High Levels of Blood Hormones Raise Prostate Cancer Risk
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 11 Nov 2019
Men with higher levels of 'free' testosterone and a growth hormone in their blood are more likely to be diagnosed with prostate cancer. Other factors such as older age, ethnicity and a family history of the disease are already known to increase a man's risk of developing prostate cancer.Posted on 11 Nov 2019
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in men. Usually prostate cancer grows slowly and is initially confined to the prostate gland, where it may not cause serious harm. However, while some types of prostate cancer grow slowly and may need minimal or even no treatment, other types are aggressive and can spread quickly.
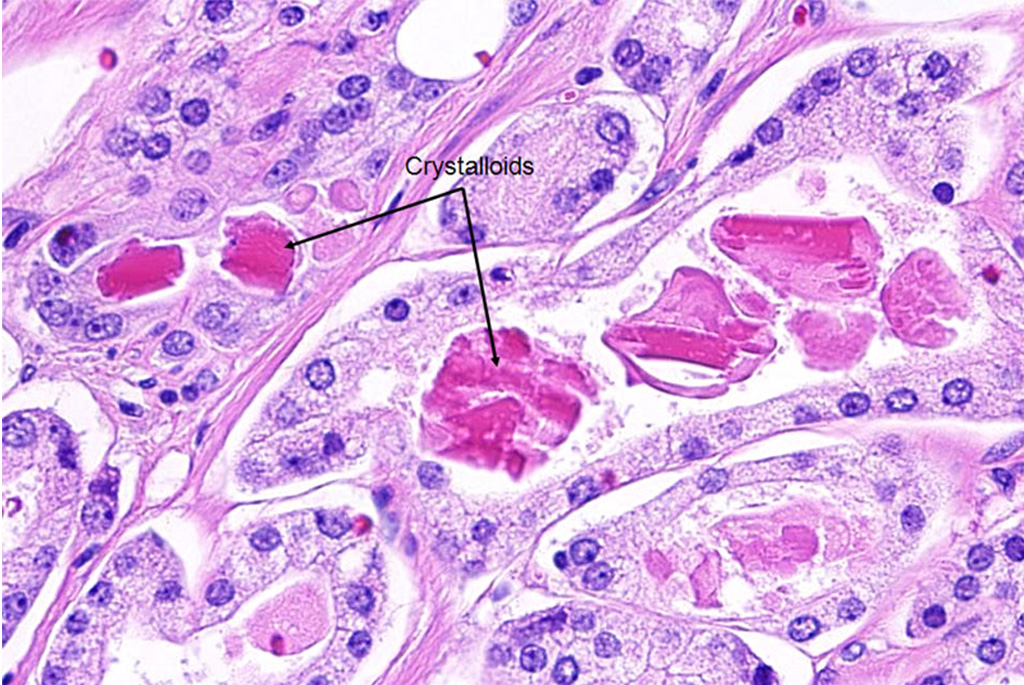
Image: Histopathology of prostate cancer: crystalloids (bright eosinophilic rhomboid to prismatic structures, seen in ~40% cancer) and amorphous eosinophilic secretions (Photo courtesy the American Urological Association).
A team of scientists working with those at the University of Oxford (Oxford, UK) studied 200,452 men who are part of the UK Biobank project. All were free of cancer when they joined the study and were not taking any hormone therapy. The men gave blood samples that were tested for their levels of testosterone and a growth hormone called insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I). The team calculated levels of free testosterone, which is testosterone that is circulating in the blood and not bound to any other molecule and can therefore have an effect in the body. A subset of 9,000 of men gave a second blood sample at a later date, to help the investigators account for natural fluctuations in hormone levels. The men were followed for an average of six to seven years to see if they went on to develop prostate cancer. Within the group, there were 5,412 cases and 296 deaths from the disease.
The scientists reported that men with higher concentrations of the two hormones in their blood were more likely to be diagnosed with prostate cancer. For every increase 5 nmol/L of IGF-I, men were 9% more likely to develop prostate cancer. For every increase of 50 pmol/L, there was a 10% increase in prostate cancer risk. Looking at the population as a whole, the scientists say their findings correspond to a 25% greater risk in men who have the highest levels of IGF-I, compared to those with the lowest. Men with the highest 'free' testosterone levels face a 18% greater risk of prostate cancer, compared to those with the lowest levels.
Hashim Ahmed, MD, a Professor Urology at Imperial College London (London, UK), said, “These results are important because they show that there are at least some factors that influence prostate cancer risk that can potentially be altered. In the longer term, it could mean that we can give men better advice on how to take steps to reduce their own risk. This study also shows the importance of carrying out very large studies, which are only possible thanks to the thousands of men who agreed to take part.” The study was presented at the National Cancer Research Institute 2019 cancer conference held November 3 – November 5, 2019 in Glasgow, UK.
Related Links:
University of Oxford
Imperial College London














