A Novel Small RNA Biomarker for Early Liver Cancer Diagnosis
Posted on 20 Apr 2022
A team of Chinese researchers has found evidence suggesting that a serum tsRNA (tRNA-derived small RNA) signature may serve as a novel biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
HCC, which makes up the majority of liver cancers, is linked to infection by hepatitis B/C virus. Biomarkers are needed to facilitate the early detection of HCC, which is often diagnosed too late for effective therapy.
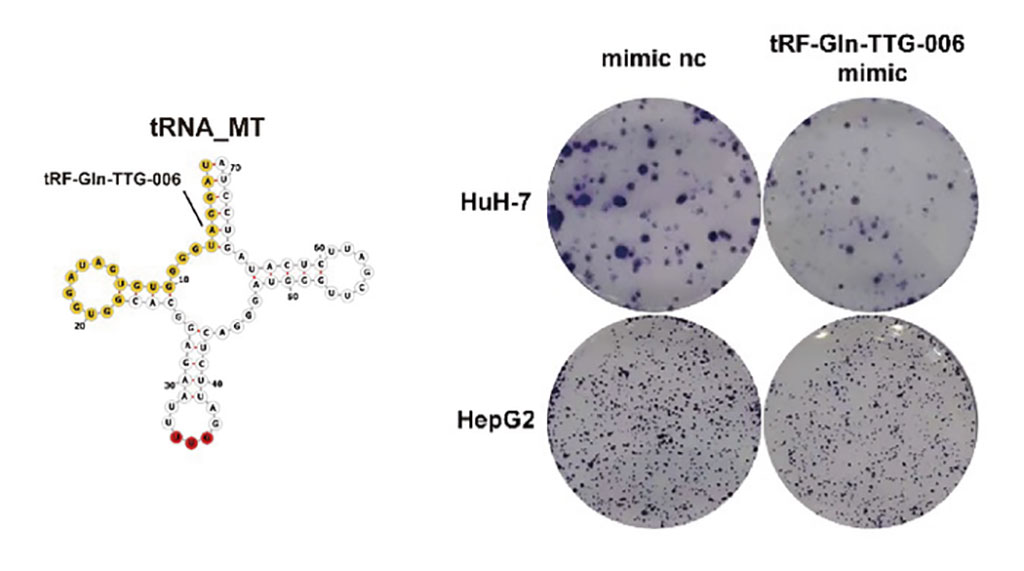
To identify potential diagnostic biomarkers for HCC, investigators at Nanjing University (China) looked at tRNA-derived small RNAs (tsRNAs). While it is known that this class of macromolecules plays vital roles in tumorigenesis and are stable in circulation, the diagnostic value and biological function of circulating tsRNAs, especially for HCC, are unknown.
In the current study, the investigators utilized RNA sequencing followed by quantitative reverse-transcription PCR to analyze tsRNA signatures in HCC serum. They identified tRF-Gln-TTG-006, which was remarkably upregulated in sera from 24 HCC patients as compared to sera from 24 healthy controls. Furthermore, they found that tRF-Gln-TTG-006 signature could distinguish HCC cases from healthy subjects with high sensitivity (80.4%) and specificity (79.4%) even in the early stage of the disease.
In vitro studies indicated that circulating tRF-Gln-TTG-006 was released from tumor cells, and its biological function in promoting disease progression could be predicted by bioinformatics assay and validated by colony formation and apoptosis assays.
Senior author Dr. Yanbo Wang, a researcher in science and technology at Nanjing University, said, "Based on our research, tsRNA is a promising biomarker of early HCC diagnosis and our study can provide more information on the relationship between tsRNAs and the development of liver cancer."
The study was published in the April 13, 2022, online edition of the journal Frontiers of Medicine.
Related Links:
Nanjing University














