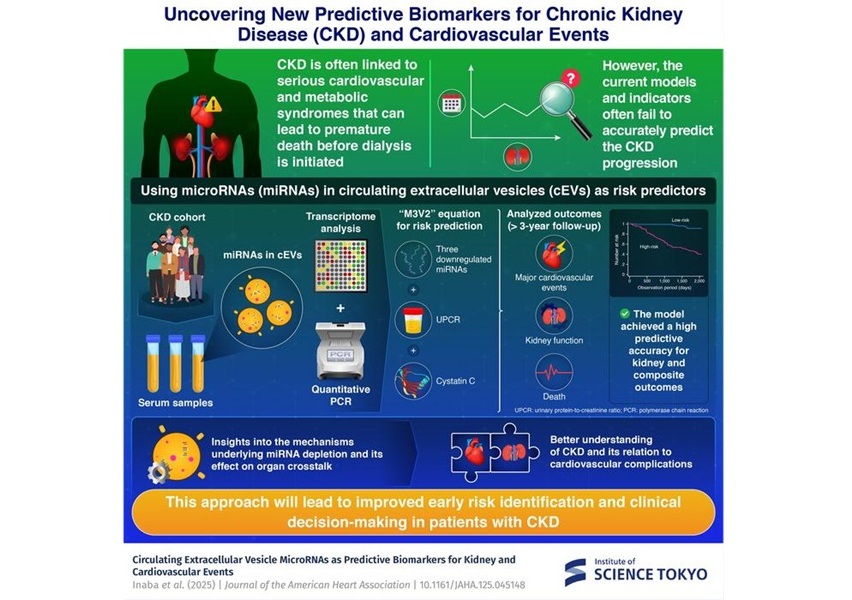
First-Ever Blood Test Detects Parkinson’s Disease
Posted on 24 Jun 2022
Until now, the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease has been based primarily on typical movement disorders such as muscle stiffness, slower movements and shaking. However, the disease starts up to 20 years before it becomes noticeable as a result of these symptoms. To date, there have been neither blood parameters nor imaging examinations to produce a definite diagnosis, let alone early recognition. Scientists around the world are looking for reliable clinically applicable biomarkers for this chronic progressive brain disease. Now, researchers have developed a method that reliably detects protein changes in blood that are typical of Parkinson's disease.
A research team at the Faculty of Medicine at Kiel University (Schleswig-Holstein, Germany) has developed a biochemical blood-based test for the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease. In a study, the test was able to distinguish the 30 Parkinson’s patients from the 50 control individuals with a very high degree of sensitivity. However, it is still no known whether early stages of the diseases can also be detected and whether the test will work for diseases that are similar to Parkinson’s.
The new method is based on three steps. The first step was to isolate the vesicles of nerve cells in the blood sample. Vesicles are small blisters that are pinched off cells and contain the protein of the original cell. The second step was to look specifically for the protein that causes the disease in these isolated nerve cell vesicles. This is a changed form of α-synuclein. This pathogenic form of α-synuclein can be detected through structure-specific antibodies. The third and most significant step of the detection method involves reproducing these misfolded α-synuclein forms of Parkinson’s patients from vesicles taken from patients’ blood.
“We developed a biochemical blood-based test for the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease. With our procedure, we were able to distinguish the 30 Parkinson’s patients from the 50 control individuals with a very high degree of sensitivity,” said Dr. Annika Kluge from the Faculty of Medicine at Kiel University. “The results are really sensational. They form the basis on which a blood test for diagnosing Parkinson's disease can be developed.”
Related Links:
Kiel University











 (3) (1).png)