Prognostic Values of Platelet Parameters in Gynecological Tumors Patients
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 24 Mar 2020
Gynecologic cancers often involve the uterus, ovaries, cervix, vulva, vagina, fallopian tubes, or the peritoneum. The most common gynecologic cancer in the USA is endometrial cancer, followed by ovarian cancer. Many gynecologic cancers manifest as pelvic masses.Posted on 24 Mar 2020
Platelets are small, hematopoietic, and anucleate cells released by bone marrow megakaryocytes in the bloodstream, and were described as the major effectors of several physiological and pathophysiological processes, such as hemostasis, thrombosis, immunological defense mechanisms, and the development of inflammation.
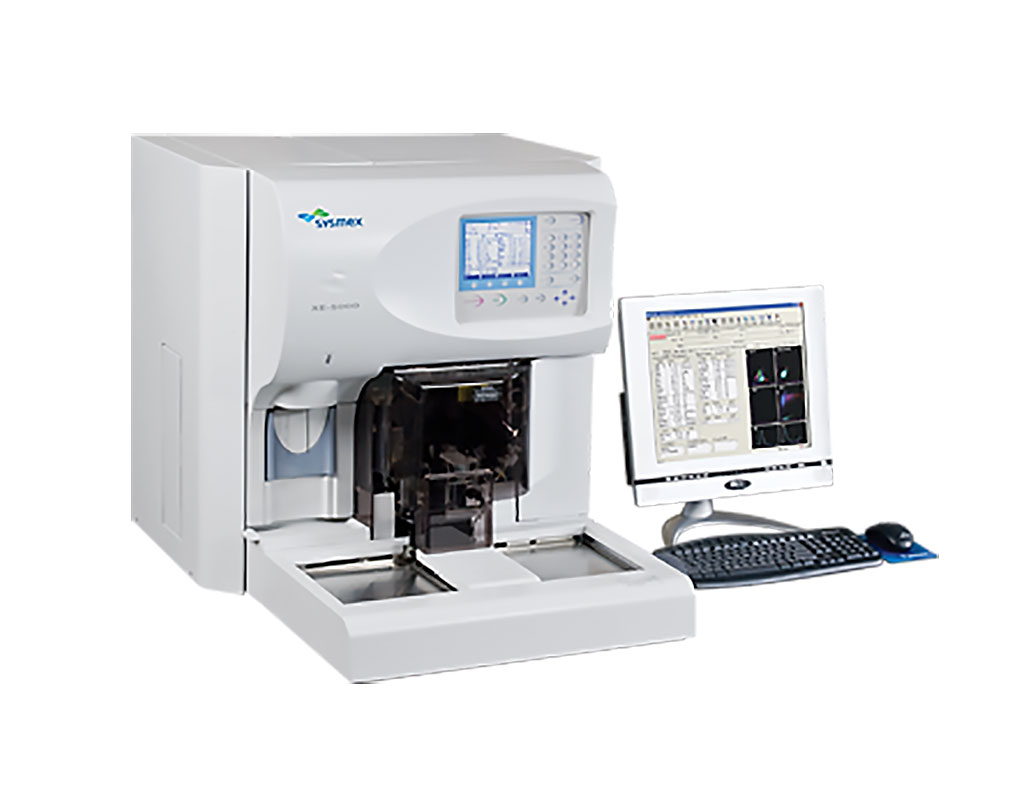

Image: The XE-5000 Hematology Analyzer is a high volume analyzer that offers unique clinical parameters to aid in better patient care (Photo courtesy of Sysmex Corporation).
Medical Laboratory Scientists at the Wenzhou Medical University (Wenzhou, China) included in a study a total of 1,062 women who underwent gynecological tumor surgery for the first time between January 2014 and February 2016. Platelet parameters were recorded on the basis of the first complete blood count (CBC) within two weeks before surgery.
Differences of platelet parameters (platelet count [PLT], plateletcrit [PCT], mean platelet volume [MPV], platelet‐large cell rate [P‐LCR], and platelet distribution width [PDW]) between different categories were analyzed by nonparametric test. Venous blood was drawn from patients after admission which would transport to the laboratory within one hour and measured by Sysmex XE5000 hematology analyzer (Sysmex Corporation, Kobe, Japan). All microscopic slides and immunohistochemistry of tissue excised intraoperatively were reviewed by two pathologists. Computed tomography (CT) scan and lymph node metastasis sites were used to detect metastatic status.
The investigators reported that the platelet count and PCT were significantly increased, and MPV and P‐LCR were significantly reduced in malign and benign gynecological tumor groups compared with the controls; PDW had no significant differences. There were no significant differences in PLT, PCT, MPV, P‐LCR, and PDW between different tumor locations and pathologic types. The optimal cutoff values of PLT, PCT, MPV and P‐LCR were 274, 0.26, 10.08, and 24.8 (AUC: 0.661, 0.643, 0.593, 0.562), and PCT had preferable sensibility and specificity (50.8% and 70.4%) in predicting the presence of gynecological tumors. According to survival analysis, increased PLT (≥274 × 109/L) and PCT (≥0.26), and induced MPV (<10.08 fL) and P‐LCR (<24.8%) were associated with shorter overall survival.
The authors concluded that the increased PLT and the decreased platelet volume were not only common in gynecological cancer, but also usual in gynecological benign tumors. PLT, PCT, MPV, and P‐LCR were useful auxiliary parameters for predicting the presence of gynecological tumor. In addition, increased PLT and PCT, or decreased MPV and P‐LCR indicated a heavier tumor burden and shorter overall survival. The study was published on March 13, 2020 in the Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.
Related Links:
Wenzhou Medical University
Sysmex Corporation