Electrochemical Sensor Platform to Enable New Diagnostic Tests in Near-Patient Settings
Posted on 28 Jun 2022
Biofouling poses a pervasive challenge to the development of electrochemistry-based diagnostics, which could be used to solve important diagnostic problems. Now, a novel electrochemical sensor platform will pave the way for the development and commercialization of cost-effective, highly sensitive and specific point-of-care diagnostics for neurological, cardiovascular, and renal diseases. The foundational discovery that started the development of this multiplexed biosensor technology was a novel antifouling nanocomposite coating that enables electrochemical electrodes to withstand the attack of biofouling molecules contained in various biofluids, including blood, and thereby maintains the electrodes’ sensing capabilities and minimizes any electrochemical background signal.
The Harvard Wyss Institute (Cambridge, MA, USA) has licensed its affinity-based, multiplexed, electrochemical sensing technology, eRapid, to StataDX Inc. (Cambridge, MA, USA), granting it exclusive worldwide access to the technology in the fields of neurological, cardiovascular, and renal diseases. The focus will be on developing diagnostic tests that can address critical unmet diagnostic needs in various near-patient settings, such as physician offices, pharmacies and eventually at home.
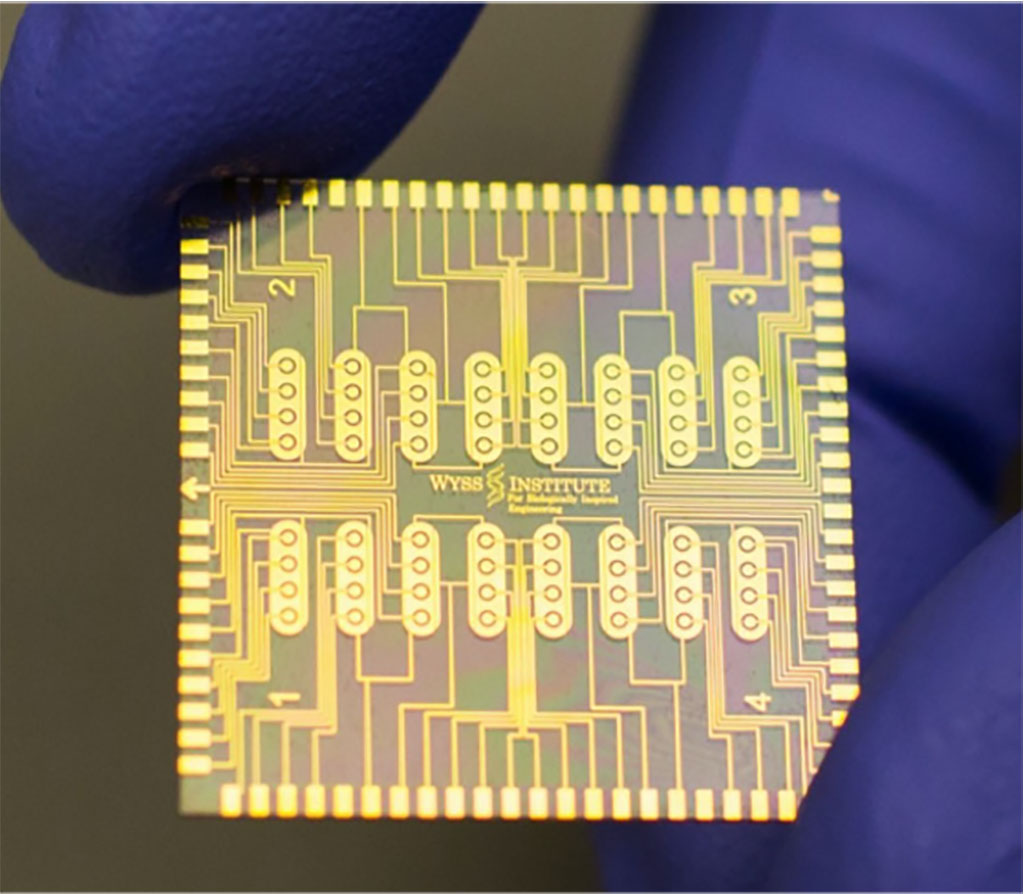
The affinity-based electrochemical sensor technology has been developed as a low-cost multiplexed diagnostics platform that can simultaneously detect and quantify a broad range of biomarkers with high sensitivity and selectivity in a small volume of blood or other complex biological fluids. By converting their original gold-based chemistry to a graphene-nanocomposite chemistry, the Wyss team further enhanced eRapid’s biomarker detection efficiency, and by developing a “dip coating method,” they reduced the time needed for coating sensor surfaces with the improved antifouling nanocomposite from 24 hours down to less than a minute. The advanced coating process dramatically reduced the fabrication costs for eRapid sensors and, in addition, made them storable for an extended period of time with minimal loss of electric signal. This increased their usefulness for future point-of-care diagnostic assays as testing can be done remotely and read on-site or sent to a central laboratory for analysis.
Importantly, the coating can be used to embed probes for a broad range of biomarkers, including proteins, antibodies, metabolites, hormones, and RNA molecules that can be simultaneously detected in multiplexed electrode arrangements. Most recently, the Wyss team presented a comprehensive framework for developing highly effective diagnostic electrochemical sensors, using a broadened range of surface materials that prevent biofouling and enhance detection of a variety of biomarkers, including the neurofilament-light (NFL) protein, which is gaining interest as a potential diagnostic biomarker for multiple sclerosis.
“Upon chemically detecting a target biomarker, eRapid sensors produce electrical signals within minutes that correlate in strength with the levels of the bound biomarkers, much like a commercial glucometer used by diabetic patients does today, but with multiplexing capability,” said Sanjay Sharma Timilsina, Ph.D., a key member of the Wyss Institute research team that extensively de-risked the technology. “This opens up a vast diagnostic space, given that many multifactorial diseases and disorders require simultaneous measurement of multiple biomarkers with high sensitivity and specificity in order to accurately diagnose, stratify, and monitor patients.”
“We showed in our extensive de-risking process at the Wyss Institute that the eRapid platform can address diverse live-threatening diseases and conditions with multiplexed biomarker measurements for which no accurate diagnosis existed before,” said Pawan Jolly, Ph.D, a Wyss senior staff scientist who led the multidisciplinary eRapid team at the Wyss Institute. “This is one of the most promising forays of an electrochemical sensing technology into commercial stages with the prospect to fill important diagnostic gaps in critical areas with unmet needs.”
“While there are many at-home tests for viral diseases such as COVID-19 available today, nothing yet exists for patients with complex chronic diseases such as multiple sclerosis, heart failure or chronic kidney disease that need periodic measurements of multiple biomarkers. The approach enabled by eRapid addresses underlying limitations of electrochemical biosensing in an elegant way, which may overcome the challenge faced by so many promising diagnostic technologies – the successful transfer to manufacturing at scale,” said Sidhant Jena, CEO and co-founder of StataDX. “Our decision to pursue neurology first stems from the significant healthcare burden of an aging population and the complete absence of a fingerprick blood test for the brain.”
Related Links:
Harvard Wyss Institute
StataDX Inc.