Researchers Recommend the Membrane Protein Flotillin as a Biomarker for Alzheimer’s Disease
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 12 Nov 2019
A team of Japanese researchers have suggested adding the protein flotillin to the arsenal of biomarkers that can be used to diagnose Alzheimer’s disease.Posted on 12 Nov 2019
Flotillins are membrane proteins that form microdomains in the plasma membrane of all mammalian cell types studied to date. They span the evolutionary spectrum, with proteins related to flotillins present in bacteria, fungi, plants, and metazoans, which suggests that they perform important, and probably conserved, functions. Flotillins have been implicated in myriad processes that include endocytosis, signal transduction, and regulation of the cortical cytoskeleton, yet the molecular mechanisms that underlie flotillin function in these different cases are still poorly understood.
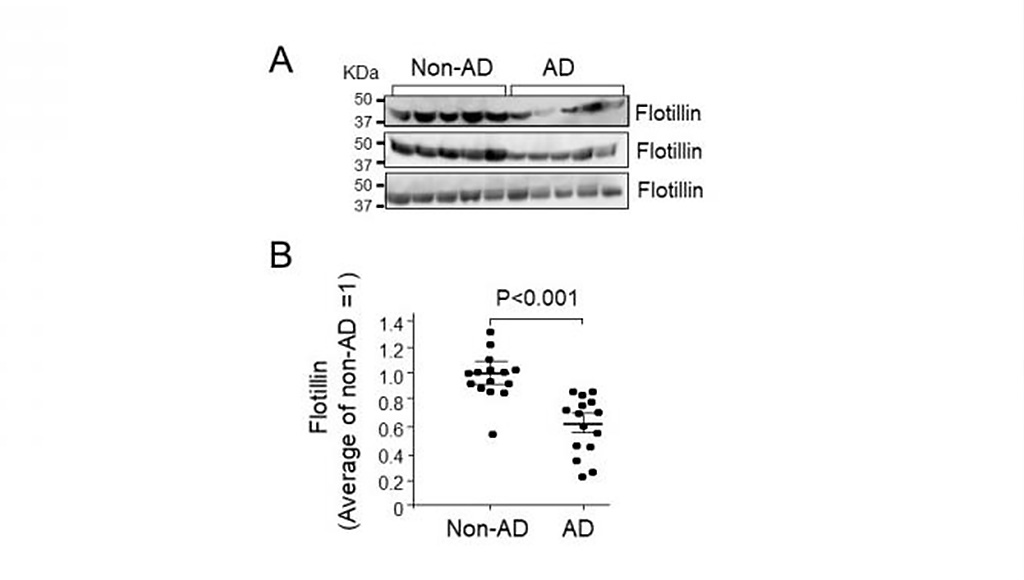
Image: Serum flotillin levels in patients with AD were lower than those in non-AD cases (Photo courtesy of Makoto Michikawa, Nagoya City University)
Investigators at Nagoya City University (Japan) had shown previously that flotillin release was reduced by amyloid beta (Abeta), a well known Alzheimer’s disease (AD) biomarker. Therefore, they designed the current study to determine whether flotillin levels would be reduced in the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) and/or serum of patients with AD.
For this study, the investigators used western blotting to analyze flotillin levels in the CSF and serum of non-AD controls and of patients with AD and mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Flotillin levels in cerebroventricular fluid (CVF) and serum of AD, vascular dementia (VaD), and non-AD autopsy cases were also analyzed.
Results revealed that flotillin levels were significantly lower in the CSF and serum of AD patients compared with those of non-AD controls. Moreover, in patients with MCI due to AD, CSF and serum flotillin levels were significantly decreased compared with those of patients with MCI not due to AD. Flotillin levels remained unchanged in CVF and serum of autopsy cases diagnosed as VaD. Serum flotillin level was negatively associated with deposition of amyloid plaques in the brain.
The investigators postulated that these results, which were published in the October 29, 2019, online edition of the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, demonstrated that serum flotillin level could serve as one of the blood markers for estimation of brain amyloid deposition and early diagnosis of AD.
Related Links:
Nagoya City University













