New Test Rapidly Identifies Platelet Function Defects
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 07 Aug 2014
A multisurface and multiparameter flow assay to characterize thrombus formation in whole blood from healthy subjects and patients with platelet function deficiencies has been created. Posted on 07 Aug 2014
Parallel-plate flow chambers have been used for the last two decades to measure platelet adhesion and activation under arterial or venous flow conditions, in particular using surfaces such as extracellular matrix or collagen, but there is a need for further standardization of devices, protocols and measurement parameters.
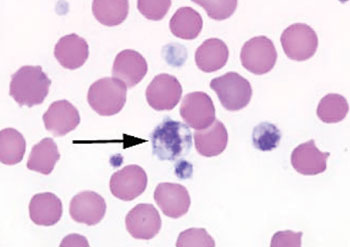
Image: Photomicrograph of a blood smear showing a giant platelet (arrowed) from a patient with hemorrhagiparous thrombocytic dystrophy (Photo courtesy of the College of American Pathologists).
A team of scientists led by those at Maastricht University (The Netherlands) obtained blood samples from healthy donors and patients who all had a well-defined platelet deficiency and mild bleeding tendency. Microspot-coated coverslips were mounted onto a transparent parallel-plate flow chamber (50 μm depth, 3 mm width and 20 mm length), and pre-rinsed. Anticoagulated whole-blood samples were perfused through the flow chamber for a time period sufficient for full-thrombus formation on collagen I spots and adherence labeled with a fluorescence marker.
A systematic comparison is made of 52 adhesive surfaces with components activating the main platelet-adhesive receptors, and of eight output parameters reflecting distinct stages of thrombus formation. Three types of thrombus formation can be identified with a predicted hierarchy of the following receptors: glycoprotein (GP) VI, C-type lectin-like receptor-2 (CLEC-2) > GPIb > α6β1 αIIbβ3 > α2β1 > CD36, α5β1, αvβ3. Application with patient blood reveals distinct abnormalities in thrombus formation in patients with severe combined immune deficiency, Glanzmann’s thrombasthenia, Hermansky–Pudlak syndrome, May–Hegglin anomaly or grey platelet syndrome. This test may be useful for the diagnosis of patients with suspected bleeding disorders or a pro-thrombotic tendency.
Johan W.M. Heemskerk, PhD, a professor and a senior author of the study said, “To develop this test we collected information on thrombosis formation in a flow chamber with flowing blood. This has never been done before on such a large scale. We can easily determine what’s wrong with the patient by counting the number of platelets in a few drops of blood. If there’s an active bleed, the platelets trigger the coagulation process to stem the bleeding. The opposite is true with thrombosis: in that case, the platelets are overactive and could cause a stroke or a heart attack.” The study was published on July 16, 2014, in the journal Nature Communications.
Related Links:
Maastricht University














