Smartphone Microscopic Method Detects Cryptosporidium and Giardia
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 30 Sep 2020
Food and water-borne illness arising from the consumption of contaminated food and water are serious health hazards globally. Cryptosporidium and Giardia are the major food and water‒borne parasites. The infection occurs mainly by (oo)cyst phase of the parasites. Posted on 30 Sep 2020
Several highly sensitive and specific methods have been described to detect Giardia cyst and Cryptosporidium oocyst in food, water, and fecal samples. Commonly used approaches are polymerase chain reaction, flow cytometry, and optical microscopic examination. However, these techniques need a good laboratory facility, well trained user and are expensive.
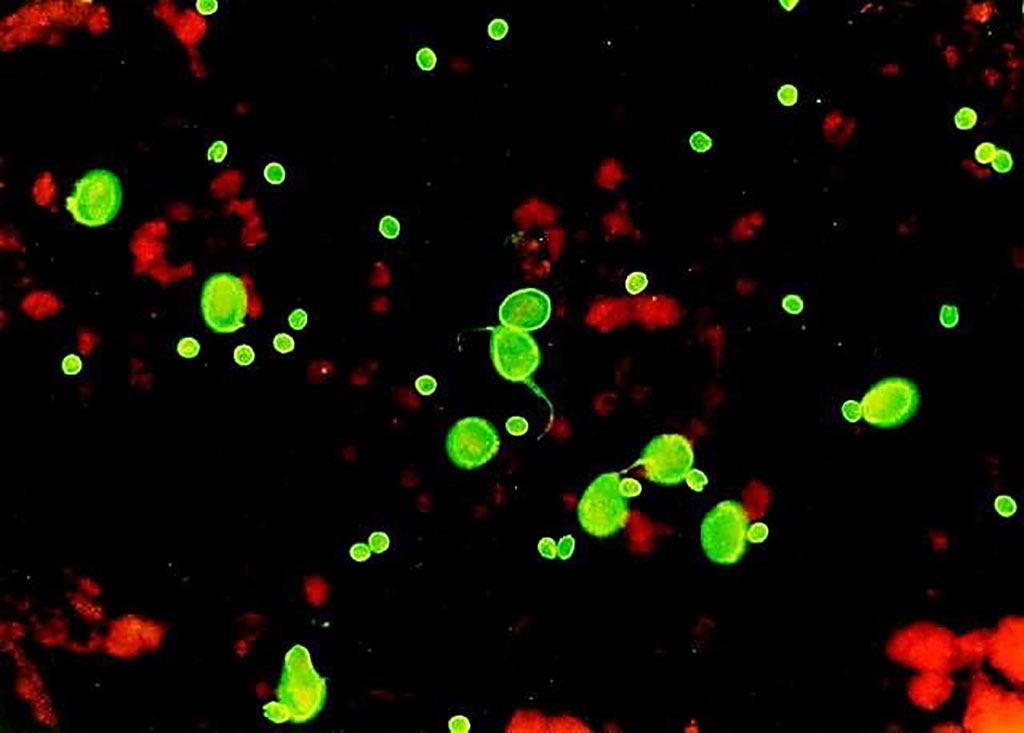
Image: Cryptosporidium oocysts and the larger Giardia cysts stained by Crypto/Giardia IFA kit (Photo courtesy of Cellabs).
Scientists at the Kathmandu Institute of Applied Sciences (Kathmandu, Nepal) developed a smartphone based microscopic assay method to screen (oo)cysts of Cryptosporidium and Giardia contamination of vegetable and water samples. The method consisting of a ball lens of 1 mm diameter, white LED as illumination source and Lugols's iodine staining provided magnification and contrast capable of distinguishing (oo)cysts of Cryptosporidium and Giardia. The analytical performance of the method was tested by spike recovery studies.
Ten microliters of concentrated sample were stained with 10 μL of diluted Lugol's iodine (1:2 in water) and subsequently loaded into hemocytometer. The sample was incubated for six minutes. The (oo)cysts were screened and enumerated in four quadrants of the hemocytometer under smartphone microscope. The cysts on the same hemocytometer were simultaneously counted by Trinocular brightfield microscope (Amscope, Irvine, CA, USA). Triplicate measurement was made for each concentrated suspension. The spiked samples were also examined with a fluorescent microscope (Labomed Inc, Los Angeles, CA, USA).
The team tested the smartphone microscope system for detecting (oo)cysts on seven types of vegetable (n = 196) and river water (n = 18) samples. They reported that 42% vegetable and 39% water samples were found to be contaminated with Cryptosporidium oocyst. Similarly, 31% vegetable and 33% water samples were contaminated with Giardia cyst. The recovery of Giardia ranged from 10.2 ± 4.0% in cabbage to 37.6 ± 2.4% in water and recovery of Cryptosporidium ranged from 26.8 ± 10.3% in cabbage to 49.2 ± 10.9% in tomato using smartphone microscope measurement.
The authors concluded that the smartphone based microscopic assay can be a low-cost alternative for screening of (oo)cyst of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in resource limited settings. The approximate cost of the microscope (excluding the cost of smartphone) is ~ USD 15. This method also has the potential to be used in clinical settings. The study was published on September 8, 2020 in the journal PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases.
Related Links:
Kathmandu Institute of Applied Sciences
Amscope
Labomed Inc














