AI Model for Brain Tumor Classification Advances Neuropathology
Posted on 28 Dec 2023
Diffuse gliomas, which comprise a large portion of malignant brain tumors in adults, include various types such as astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma, and glioblastoma. Diagnosing these types of gliomas traditionally relies on an analysis that integrates histological characteristics with molecular details, a method that presents significant complexities when attempting to develop a comprehensive diagnostic model from whole-slide images (WSIs). The immense gigapixel resolution of WSIs renders the use of standard convolutional neural networks for analysis impractical. To address this challenge, researchers have now introduced a novel integrated diagnostic model that can automatically classify adult-type diffuse gliomas directly from unannotated standard whole-slide pathological images, eliminating the need for additional molecular testing.
Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS, Beijing, China) have devised this deep learning model capable of parsing WSIs and categorizing gliomas without the need for detailed manual annotations. This model adheres to the strict classification guidelines outlined in the 2021 fifth edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System. The model underwent training and validation across a diverse dataset comprising 2,624 patient cases collected from three different hospitals.
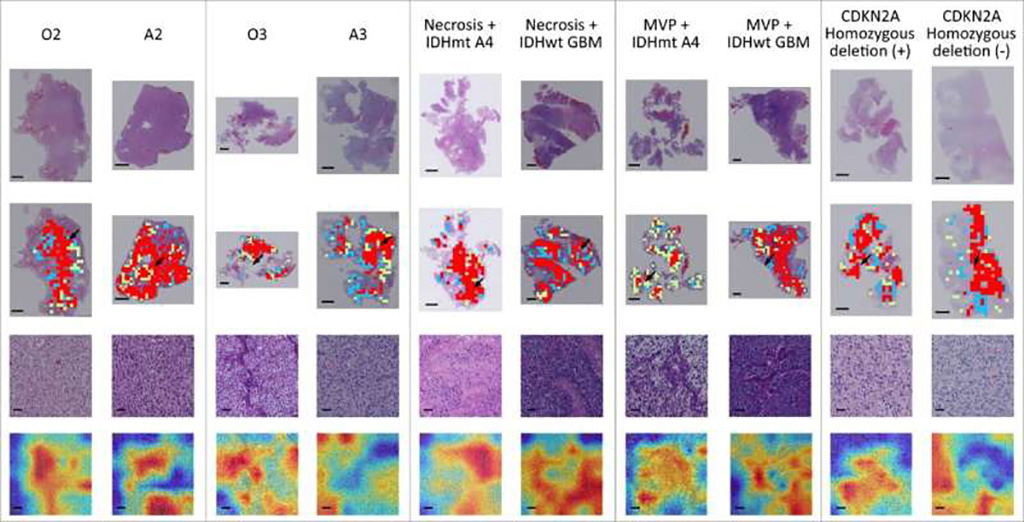
The model's effectiveness was evaluated based on its classification accuracy, sensitivity to various glioma types and grades, and its capability to differentiate between genotypes that exhibit similar histological characteristics. The outcomes of the experiments indicate that the model demonstrates robust performance, with all areas under the receiver operator curve exceeding 0.90. This performance was noted in its ability to classify major tumor types, identify tumor grades within each type, and, notably, distinguish between tumor genotypes that share the same histological features.
"Our integrated diagnosis model has the potential to be used in clinical scenarios for automated and unbiased classification of adult-type diffuse gliomas," said CAS Prof. Li Zhicheng who led the research team. "The future research will focus on improving this model to have multi-center, multi-racial datasets."
Related Links:
Chinese Academy of Sciences













