Lipid-ELISA Improves Detection of Potential PD Biomarker
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 31 Jul 2017
Researchers have developed a novel diagnostic approach for Parkinson’s Disease (PD), which enabled assaying of total alpha-synuclein in whole blood cells (WBC), cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and saliva. The new ELISA assay could lead to early diagnosis and improved monitoring of PD progression and patient response to therapy.Posted on 31 Jul 2017
Making an accurate diagnosis of PD is particularly difficult in early stages and mild cases. There are currently no standard diagnostic tests other than clinical information provided by the patient and findings of neurological examination. One of the best hopes for improving diagnosis is to develop a reliable test for identifying changes in the severity of the disease, which would also allow drug companies to test potential drugs at higher efficacy.
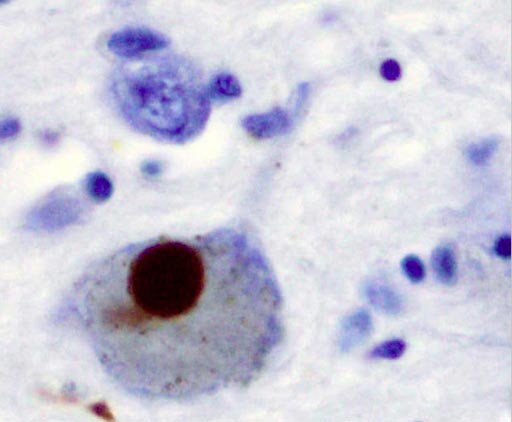
Image: Immunohistochemistry for alpha-synuclein showing positive staining (brown) of an intraneural Lewy-body in the brain substantia nigra in Parkinson\'s disease (Photo courtesy of Wikimedia).
The new assay was developed by a research team at the Faculty of Medicine of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem (Jerusalem, Israel) under the supervision of Dr. Ronit Sharon. First author and PhD student Suaad Abd-Elhadi was awarded Hebrew U’s Kaye Innovation Award for 2017 in recognition of her especially important role in developing the assay.
The assay detects the protein alpha-synuclein, a potentially important PD biomarker as it is closely associated with tissues where PD can be detected and with the neurological pathways along which the disease progresses, causing its characteristic symptoms. However, ELISA capture of alpha-synuclein using antibodies raises a concern regarding efficacy for the intracellular, unfolded pool of alpha-synuclein. An alternative to antibodies is capture by membrane lipids based on utilizing the biochemical property of alpha-synuclein to specifically bind membrane lipids and to acquire a characteristic structure following binding.
They determined alpha-synuclein levels in human samples using immobilized lipids for alpha-synuclein capture. Lipids used consisted of phosphatidyl inositol (PI), phosphatidyl serine (PS), and phosphatidyl ethanolamine (PE). Addition of mono-sialoganglioside to the immobilized lipids improved the system. Following capture, the lipid-bound alpha-synuclein was detected using an anti- alpha-synuclein antibody.
The development of a simple and highly sensitive diagnostic tool that can detect PD biomarkers could lead to a minimally invasive and cost-effective way to improve the lives of Parkinson’s patients. Toward this end, the researchers have recently demonstrated a proof-of-concept to the high potential of their lipid-ELISA assay in differentiating healthy and Parkinson’s affected subjects. They are now in the process of analyzing a large cohort as part of a clinical study, including patients with moderate and severe PD. The Hebrew University has signed an agreement with Integra Holdings for further development.
The related study, Abd-Elhadi S by et al, was published November 2016 in the journal Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry.
Related Links:
Hebrew University of Jerusalem









 (3) (1).png)




