Fast Low-Cost Alzheimer’s Tests Could Detect Disease in Early and Silent Stages
Posted on 11 Nov 2025
Early diagnosis remains one of the greatest challenges in combating Alzheimer’s disease, the most common cause of age-related dementia. With symptoms like memory loss and confusion typically appearing long after the disease has silently progressed, patients often miss the window for effective intervention. Now, researchers have developed two rapid, low-cost blood tests that can detect Alzheimer’s biomarkers long before clinical signs emerge.
Researchers at the University of Connecticut (Storrs, CT, USA) combined advanced molecular detection tools into compact, efficient systems that analyze small blood plasma samples for microRNA molecules linked to Alzheimer’s pathology. The new tests, featured in Biosensors and Biosensors and Bioelectronics, integrate CRISPR-Cas13A technology — a bacterial protein system known for gene editing — with fluorescence and electrochemiluminescence detection methods. Cas13A acts like molecular scissors that recognize and cut specific RNA sequences.
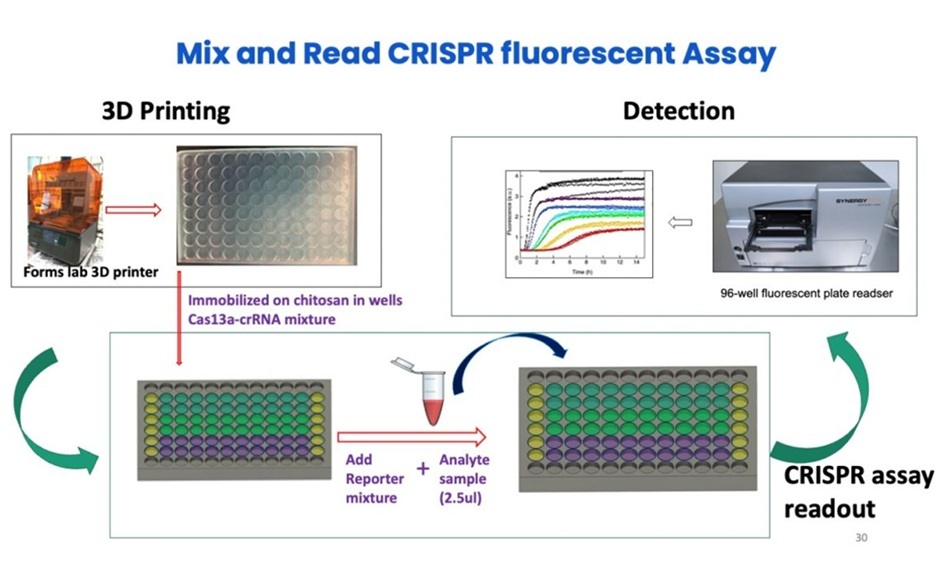
When Alzheimer's-related RNA biomarkers are present, the enzyme activates a dye molecule, causing it to glow. The intensity of this signal reveals the presence of disease-associated microRNAs. In one version, researchers built a 3D-printed tray with 96 micro-wells to anchor the Cas13A molecules for fluorescence-based detection. In the second version, the team created a miniaturized electrochemical array that can simultaneously detect three RNA biomarkers, allowing for broader and faster screening.
Their approach offers the potential for rapid, noninvasive screening directly in clinical settings, enabling doctors to detect disease markers years before cognitive symptoms appear. The team is now testing additional patient samples and tracking outcomes over time to validate predictive accuracy.
“Over the long term, we’d like to come up with a single assay that could monitor multiple types of blood biomarkers for early Alzheimer’s,” said UConn chemist Jim Rusling, who co-led the study.
Related Links:
University of Connecticut