Circulating Tumor DNA Test Clinically Validated
Posted on 24 May 2022
Next-generation sequencing of circulating tumor DNA presents a promising approach to cancer diagnostics, complementing conventional tissue-based diagnostic testing by enabling minimally invasive serial testing and broad genomic coverage through a simple blood draw to maximize therapeutic benefit to patients.
The diagnosis and sub-classification of cancers, fundamental to any cancer treatment algorithm, has historically been achieved through the study of the primary tumor tissue. The availability of high-quality diagnostic material suitable for high-end genomic technologies, including multiplexed tissue-based genotyping, is often limiting and associated with high risks and costs.
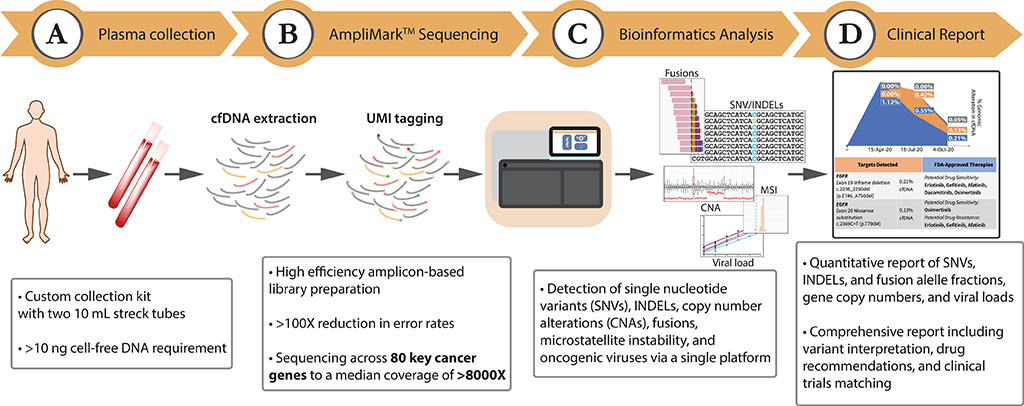
Scientists from Lucence Diagnostics Pte Ltd (Singapore, Singapore) collected 1,592 consecutive clinical samples included in the observational analyses were received as routine clinical samples and underwent standard processing and reporting at a CAP- and CLIA-accredited laboratory. Tubes of whole blood were collected for each patient in Streck Cell-Free DNA BCT (Streck, La Vista, NE, USA), shipped to Lucence Diagnostics at ambient temperature, and processed within 6–48 hours of sample collection.
The team used the Lucence Diagnostics’ LiquidHALLMARK which is an amplicon-based next-generation sequencing assay developed for the genomic profiling of plasma-derived cell-free DNA (cfDNA). The comprehensive 80-gene panel profiles point mutations, insertions/deletions, copy number alterations, and gene fusions, and further detects oncogenic viruses (Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and hepatitis B virus (HBV)) and microsatellite instability (MSI).
The investigators reported analytical validation using reference genetic materials demonstrated a sensitivity of 99.4% for point mutations and 95.8% for insertions/deletions at 0.1% variant allele frequency (VAF), and a sensitivity of 91.7% for gene fusions at 0.5% VAF. In non-cancer samples, a high specificity (≥99.9999% per-base) was observed.
The limit of detection for copy number alterations, EBV, HBV, and MSI were also empirically determined. Orthogonal comparison of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) variant calls made by LiquidHALLMARK and a reference allele-specific polymerase chain reaction (AS-PCR) method for 355 lung cancer specimens revealed an overall concordance of 93.8%, while external validation with cobas EGFR Mutation Test v2 (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) for 50 lung cancer specimens demonstrated an overall concordance of 84.0%, with a 100% concordance rate for EGFR variants above 0.4% VAF.
Clinical application of LiquidHALLMARK in 1,592 consecutive patients demonstrated a high detection rate (74.8% circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA)-positive in cancer samples) and broad actionability (50.0% of cancer samples harboring alterations with biological evidence for actionability). Among ctDNA-positive lung cancers, 72.5% harbored at least one biomarker with a guideline-approved drug indication.
The authors concluded that their results established the high sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and precision of the LiquidHALLMARK assay and supports its clinical application for blood-based genomic testing. The study was published on April 29, 2022 in the journal PLOS ONE.
Related Links:
Lucence Diagnostics Pte Ltd
Streck
Roche














