High Cell-Free DNA Integrity Is a Biomarker for Poor Breast Cancer Survival
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 12 Oct 2021
A team of Finnish researchers has refined a liquid biopsy analysis technique to act as a more specific biomarker in order to more accurately predict poor prognosis for patients with aggressive breast cancer.Posted on 12 Oct 2021
Breast cancer (BC) research has focused lately on the utilization of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) and its concentration (cfDConc) and integrity (cfDI) as potential biomarkers. The cfDI describes the ratio of large and small cfDNA fragments. While the association of cfDConc and poor survival has already been recognized, studies on the prognostic value of cfDI have had contradictory results.
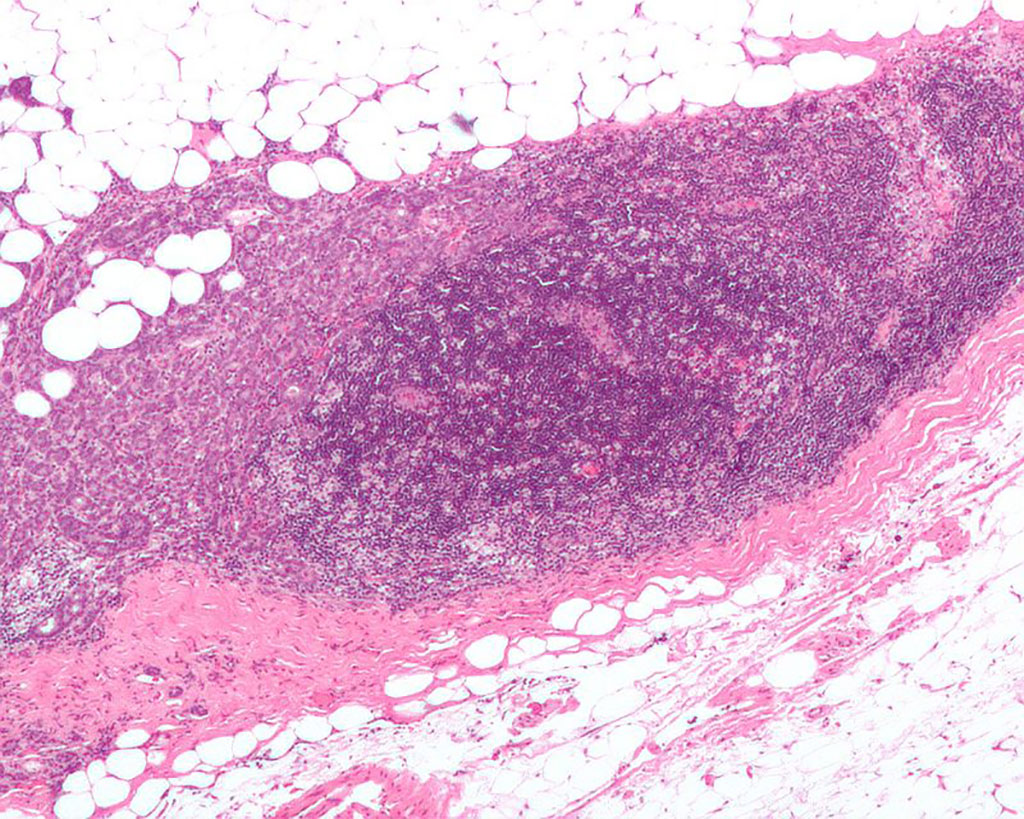
Image: Micrograph showing a lymph node invaded by ductal breast carcinoma, with an extension of the tumor beyond the lymph node (Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons)
To clarify the situation, investigators at the University of Eastern Finland (Kuopio, Finland) evaluated the prognostic potential of cfDConc and cfDI in Eastern Finnish BC cases with a non-metastatic disease.
For this study, the investigators selected 204 Eastern Finnish BC cases with non-metastatic disease and isolated cfDNA from the serum collected at the time of diagnosis before any treatment was given. The cfDConc and cfDI were measured with a fluorometer and electrophoresis, and the results were analyzed together with 25 years of survival data from the Kuopio Breast Cancer Project (KBCP), which was initiated in the 1990s.
Results revealed that high cfDConc was not an independent prognostic factor, while high cfDI was found to be an independent prognostic factor for poor overall survival (OS) and breast cancer-specific survival (BCSS). Inclusion of cfDI in the commonly used multivariate logistic regression model improved the predictive performance.
The results showing that high cfDI was an independent prognostic factor for poor OS and BCSS and improved the predictive performance of logistic regression models demonstrated its prognostic potential.
“Our results show that together with traditional prognostic factors, measuring the integrity of cfDNA can in the future help us to identify breast cancer patients with a poor prognosis earlier and more accurately than before. This would allow patients requiring more intensive care to be placed under intensified care and monitoring earlier,” said senior author Dr. Arto Mannermaa, professor of clinical medicine at the University of Eastern Finland.
The study was published in the September 18, 2021, online edition of the journal Cancers.
Related Links:
University of Eastern Finland














