Lung Progenitor Cells Enable Culture of 3D Organoids for Studies
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 15 Mar 2018
An in vitro system for growth of three-dimensional lung organoids was used to characterize a line of alveolar stem cells that plays a critical role in repairing lung tissues damaged by severe influenza or other respiratory ailments such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).Posted on 15 Mar 2018
Functional tissue regeneration is required for the restoration of normal organ function after severe injury. Some organs, such as the intestine, harbor active stem cells throughout homeostasis and regeneration; more quiescent organs, such as the lung, often contain facultative progenitor cells that are recruited after injury to participate in regeneration.
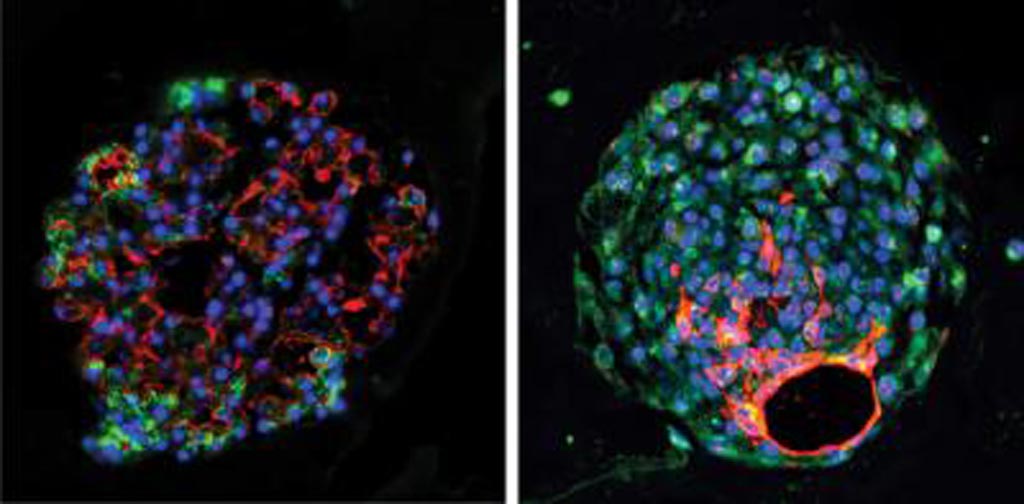
Image: Mouse (left) and human (right) alveolar progenitor cells grow into large lung organoids in culture, and make multiple types of epithelial cells including gas exchange type 1 cells (red) and surfactant-producing type 2 cells (green) (Photo courtesy of the Morrisey Laboratory, University of Pennsylvania).
To better understand the processes involved in lung tissue regeneration, investigators at the University of Pennsylvania (Philadelphia, USA) examined the epithelial cells that line the surfaces of lung gas-exchange alveoli for stem cell behavior that could restore normal respiratory function after severe injury.
The investigators reported in the February 28, 2018, online edition of the journal Nature that they had identified an alveolar epithelial progenitor (AEP) lineage, which was embedded in a larger population of epithelial cells called alveolar type 2 cells (AT2s). AEPs were shown to be a stable lineage during alveolar homeostasis but expanded rapidly to regenerate a large proportion of the alveolar epithelium after acute lung injury. AEPs exhibited a distinct transcriptome, epigenome, and functional phenotype and responded specifically to Wnt and fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling.
Human AEPs could be selectively isolated by targeting the conserved cell surface marker TM4SF1. Once isolated, these cells were used as functional human alveolar epithelial progenitor cells for growing three-dimensional lung organoids.
"From our organoid culture system, we were able to show that AEPs are an evolutionarily conserved alveolar progenitor that represents a new target for human lung regeneration strategies," said senior author Dr. Edward E. Morrisey, professor of cell and developmental biology at the University of Pennsylvania. "One of the most important places to better understand lung regeneration is in the alveoli, the tiny niches within the lung where oxygen is taken up by the blood and carbon dioxide is exhaled. To better understand these delicate structures, we have been mapping the different types of cells within the alveoli. Understanding cell-cell interactions should help us discover new players and molecular pathways to target for future therapies."
Related Links:
University of Pennsylvania