LAMP Assay Developed to Diagnose High HBV DNA Levels
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 05 May 2021 |

Image: The AMPLIX real-time polymerase chain reaction system (Photo courtesy of Biosynex)
Worldwide, 257 million people are chronically infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) and 887,000 annually die from cirrhosis or liver cancer. Since more than 95% of HBV-infected people live in low-income and middle-income countries (LMICs) and only 12-25% of infected people are eligible for anti-HBV therapy.
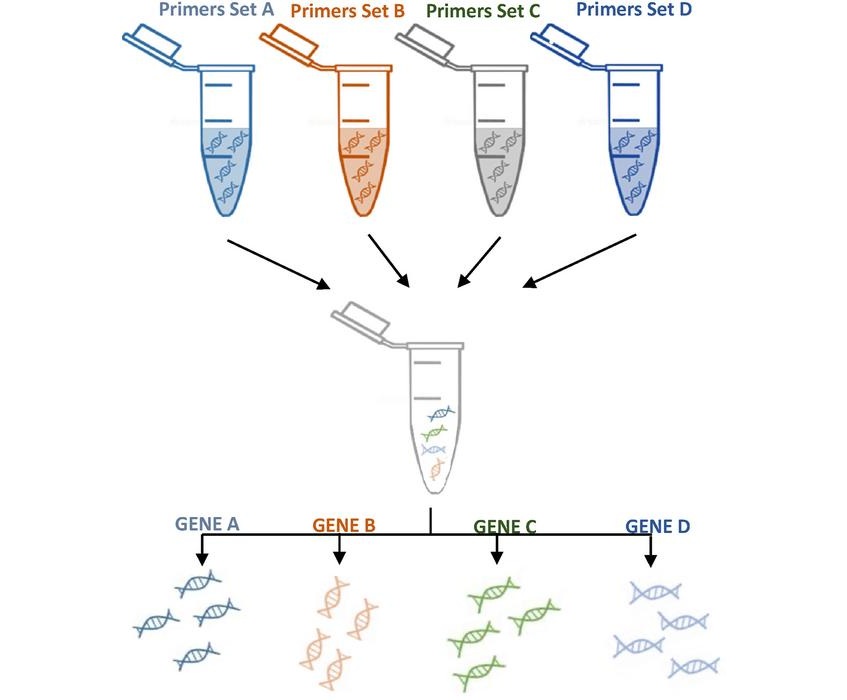
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay is a nucleic acid test (NAT) using DNA polymerase with high auto-cycling strand displacement activity and six specially designed primers. LAMP has the following characteristics allowing its use as a rapid, reliable and inexpensive point-of-care test in LMICs with a high amplification efficiency enabling rapid detection of nucleic acids.
A large team of medical scientists associated with the Pasteur Institute (Paris, France) designed Pan-genotypic primer sets on conserved HBV gene regions. Accuracy of LAMP to identify highly viremic patients was evaluated in 400 and 550 HBV-infected people in France and Senegal, respectively. Analytical validation was performed using real-time turbidimetric LAMP (Loopamp LA-500, Eiken Chemical, Japan). Viral loads were quantified using an AMPLIX real-time PCR (Biosynex, Illkirch-Graffenstaden France).
The team reported that their primers successfully detected eight major HBV genotypes/sub-genotypes (A1/2/3/B/C/D/E/F) with a detection limit ranging between 40-400 IU/mL. In France, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC), sensitivity and specificity of bead-based extraction and real-time turbidimetric LAMP were 0.95, 91.1% and 86.0%, respectively, to diagnose HBV DNA ≥20,000 IU/mL; and 0.98, 98.0% and 94.6% for ≥200,000 IU/mL. The performance did not vary by viral genotypes. In Senegal, using a field-adapted method, reagent-free boil-and-spin extraction and inexpensive end-point fluorescence detection, the AUROC, sensitivity and specificity were 0.95, 98.7% and 91.5%, respectively, to diagnose HBV DNA ≥200,000 IU/mL. The assay was not adapted to discriminate low-level viremia.
The authors concluded that they had developed a simple, rapid (60 minutes), and inexpensive (USD 8/assay) alternative to PCR to diagnose high viremia ≥200,000 IU/mL. HBV-LAMP may contribute to eliminating HBV mother-to-child transmission by identifying high-risk pregnant women eligible for antiviral prophylaxis in resource-limited countries. The study was published on April 7, 2021 in the journal Clinical Microbiology and Infection.
Related Links:
Pasteur Institute
Eiken Chemical
Biosynex
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay is a nucleic acid test (NAT) using DNA polymerase with high auto-cycling strand displacement activity and six specially designed primers. LAMP has the following characteristics allowing its use as a rapid, reliable and inexpensive point-of-care test in LMICs with a high amplification efficiency enabling rapid detection of nucleic acids.
A large team of medical scientists associated with the Pasteur Institute (Paris, France) designed Pan-genotypic primer sets on conserved HBV gene regions. Accuracy of LAMP to identify highly viremic patients was evaluated in 400 and 550 HBV-infected people in France and Senegal, respectively. Analytical validation was performed using real-time turbidimetric LAMP (Loopamp LA-500, Eiken Chemical, Japan). Viral loads were quantified using an AMPLIX real-time PCR (Biosynex, Illkirch-Graffenstaden France).
The team reported that their primers successfully detected eight major HBV genotypes/sub-genotypes (A1/2/3/B/C/D/E/F) with a detection limit ranging between 40-400 IU/mL. In France, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC), sensitivity and specificity of bead-based extraction and real-time turbidimetric LAMP were 0.95, 91.1% and 86.0%, respectively, to diagnose HBV DNA ≥20,000 IU/mL; and 0.98, 98.0% and 94.6% for ≥200,000 IU/mL. The performance did not vary by viral genotypes. In Senegal, using a field-adapted method, reagent-free boil-and-spin extraction and inexpensive end-point fluorescence detection, the AUROC, sensitivity and specificity were 0.95, 98.7% and 91.5%, respectively, to diagnose HBV DNA ≥200,000 IU/mL. The assay was not adapted to discriminate low-level viremia.
The authors concluded that they had developed a simple, rapid (60 minutes), and inexpensive (USD 8/assay) alternative to PCR to diagnose high viremia ≥200,000 IU/mL. HBV-LAMP may contribute to eliminating HBV mother-to-child transmission by identifying high-risk pregnant women eligible for antiviral prophylaxis in resource-limited countries. The study was published on April 7, 2021 in the journal Clinical Microbiology and Infection.
Related Links:
Pasteur Institute
Eiken Chemical
Biosynex
Latest Molecular Diagnostics News
- New Blood Test for Leukemia Risk Detection Could Replace Bone Marrow Sampling
- Blood Test Detects Preeclampsia Risk Months Before Symptoms Appear
- mNGS CSF Test Outperforms Traditional Microbiological Testing for Infectious Diseases
- Point-Of-Care Test to Transform Early-Stage Cervical Cancer Diagnosis
- PET/ctDNA-Guided Approach Helps Determine Lymphoma Treatment
- Next-Generation 'Agnostic Diagnostics' to Detect Respiratory Viruses at POC
- First-Ever Test of Cure for Chagas Disease Determines Treatment Effectiveness
- Capsule Sponge Test Could Replace Endoscopies for Monitoring Esophageal Cancer Risk
- Nasal Swab Test Offers Simpler and Less Costly Virus Screening in High-Risk Settings
- DNA Test Accurately Predicts Resistance to Common Chemotherapy Treatments
- Umbilical Cord Blood Test Can Detect Early Sepsis in Preterm Infants
- Simple Blood Test Predicts Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer's Patients
- Molecular Biomarkers Pave Way for New Tests to Diagnose and Predict Breast Cancer
- Portable CRISPR-Based Molecular Technology Brings Highly Accurate Diagnostics to Point of Need
- Palm-Sized Device Detects Disease-Related Genetic Material In 45 Minutes
- Advanced Computational Tool Paves Way for Diagnostic Tests to Detect Hidden Genetic Mutations
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
New Reference Measurement Procedure Standardizes Nucleic Acid Amplification Test Results
Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) play a key role in diagnosing a wide range of infectious diseases. These tests are generally known for their high sensitivity and specificity, and they can be developed... Read more
Pen-Like Tool Quickly and Non-Invasively Detects Opioids from Skin
Opioid drugs such as fentanyl, morphine, and oxycodone are the primary substances associated with overdose cases in the United States. Standard drug screening procedures typically involve collecting blood,... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
New Blood Test for Leukemia Risk Detection Could Replace Bone Marrow Sampling
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is a condition typically associated with aging, where blood stem cells fail to develop into fully functional blood cells. Early and accurate diagnosis is vital, as MDS can... Read more
Blood Test Detects Preeclampsia Risk Months Before Symptoms Appear
Preeclampsia, a pregnancy-related complication characterized by elevated blood pressure and organ dysfunction, remains a major contributor to maternal and infant health issues globally. Existing screening... Read moreHematology
view channel
Disposable Cartridge-Based Test Delivers Rapid and Accurate CBC Results
Complete Blood Count (CBC) is one of the most commonly ordered lab tests, crucial for diagnosing diseases, monitoring therapies, and conducting routine health screenings. However, more than 90% of physician... Read more
First Point-of-Care Heparin Monitoring Test Provides Results in Under 15 Minutes
Heparin dosing requires careful management to avoid both bleeding and clotting complications. In high-risk situations like extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), mortality rates can reach about 50%,... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Blood Test Detects Organ Rejection in Heart Transplant Patients
Following a heart transplant, patients are required to undergo surgical biopsies so that physicians can assess the possibility of organ rejection. Rejection happens when the recipient’s immune system identifies... Read more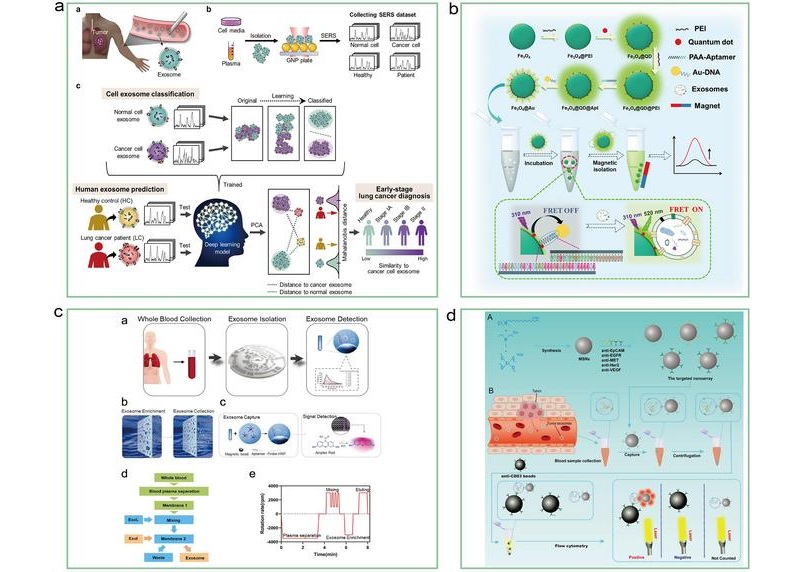
Liquid Biopsy Approach to Transform Diagnosis, Monitoring and Treatment of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer continues to be a major contributor to cancer-related deaths globally, with its biological complexity and diverse regulatory processes making diagnosis and treatment particularly difficult.... Read more
Computational Tool Exposes Hidden Cancer DNA Changes Influencing Treatment Resistance
Structural changes in tumor DNA are among the most damaging genetic alterations in cancer, yet they often go undetected, particularly when tissue samples are degraded or of low quality. These hidden genomic... Read morePathology
view channel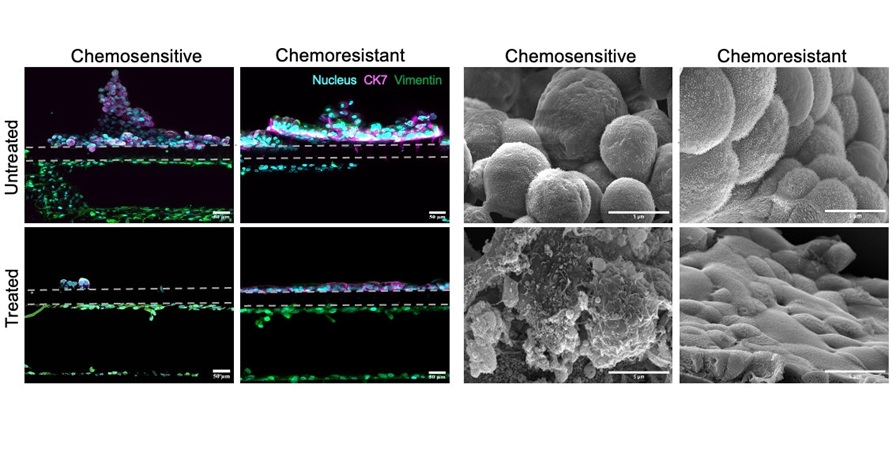
Cancer Chip Accurately Predicts Patient-Specific Chemotherapy Response
Esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC), one of the two primary types of esophageal cancer, ranks as the sixth leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide and currently lacks effective targeted therapies.... Read more
Clinical AI Solution for Automatic Breast Cancer Grading Improves Diagnostic Accuracy
Labs that use traditional image analysis methods often suffer from bottlenecks and delays. By digitizing their pathology practices, labs can streamline their work, allowing them to take on larger caseloads... Read more
Saliva-Based Testing to Enable Early Detection of Cancer, Heart Disease or Parkinson’s
Saliva is one of the most accessible biological fluids, yet it remains underutilized in clinical practice. While saliva samples are used to perform genetic tests to determine, for example, paternity, the... Read moreTechnology
view channel
New POC Biosensing Technology Improves Detection of Molecular Biomarkers
Traditional diagnostic procedures in medicine typically involve sending a patient’s blood or tissue samples to clinical laboratories, where trained scientists perform testing and data interpretation.... Read more
Enhanced Lab Data Management and AI Critical to Labs of the Future, Finds Survey
Data plays a key role in the transformation of today’s digital laboratories, acting both as a key challenge and a catalyst for innovation, as revealed by a survey of over 150 scientists.... Read moreIndustry
view channel
AMP Releases Best Practice Recommendations to Guide Clinical Laboratories Offering HRD Testing
Homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) testing identifies tumors that are unable to effectively repair DNA damage through the homologous recombination repair pathway. This deficiency is often linked... Read more







.jpg)