Smartphone-Controlled Microfluidic Device Enables Rapid Influenza Detection
Posted on 15 Jul 2024
The influenza virus represents a significant public health concern, annually causing epidemics with high morbidity and mortality rates. The virus is known for its high mutation rate and the existence of multiple subtypes, which require varied clinical approaches. Consequently, there is a critical need for an accurate, rapid, and portable method to differentiate between influenza virus subtypes to manage virus transmission and inform clinical treatment decisions. Researchers have now developed a spatial encoding of a centrifugal microfluidic disc-integrated smartphone-controlled (SEDphone) platform for detecting influenza virus subtypes.
In a study, researchers from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Anhui, China) developed a novel approach that combines Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) with CRISPR/Cas12a technologies for rapid and accurate detection of various influenza viruses. This method amplifies target sequences using LAMP and detects them through CRISPR/Cas12a-mediated trans-cleavage activity, thus cleaving reporter probes and emitting fluorescent signals. This technique is highly sensitive and reduces the occurrence of false positives. To aid the detection of different influenza strains, the researchers devised a flexible model capable of targeting multiple flu types. Following optimization, this method can identify five influenza types (H1N1, H3N2, H5N1, H7N9, and Influenza B) within 45 minutes, even at low viral concentrations (10 copies/μL).
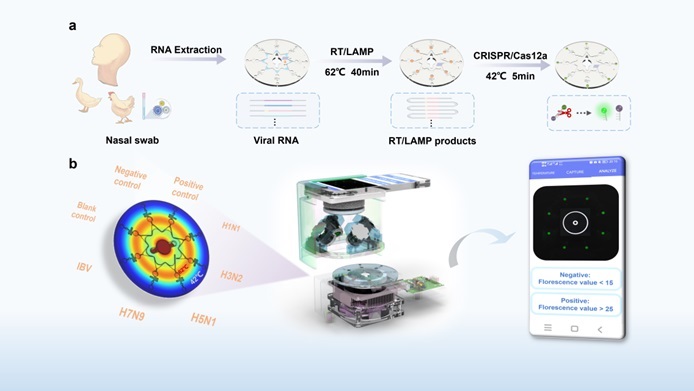
Furthermore, to facilitate simultaneous LAMP amplification and CRISPR detection, the team engineered a centrifugal microfluidic chip with spatial encoding features. They also developed a portable testing device, dubbed SEDphone, which operates via smartphone control. This device can simultaneously amplify and detect multiple influenza virus types. Incorporating a dual temperature zone design, it addresses the temperature variance required for both technologies. Clinical sample testing confirmed that this innovative method and the SEDphone device are effective in rapidly identifying various influenza subtypes. The research results were published in Sensors and Actuators: B. Chemical.
"Our research offers a new way to quickly and accurately detect various pathogens in real-time. This method can be used in fever clinics or at home, helping to reduce the risk of unnecessary cross-infection and easing the burden on healthcare systems," said Dr. ZHU Cancan, a member of the research team.
Related Links:
Hefei Institutes of Physical Science









 (3) (1).png)