New Database Provides First-Ever Map of Proteome Signature in Blood from Cancer Patients
Posted on 10 Jan 2023
Cancer prediction medicine has received a boost with the recent unveiling of a new cancer protein profile database compiled from AI and machine learning that enables identification of individual cancer types based on a drop of blood.
The new open-access Disease Blood Atlas produced by the Human Protein Atlas (Sweden) consortium provides a first-ever map of the proteome signature in blood from cancer patients. The Disease Blood Atlas highlights 1,463 proteins associated with 12 different types of cancer, and presents proteins that can be used to identify individual cancer types based on a drop of blood.
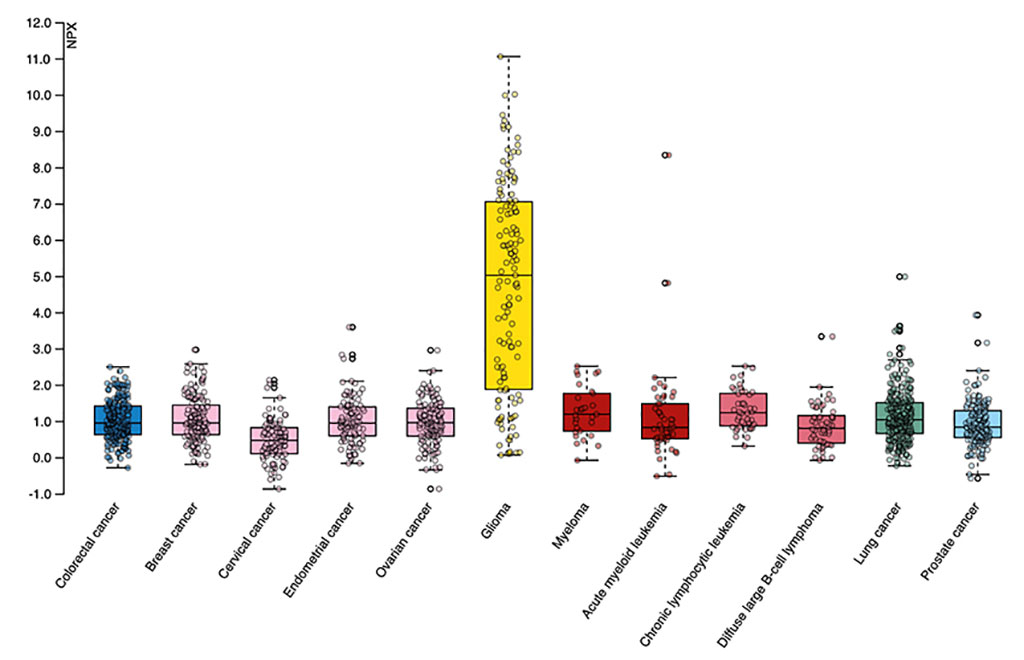
The Disease Blood Atlas was compiled from measurements of minute amounts of blood plasma collected from 1,400 cancer patients at the time of diagnosis and before treatment. The blood samples underwent a combination of statistical analysis of gene expression and machine-learning-based disease prediction. The release marks the 22nd version of the open-access Human Protein Atlas, a resource for profiling human proteins, which contains 12 sections each exploring the human proteins from different angles, including the new Disease Blood Atlas and the Protein 3-D Structure sections.
The release is accompanied by five million pages of updates in the Human Protein Atlas’ databases of tissues and cell lines. The Protein 3-D Structure section shows the 3-D structures for all human proteins using an AI-based prediction model (AlfaFold). In addition, a major update of the Tissue Atlas section provides detailed multiplex spatial profiling of proteins specific for human testis and kidney. More data is also provided on single cell analysis of tissues and organs, as well as data from an extensive catalogue of human cell lines.
“This is a novel pan-cancer strategy for exploring the proteome signature in blood from cancer patients,” said KTH Royal Institute of Technology Professor Mathias Uhlén who led the Human Protein Atlas consortium. “We believe that the new sections of the open access Human Protein Atlas with large amounts of novel data covering all human proteins provides new dimensions of valuable information for researchers interested in human biology and disease.”
Related Links:
Human Protein Atlas








 Analyzer.jpg)





