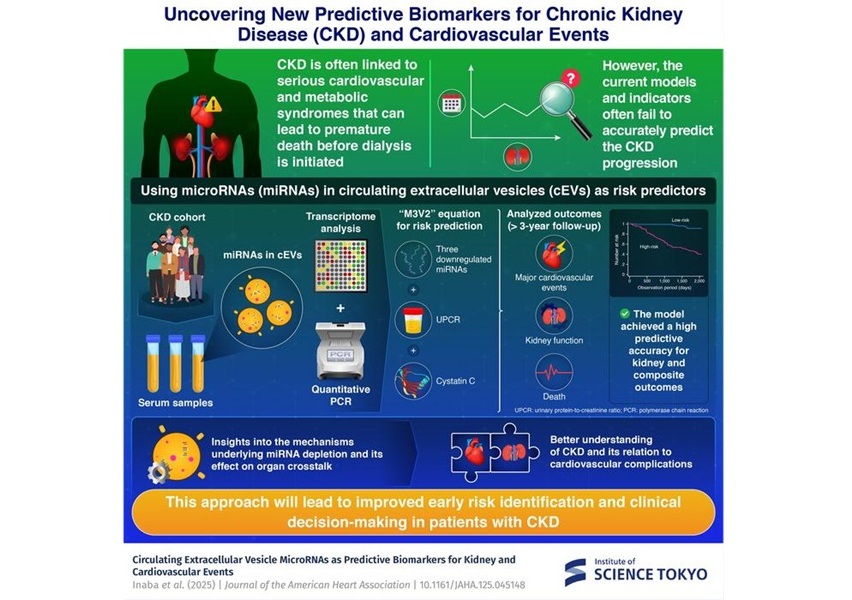
Blood Tests Can Reveal Brain Damage Caused by Neurosurgery
Posted on 01 Jun 2023
Currently, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the go-to method following brain surgery to determine potential damage to the patient's brain. MRI is useful for detecting signs of hemorrhage and areas of the brain affected by ischemia due to poor blood flow. However, its limitations lie in providing an accurate estimate of the degree of cell injury. Now, it may be possible to assess damage to the brains of patients operated on for brain tumors by measuring biomarkers in the pre-and post-surgery. The increase in these markers is correlated with the damage caused by inadequate blood flow, according to the findings of a new study.
Researchers at The University of Gothenburg (Gothenburg, Sweden) investigated the biomarkers, namely neurofilament light (NfL), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), and tau protein, in patients operated on for brain tumors. The role of these biomarkers in neurological diseases, especially Alzheimer's and other dementias, and in patients with traumatic brain injuries, has been well researched. NfL is indicative of nerve cell fiber damage, GFAP signifies injury to the brain's supporting cells, while tau points to nerve cell impairment.
In the present study, 34 adult patients diagnosed with glioma, a common brain tumor type, were included. The biomarkers' concentration was first measured a day before surgery, then successively on days one, three, five, and ten post-operation. The study found that the blood markers' levels were in sync with both the degree of injury from oxygen deprivation during surgery and the severity of the neurological deficit experienced by the patients. This means that the practice of measuring blood biomarkers could potentially pave the way for a novel approach to assess neurosurgery-induced injuries, consequently facilitating the comparison of different surgical methodologies.
“It’s also conceivable that high levels of these markers might be signs of damage that could cause brain fatigue or other cognitive problems for the patients in the somewhat longer term,” said Isak Michaëlsson, a doctoral student at the University of Gothenburg and resident in neurosurgery at Sahlgrenska University Hospital. “If so, the markers could be used to identify patients at an early stage so that they get the right kind of rehabilitation.”
Related Links:
The University of Gothenburg