Improved ALS Blood Test Requires Less Stringent Storage and Work Conditions
Posted on 05 Sep 2022
Improvements to the method for isolating extracellular vesicles from the blood of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) patients have yielded a more robust test for detection of the disorder that may be used under routine laboratory conditions.
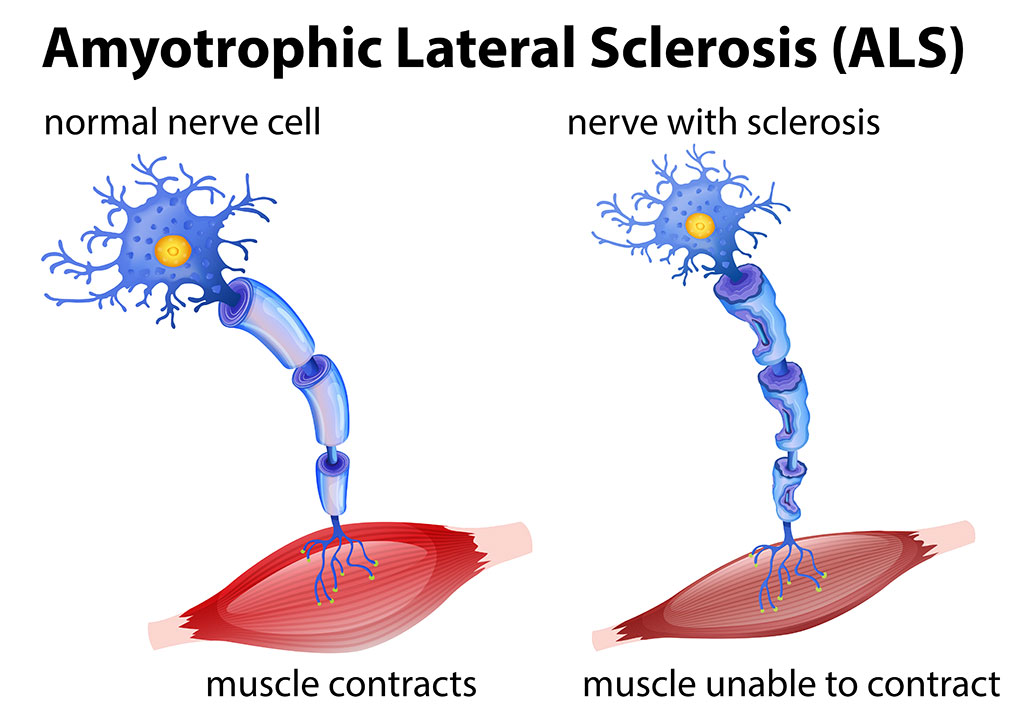
ALS is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by the selective and progressive death of upper and lower motor neurons. This leads to progressive muscle weakness, and death of the patient usually occurs within two to five years after the onset of symptoms. An EV-based blood test for ALS was described by investigators at Brain Chemistry Labs (Jackson, WY, USA) in 2020. However, the precise protocols for shipping and storage of blood samples, which were maintained at -80 degrees Celsius, meant that most doctors’ offices and routine clinical laboratories were unable to utilize the test.
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are small, non-replicating particles released from cells that contain material from the source cell and are surrounded by lipid bilayer membranes. Molecules within EVs are considered to be promising material for prospective biomarkers because of the lipid bilayer membrane that protects them from degradation. Among these molecules are short non-coding RNA strands or micro RNA (miRNA), which function to regulate post-transcriptional gene expression. In an earlier study the investigators identified eight miRNAs extracted from EVs that were diagnostic of early-stage ALS.
In the current study, the investigators tested the hypotheses that miRNA extracted from extracellular vesicles using immunoaffinity purification techniques would be robust and repeatable across investigators, laboratories and in a broad ALS population. The immunoaffinity purification protocol was based on the L1 cell adhesion molecule (L1CAM), which is a cell surface glycoprotein having a 1253 amino acid protein sequence. The extracellular portion is formed of six immunoglobulin domains followed by five fibronectin type III domains which are connected to a small intracellular domain by a transmembrane helix.
In this study, patient blood plasma samples obtained from the U.S. National ALS Biorepository were compared with plasma from non-ALS controls. Extracellular vesicles were extracted and isolated using L1CAM immunoaffinity purification. Total RNA was extracted, and miRNA quantified using qPCR following careful quality control measures.
One hundred blinded, blood plasma samples were analyzed. A group of 35 men and 15 women with ALS were compared with controls consisting of 30 men and 20 women. None of the ALS patient cohort reported family members with ALS, suggesting sporadic ALS. Five of the eight biomarkers previously published were found to discriminate ALS patient samples from control samples. The consistency of the results across different ALS patient populations under less stringent plasma collection/storage parameters provided evidence of the value of miRNA derived from L1CAM-enriched EVs for ALS diagnosis.
“We were surprised that the microRNA test worked for samples collected from a variety of investigators under differing conditions,” said first author Dr. Sandra Banack, senior scientist at Brain Chemistry Labs. Her colleagues, Dr. Rachael Dunlop and Dr. Paul Cox added, “We expected samples would need to be stringently collected and stored. Apparently, the extracellular vesicles shed into the blood protect their genetic cargo against differing environmental conditions.”
The report was published in the August 29, 2022, online edition of the Journal of the Neurological Sciences.
Related Links:
Brain Chemistry Labs