Liquid Biopsy of Cerebrospinal Fluid for Diagnosis of Medulloblastoma
Posted on 08 Mar 2022
A recent study found that young patients with the aggressive brain cancer medulloblastoma have a unique molecular makeup in their cerebrospinal fluid, which might be useful for diagnosis and monitoring the presence of a tumor in the central nervous system.
Medulloblastoma (MB) is the most common malignant tumor of the cerebellum in children, and it accounts for 10–15% of pediatric central nervous system (CNS) tumors. MB has a propensity to invade and disseminate in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), with disseminated CNS disease occurring in 30–40% of cases at initial diagnosis and most patients at recurrence. The current diagnosis of MB is based on clinical assessment, imaging, and subsequent histopathological examination of biopsies, with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and lumbar puncture often performed to monitor treatment responses and to detect recurrences.
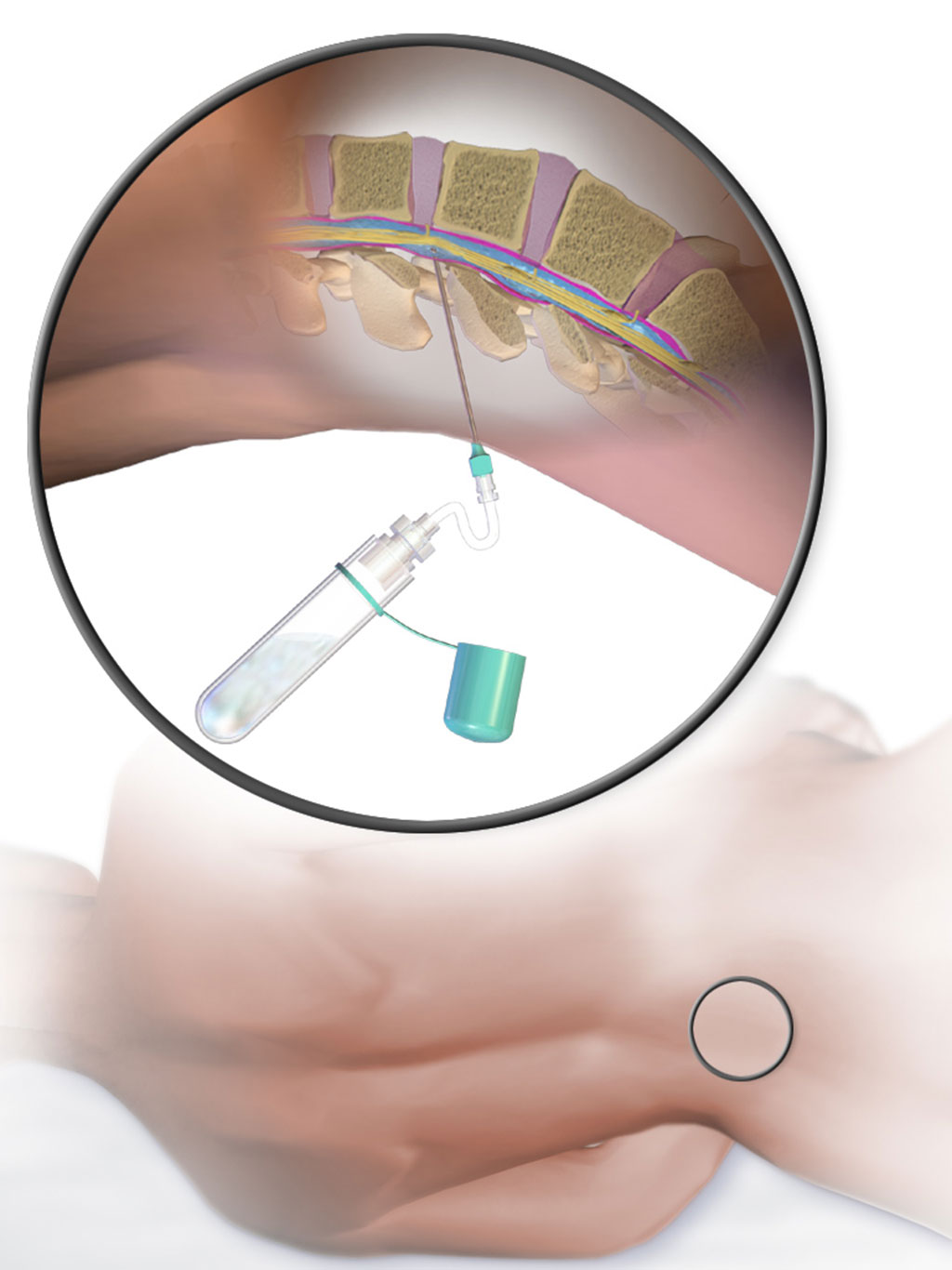
As CSF provides a window into the central nervous system, investigators at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine (Baltimore, MD, USA) proposed that liquid biopsy of CSF could provide a relatively non-invasive means for diagnosis of MB.
To this end, they used RNA-sequencing and high-resolution mass spectrometry to analyze the transcriptomic, metabolomic, and lipidomic landscapes of CSF samples obtained from forty patients with primary or recurrent MB and eleven normal controls.
Results revealed that 110 genes and 10 circular RNAs were differentially expressed in MB CSF compared with normal, representing TGF-beta (transforming growth factor beta) signaling, TNF-alpha (tumor necrosis factor alpha) signaling via NF-kappaB (nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B-cells), and adipogenesis pathways. Tricarboxylic acid cycle and other metabolites (malate, fumarate, succinate, alpha-ketoglutarate, hydroxypyruvate, N-acetyl-aspartate) and total triacylglycerols were significantly upregulated in MB CSF compared with normal CSF.
Although the analysis could not distinguish among the four subtypes of medulloblastoma, the results could be used to identify the presence of cancer versus normal fluid. Furthermore, metabolic and lipidomic profiles both contained indicators of tumor hypoxia.
"We believe this is the first comprehensive, integrated molecular analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid in medulloblastoma patients," said senior author Dr. Ranjan Perera, associate professor of oncology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. "Our study provides proof of principle that all three molecular approaches—studying RNA, lipids, and metabolites—can be successfully applied to cerebrospinal fluid samples, not only to differentiate medulloblastoma patients from those without the disease, but also to provide new insights into the pathobiology of the disease."
The medulloblastoma study was published in the February 24, 2022 online edition of the journal Acta Neuropathologica Communications.
Related Links:
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine














