Genetic Scores Stratify Risk of Developing Type 1 Diabetes
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 15 May 2018
Approximately 0.3% of newborns will develop autoimmunity to pancreatic beta cells in childhood and subsequently develop type 1 diabetes before adulthood. Primary prevention of type 1 diabetes will require early intervention in genetically at-risk infants.Posted on 15 May 2018
Precision medicine typically relies on the ability to identify individuals with precise genetic elements that define a disease. These elements may be used not only to select optimal treatment modalities, but also to identify individuals who may benefit from preventative interventions.
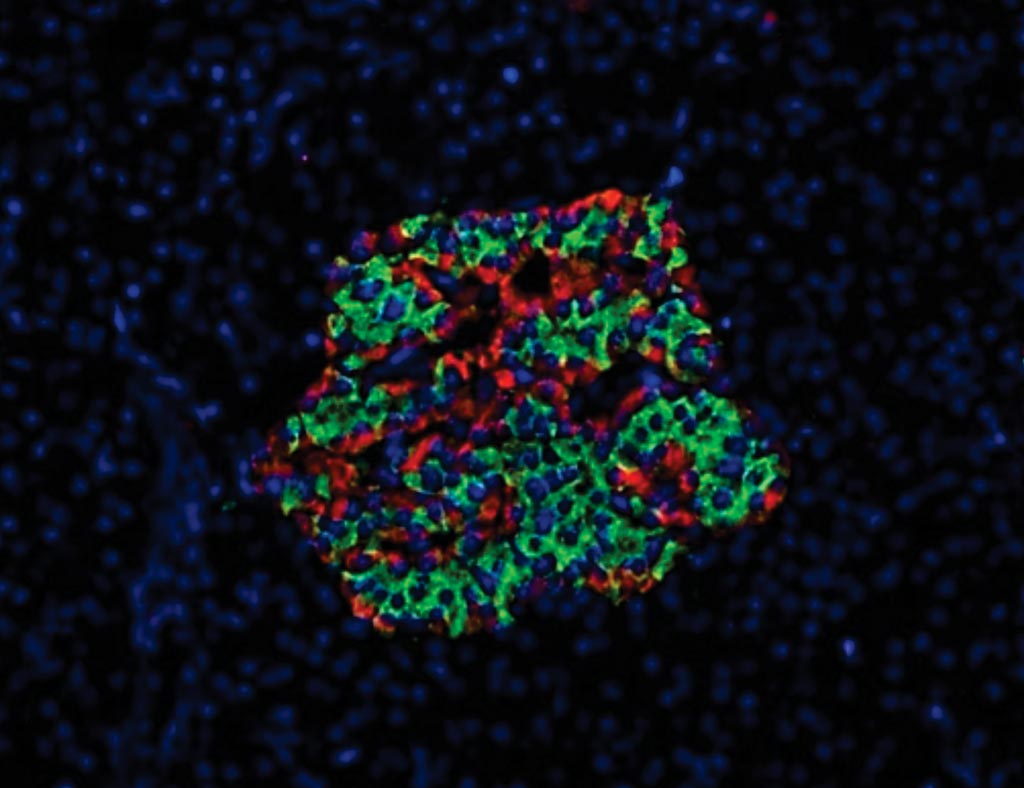
Image: Islet of Langerhans from the pancreas of a patient with chronic type 1 diabetes of 19 years duration. A single lobe of the pancreas was found to contain islets rich in residual beta cells (alpha cells in red; beta cells in green) (Photo courtesy of Diapedia).
An international team of scientists led by those at the Technische Universität Dresden (Dresden, Germany) performed a case-control study and followed genetically at-risk children at 3- to 6-monthly intervals from birth for the development of islet autoantibodies and type 1 diabetes. Infants were enrolled between September 1, 2004 and February 28, 2010 and monitored until May 31, 2016. A total of 421,047 newborn children were screened for high-risk Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genotypes for type 1 diabetes.
The risk (positive predictive value) for developing multiple islet autoantibodies (pre-symptomatic type 1 diabetes) and type 1 diabetes was determined in 4,543 children who had no first-degree relatives with type 1 diabetes and either a heterozygous HLA DR3 and DR4-DQ8 risk genotype or a homozygous DR4-DQ8 genotype, and in 3,498 of these children in whom genetic scores were calculated from 41 single nucleotide polymorphisms.
The scientists found that in the children with the HLA risk genotypes, risk for developing multiple islet autoantibodies was 5.8% by age six years, and risk for diabetes by age 10 years was 3.7%. Risk for developing multiple islet autoantibodies was 11.0% in children with a merged genetic score of >14.4 (n = 907) compared to 4.1% in children with a genetic score of equal to or less than 14.4 (n = 2,591). Risk for developing diabetes by age 10 years was 7.6% in children with a merged score of >14.4 compared with 2.7% in children with a score of ≤14.4. In children with a merged score of >14.4, risk for multiple islet autoantibodies was similar and consistently >10% in Europe and in the USA and the risk was greater in males than in females.
The authors concluded that a type 1 diabetes genetic score identified infants without family history of type 1 diabetes who had a greater than 10% risk for pre-symptomatic type 1 diabetes, and a nearly two-fold higher risk than children identified by high-risk HLA genotypes alone. This finding extends the possibilities for enrolling children into type 1 diabetes primary prevention trials. The study was published on April 3, 2018, in the journal PLoS Medicine.
Related Links:
Technische Universität Dresden