Novel, High-Accuracy Blood Test Can Screen for Multiple Cancers
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 26 Nov 2019
A new targeted methylation-based assay has been developed that is able to screen blood samples for more than 20 types of cancer at all stages, including lung cancer, with high accuracy and it also correctly pinpoints the tissue of origin (TOO).Posted on 26 Nov 2019
Methylation works to activate or deactivate genes, and altered methylation suggests cancer. Besides lung cancer, the methylation-based assay screens for anal, bladder, colorectal, esophageal, head and neck, liver/bile duct, lymphoma, ovarian, pancreatic, plasma cell neoplasm, and stomach cancers, among others. Methylation works to activate or deactivate genes, and altered methylation suggests cancer.
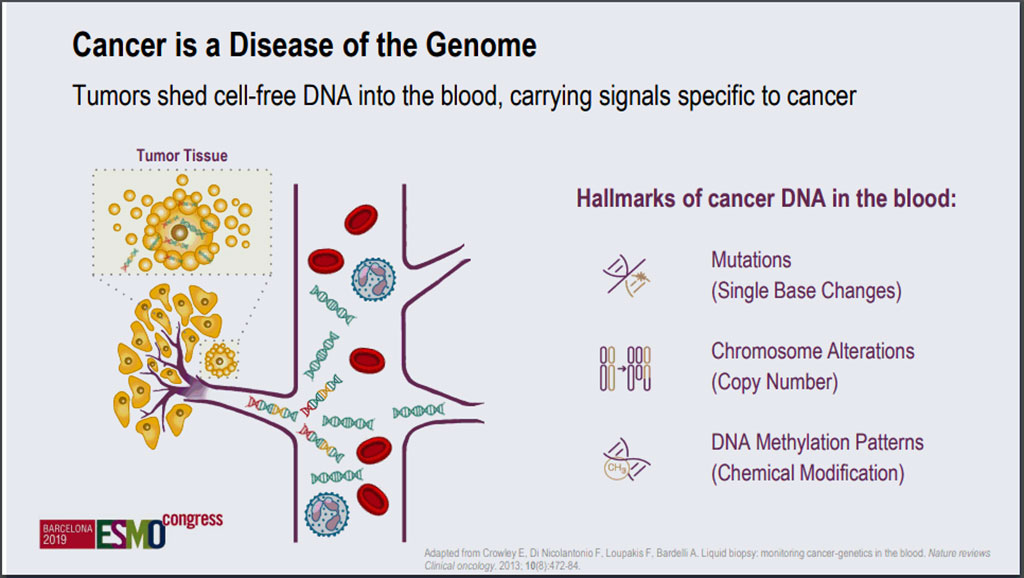
Image: Novel, high-accuracy blood test can screen for multiple cancers (Photo courtesy of European Society for Medical Oncology)
Scientists from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (Boston, MA, USA) and their colleagues in a prospective study colleagues analyzed cell-free DNA (cfDNA), DNA that is released into the bloodstream following cell death, in 3,583 blood samples, of which 1,530 were from patients with cancer and 2,053 were from cancer-free individuals. The assay functions by quantifying abnormal methylation patterns in cfDNA, whereas liquid biopsies isolate genetic mutations or other types of DNA alterations.
The team reported that the overall specificity of the assay was 99.4%, and the sensitivity for aggressive cancers was 76%. Specifically, sensitivity was 32% in stage I cancer, 76% in stage II cancer, 85% in stage III cancer, and 93% in stage IV cancer. In all cancer types, sensitivity was 55%. The scientists also noted that 97% of samples yielded TOO results, with correct TOO recorded in 89% of samples. For diagnosing non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), biopsy is currently the gold standard, while molecular testing is used to shed light on treatment options in advanced-stage or even early-stage NSCLC.
The scientists stated that in many types of cancer, methylation is better reflective of cancer diagnosis than are other types of mutations. Indeed, they had previously found that whole-genome bisulfite sequencing (i.e., the methylation assay) outperformed whole-genome and targeted-sequencing strategies in detecting cancer. Ultimately, if this new methylation-based assay was to pick up even a small number of early-stage cancer types, many patients would benefit from earlier treatment.
Geoffrey R. Oxnard, MD, a medical oncologist and lead author of the study, said, “Our previous work indicated that methylation-based assays outperform traditional DNA-sequencing approaches to detecting multiple forms of cancer in blood samples. The results of the new study demonstrate that such assays are a feasible way of screening people for cancer.” The study was presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress, (ESMO), held in September 27–October 1, 2019, in Barcelona, Spain.
Related Links:
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute