Integrating Cardiovascular Risk Biomarkers Aids in Detection of ‘Inflammaging’
Posted on 31 Oct 2024
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) continue to be the leading cause of death globally, responsible for nearly one-third of all fatalities worldwide. Traditionally, risk assessment for CVD has focused on well-established factors associated with atherosclerosis, such as demographics, lifestyle choices like smoking and physical activity, and health conditions including diabetes, hypertension, and obesity. Biomarkers, particularly non-HDL cholesterol, have also been crucial in identifying individuals at risk. Nonetheless, there remains a significant residual cardiovascular risk even after managing these known factors, indicating that additional, unexamined contributors to cardiovascular health may exist. In a new paper published in Aging, researchers have investigated how the integration of specific cardiovascular biomarkers could assist in evaluating this residual inflammatory risk, especially in the context of aging-related inflammation, known as "inflammaging."
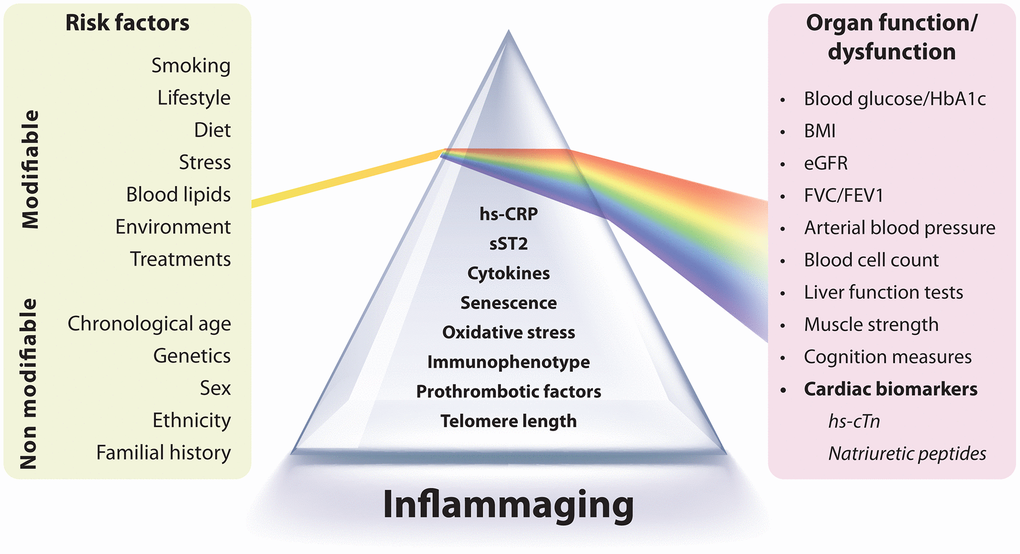
The study, conducted by researchers from Marche Polytechnic University (UNIVPM, Ancona, Italy) and IRCCS INRCA (Ancona, Italy), focused on biomarkers such as high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn), and natriuretic peptides, which are valuable indicators of both inflammatory burden and early cardiovascular risk. The researchers propose a more comprehensive biomarker-based strategy for assessing cardiovascular risk that includes two distinct dimensions. The first set of biomarkers—comprising cytokines, immune cell phenotypes, and mediators released by senescent or dysfunctional cells, known as the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP)—can indicate the overall burden of inflammaging and, by extension, residual inflammatory risk. The second set, which includes hs-cTn and natriuretic peptides (NPs), functions as surrogate markers that reflect the influence of inflammaging on organ function.
Importantly, the biomarkers in this second group can also serve as endpoints, as numerous studies have shown their responsiveness to therapeutic interventions. Establishing a mediating relationship between these two groups of biomarkers would enhance the understanding of the mechanistic connections between inflammaging and age-related organ dysfunction and disease. In summary, the researchers demonstrated that combining markers of chronic inflammation with cardiac health indicators provides a more comprehensive view of cardiovascular risk, highlighting the effects of aging-related inflammation, or "inflammaging," on heart health. They suggest that this approach could pave the way for targeted interventions in aging populations.










 (3) (1).png)