Hematological Biomarkers Predict Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 12 Oct 2020
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an inflammation-related cancer, where non-resolving inflammation contributes to its development and progression. Peripheral inflammatory cells have been shown to be associated with the prognosis of various types of cancer. Posted on 12 Oct 2020
Immune cells conduct their functions in the tumor microenvironment, and in the peripheral blood to promote metastasis The quantification of peripheral blood inflammatory cells such as neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, and platelets, as well as their ratios, have been identified and validated as novel biomarkers with prognostic significance in several cancers.
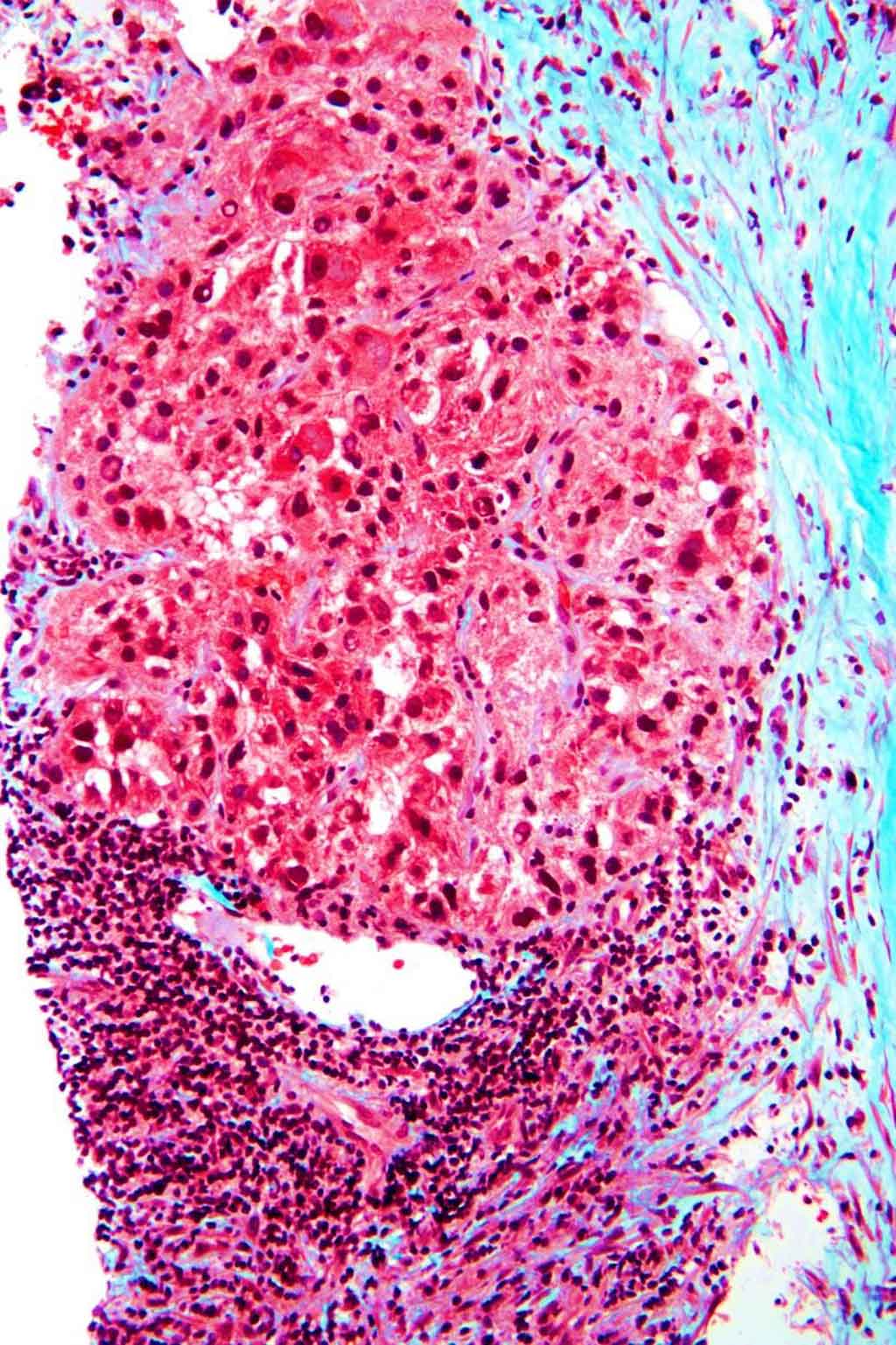
Image: Photomicrograph of histopathology of hepatocellular carcinoma, the most common form of primary liver cancer, showing end-stage cirrhosis - blue collagen (fibrosis) Mallory bodies; loss of normal liver architecture; and nuclear atypia. (Photo courtesy of Nephron).
A team of hepatologists at the Pusan National University School of Medicine (Yangsan, Republic of Korea) and their associate retrospectively analyzed 1,681 patients with HCC who were newly diagnosed between November 2008 and March 2018. Included in the study were 1,335 (79.4%) males and 346 (20.6%) females. The patients ranged in age from 27 to 88 years, and the median age was 60 years. Hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and alcoholic liver disease were diagnosed in 1,039 (61.8%), 279 (16.6%), and 184 (11.0%) patients, respectively. The frequency of patients with underlying liver cirrhosis was 85.1%.
All pretreatment routine blood cell examinations that were performed within two weeks before treatment were used for the analysis. Overall survival (OS) was calculated from the date of HCC diagnosis to the date of death or last follow-up. OS was compared for between patients with high and low neutrophils, lymphocytes, and monocytes (dichotomized by median values).
The scientist used univariate and multivariate analyses, and found that individual neutrophil, lymphocyte and monocyte cell counts were independent indicators of poor OS. High neutrophil (≥3100 × 106/L) and, monocyte (≥470 × 106/L) counts and low lymphocyte counts (< 1640 × 106/L) significantly associated with reduced OS. Neutrophil and, monocyte cell counts rose and lymphocyte counts decreased in association with advancing the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage.
The team also analyzed the combination score and found that higher neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and lower lymphocyte to monocyte ratio (LMR) had worse OS. Patients with high neutrophils and monocytes were more likely to have larger tumor size. The presence of vascular invasion was associated with high neutrophil and, monocyte counts and with low lymphocyte counts. High neutrophils and monocyte counts were associated with extrahepatic metastasis.
The authors concluded that pretreatment peripheral neutrophils, lymphocytes, and monocytes are independently associated with outcomes of patients with HCC. These cells provide a noninvasive, low-cost, easy, and reproducible biomarker that can be used in routine clinical practice to predict the prognosis of patients with HCC. The study was published on September 29, 2020 in the journal BMC Cancer.
Related Links:
Pusan National University School of Medicine










 Analyzer.jpg)



