An Extracellular Vesicle-based Liquid Biopsy for Early Cancer Detection
Posted on 24 Mar 2022
An extracellular vesicle-based liquid biopsy method was shown to be a promising approach for the diagnosis of stages I and II pancreatic, ovarian, and bladder cancers.
Detecting cancer at early stages significantly increases patient survival rates. Because lethal solid tumors often produce few symptoms before progressing to advanced, metastatic disease, diagnosis frequently occurs when surgical resection is no longer helpful. One promising approach to detect early-stage, curable cancers uses biomarkers present in circulating extracellular vesicles.
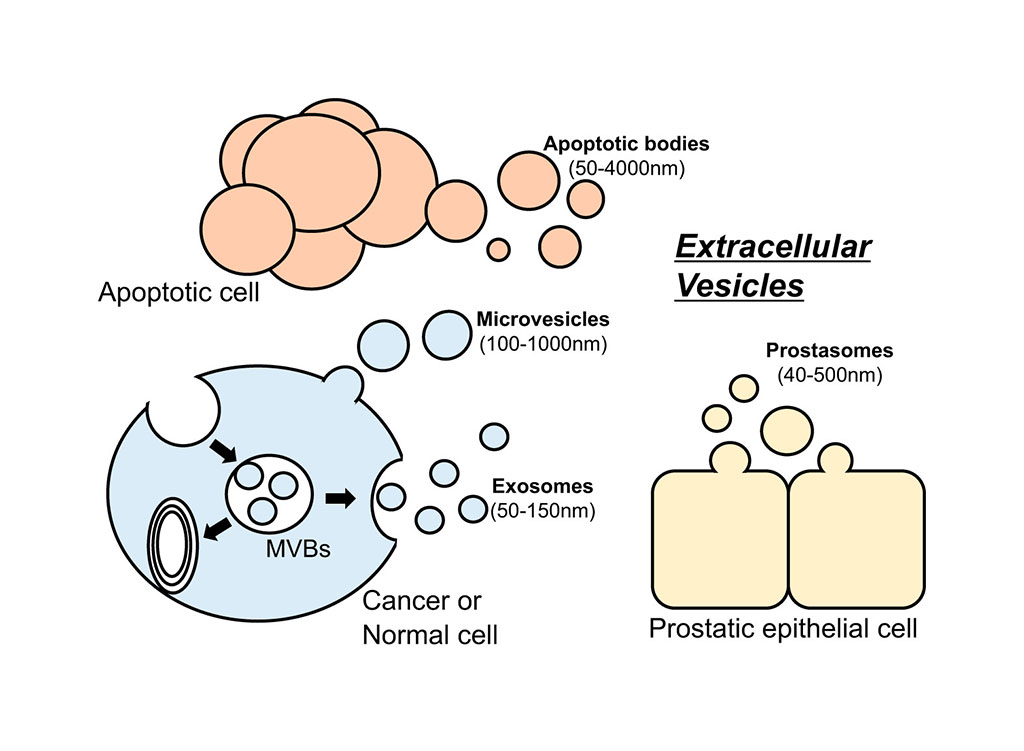
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are 40 to 200 micron cell-derived vesicles which play a critical role in cell-to-cell communication, and disease progression. These vesicles, which are present in all biological fluids, contain a wide variety of molecular species such as RNA, DNA, proteins, and lipids from their origin cells, offering a good source of biomarkers. However, existing methods for the isolation of EVs are time-consuming, lack yield and purity, and are expensive.
The clinical relevance of EVs has remained largely undetermined, partially owing to challenges in EV analysis. EVs, which contain molecules that are reflective of the cell type of origin, are increasingly being recognized as important vehicles of communication between cells and as promising diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in cancer. Despite this huge clinical potential, the wide variety of methods for separating EVs from biofluids, which provide material of highly variable purity, and the lack of knowledge regarding methodological reproducibility have impeded the entry of EVs into the clinical arena.
In this regard, investigators at the University of California, San Diego (USA) developed a liquid biopsy approach that capitalized on an alternating current electrokinetics (ACE) platform to purify EVs from plasma. They used multi-marker EV-protein measurements to develop a machine learning algorithm that could discriminate cancer cases from controls. The ACE isolation method required small sample volumes, and the streamlined process permitted integration into high-throughput workflows. The current study comprised 139 stage I and II cancer patients and 184 control subjects.
The investigators found that using ACE purification of EVs, followed by a specialized analysis of the EV protein biomarkers, successfully predicted the presence of early stage I–II pancreatic, ovarian, and bladder cancers with a sensitivity of 71.2% at 99.5% specificity. To their knowledge, this was the first report of feasibility of a blood based, multi-cancer early diagnosis (MCED) test for the detection of stage I and II cancers that employed circulating EV proteins exclusively.
"The pancreatic cancer result is particular promising," said contributing author Dr. Scott M. Lippman, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego. "These results are five times more accurate in detecting early-stage cancer than current liquid biopsy multi-cancer detection tests. Liquid biopsy tests produce promising results for cancer therapy monitoring and disease relapse, but they can cause real harm to otherwise healthy people when used for early-disease screening due to unacceptably high false-positive rates that lead to diagnostic tests that are not only expensive, but often dangerous."
The EV-based liquid biopsy method was described in the March 17, 2022, online edition of the journal Nature Communications Medicine.
Related Links:
University of California, San Diego