miR-194 was a driver of prostate cancer metastasis. Prostate tissue levels of miR-194 were associated with disease aggressiveness and poor outcome. Ectopic delivery of miR-194 stimulated migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human prostate cancer cell lines, and stable overexpression of miR-194 enhanced metastasis of tumor xenografts. Conversely, inhibition of miR-194 activity suppressed the invasive capacity of prostate cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo.
At the molecular level the investigators found that the ubiquitin ligase SOCS2 was a direct, biologically relevant target of miR-194 in prostate cancer. Low levels of SOCS2 - caused by overexpression of miR-194 - correlated strongly with disease recurrence and metastasis in clinical specimens.
Senior author Dr. Luke A. Selth, senior research fellow at the University of Adelaide, said, "This new work explains why miR-194 is associated with a poor outcome, and in the process reveals a completely novel pathway regulating prostate cancer metastasis. Importantly, measuring miR-194 in a patient's blood at the time of diagnosis could become a test for the likelihood of metastasis. Patients with high levels of miR-194 in their blood could receive more aggressive treatment to reduce the chance of the cancer spreading to other parts of the body. There are currently no drugs that effectively inhibit the spread of prostate cancer. We propose that inhibiting miR-194 could reduce rates of metastasis in patients with aggressive disease, but the development of a drug to achieve this goal is still a long way off."














