Newly Identified Biomarker Indicates Risk of Breast Cancer Bone Metastasis
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 29 Sep 2015
Cancer researchers have identified a gene that is critically linked to the ability of some breast cancer tumors to metastasize to the bone and which may be developed into a biomarker to identify patients at risk for this development.Posted on 29 Sep 2015
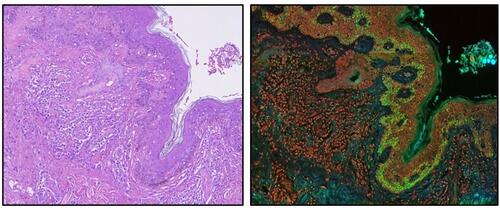
There are currently no biomarkers for early breast cancer patient populations at risk of bone metastasis, which occurs in about 15%–20% of patients with estrogen-receptor-positive breast tumors. These tumors tend to metastasize to the bone, and represent 80% of all breast cancers.
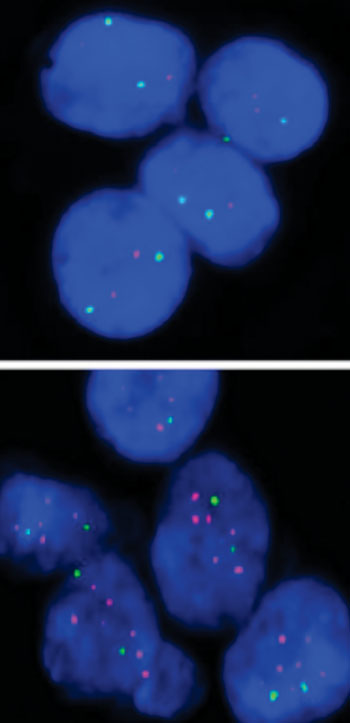
Image: Top, breast cancer tumor cells negative for the bone metastasis marker, MFA. Bottom, breast cancer tumor cells positive for the marker (Photo courtesy of Gomis Laboratory, Institute for Research in Biomedicine, Barcelona).
Investigators at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (Barcelona, Spain) analyzed more than 900 clinical samples of primary breast tumors while looking for genetic variations that favored bone metastasis.
They reported in the September 15, 2015, online edition of the Journal of the National Cancer Institute that patients with tumors in which the MAF (v-maf avian musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog) gene was altered had a risk of metastasis to the bone that was 14 times higher than in those patients in which the gene was unaltered.
"This gene reliably predicts metastasis to the bone. Studying whether it is highly expressed in breast cancer patients to determine whether this also happens in a clinical setting is an important next step. It could improve the quality of life of these patients and the way clinicians manage their cancer. And this is exactly what we are doing," said senior author Dr. Roger Gomis, oncology group leader at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine.
The findings obtained in this study have led to the creation of the company Inbiomotion (Barcelona, Spain), which has developed the tools necessary to begin clinical trials. An initial clinical trial will validate the use of the marker in some 3,300 patients.
Related Links:
Institute for Research in Biomedicine
Inbiomotion