Advanced Sequencing Techniques Determine Cancer Genome Variants in Young Patients
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 03 Aug 2021
A recent paper described a three-platform sequencing approach, including whole genome (WGS), exome, and RNA sequencing, that was used to examine tumor and germline genomes from prospectively identified children with newly diagnosed or relapsed/refractory cancers.Posted on 03 Aug 2021
Investigators at St. Jude Children's Research Hospital (Memphis, TN, USA) analyzed samples obtained from participants in the "Genomes for Kids" study. Genomes for Kids, which has enrolled about 2,700 cancer patients, is St. Jude’s clinical genomics program. Data generated through the Genomes for Kids project has been made available at no cost to the international research community.
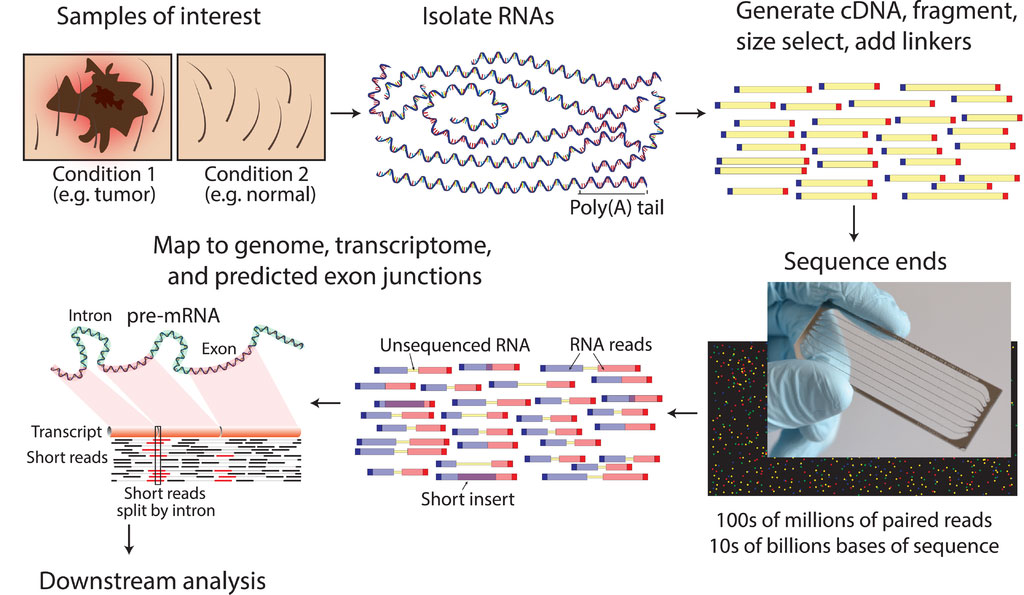
Typical RNA sequencing workflow (Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons)
For the current study, whole genome, whole exome, and RNA sequencing of tumor DNA was carried out for 253 patients for whom adequate tumor samples were available.
Results revealed that 86% of patients harbored diagnostic (53%), prognostic (57%), therapeutically-relevant (25%), and/or cancer predisposing (18%) variants. Inclusion of WGS enabled detection of activating gene fusions and enhancer hijacks (36% and 8% of tumors, respectively), small intragenic deletions (15% of tumors), and mutational signatures revealing of pathogenic variant effects. Germline variations in one of 156 known, cancer-predisposition genes were identified in 18% of the patients.
Almost two-thirds of the germline variations identified would not have been detected based on current screening guidelines.
"This study showed the feasibility of identifying tumor vulnerabilities and learning to exploit them to improve patient care," said senior author Dr. David Wheeler, director of the precision genomics team at St. Jude Children's Research Hospital. "We want to change the thinking in the field. We showed the potential to use genomic data at the patient level. Even in common pediatric cancers, every tumor is unique, every patient is unique."
The Genomes for Kids study was published in the July 23, 2021, online edition of the journal Cancer Discovery.
Related Links:
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital














