Preoperative Bacteriuria Unconnected to Joint Infection
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 22 Aug 2017
Patients who undergo elective joint replacement are traditionally screened and treated for preoperative bacteriuria in order to prevent periprosthetic joint infection (PJI), but more recently, this practice has been questioned.Posted on 22 Aug 2017
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is one of the most challenging and frequent complications after lower-extremity joint (hip and knee) arthroplasty. However, there is no single accepted set of diagnostic criteria for PJI. Various definitions have been proposed; however, none have been widely adopted.
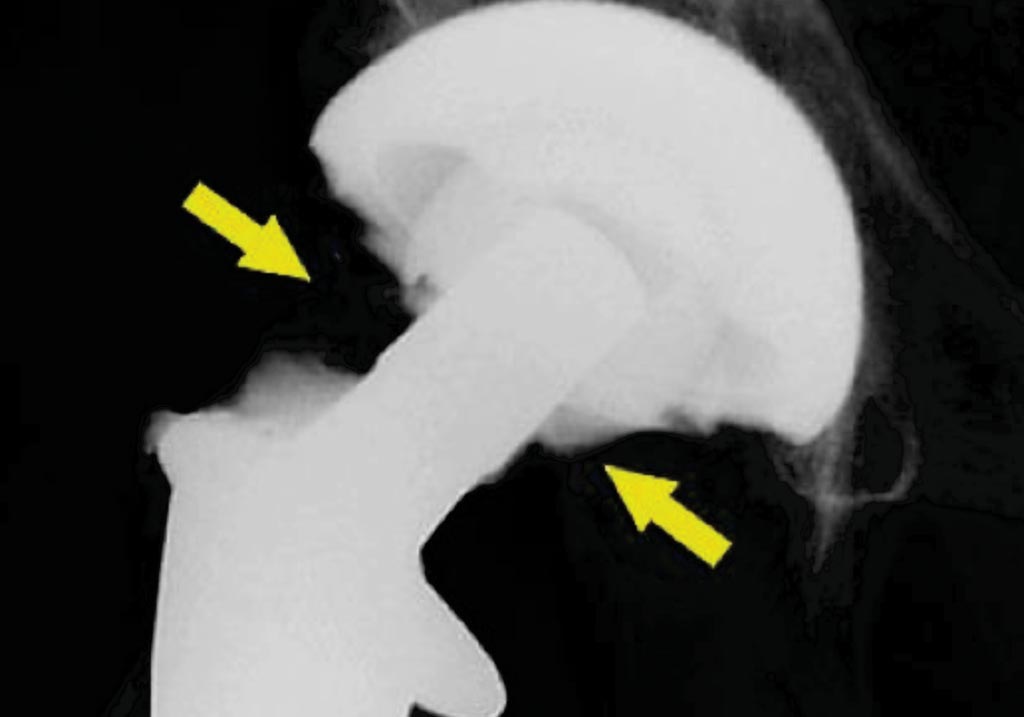
Image: An arthrogram is used to help confirm periprosthetic joint infection (Photo courtesy of Dr. Robin Smithuis, MD).
A team of scientists at Tampere University Hospital (Tampere, Finland) identified patients between September 2002 and December 2013 who had undergone a primary hip or knee replacement in a tertiary care hospital from the hospital database that included 23,171 joint replacements, 10, 200 hips, and 12,971 knees. Patients with subsequent PJI or superficial wound infection in a one-year follow-up period were identified based on prospective infection surveillance. The association between bacteriuria and PJI was examined using a multivariable logistic regression model.
The team found the incidence of PJI was 0.68%, a total of 158 patients. Preoperative bacteriuria was not associated with an increased risk of PJI either in the univariate 0.51% versus. 0.71%; Odds ratio (OR) = 0.72, (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.34 – 1.54) or in the multivariable the OR = 0.82, (95% CI 0.38 – 1.77) analysis. There were no cases where PJI was caused by a pathogen identified in the preoperative urine culture. Results were similar for superficial infections.
The authors concluded that there was no association between preoperative bacteriuria and postoperative surgical site infection. Based on these results, it seems that the preoperative screening and treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria is not required. The study was published on July 28, 2017, in the journal Clinical Microbiology and Infection.
Related Links:
Tampere University Hospital













