New Portable Test Detects SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in People Who Have Tested Positive for COVID-19
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 31 Mar 2021
A new easy-to-produce test quickly detects coronavirus spike-protein binding antibodies in people who have tested positive for COVID-19.Posted on 31 Mar 2021
An international research team led by scientists at the University of Oxford (Oxford, UK) has developed a portable test for antibodies that fight the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19. The test, which spots the presence of virus-fighting antibodies rather than a coronavirus infection, can be adapted to work on blood from a finger prick - making it quick and easy to use. The research team, which includes scientists from Taiwan, India, Thailand and France, as well as UK university and NHS researchers, trialed the test on patients with COVID-19, but now hope to adapt it to identify those who have successfully generated antibodies after a vaccine, versus those who may need a booster.
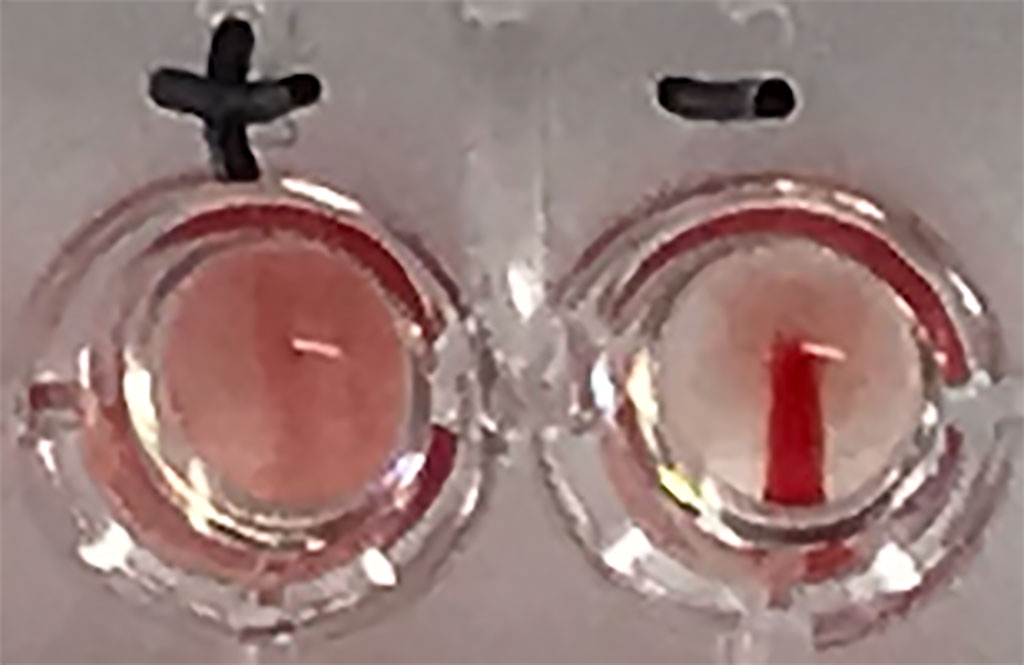

Image: New Portable Test Detects SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in People Who Have Tested Positive for COVID-19 (Photo courtesy of University of Oxford)
The scientists also hope that the large-scale use of their tests might help researchers and policy-makers track levels of protective immunity in the community. Antibodies are large proteins that lock onto and help the body’s immune system fight off disease-causing organisms, such as the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19. Both infection with the virus and vaccines can generate antibodies. There are already several commercial tests, which can detect whether someone has antibodies against the novel coronavirus, but these tests are expensive and usually need a central laboratory to analyze them. This is especially a problem in low-income countries.
The test relies on linking a part of the viral spike protein to the surface of red blood cells. When antibodies to the virus are present they create a clump of red blood cells. This clump is big enough to be seen by eye. The test also does not require any special equipment or take a long time to show the results, and is accurate. It correctly identifies coronavirus spike protein antibodies 90% of the time, with less than a 1% false positive rate. The researchers note that they can be adapted to work using blood from a finger prick sample. They now plan to use this very simple test in future trials to see if it can identify those who are protected against COVID-19 from those who may need a booster vaccination.
“Our test is very cheap to produce, so we are using existing funding from charitable donations to offer 10 million tests for research purposes to countries that cannot support very high-tech solutions,” said study lead Professor Alain Townsend from the MRC Human Immunology Unit at Oxford University.
Related Links:
University of Oxford