A Rapid Metabolomic Test for Early Diagnosis of Myocardial Infarction
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 03 May 2021
A metabolomic platform with GC/MS (gas chromatography–mass spectrometry) and LC/MS (liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry) instrumentation has been developed to profile plasma metabolites of patients with chest pain for early detection of myocardial infarction (MI).Posted on 03 May 2021
Investigators at Nanjing Medical University (People’s Republic of China) were working to develop a simple blood test to aid clinicians in diagnosing a heart attack with a rapid, noninvasive assay method.
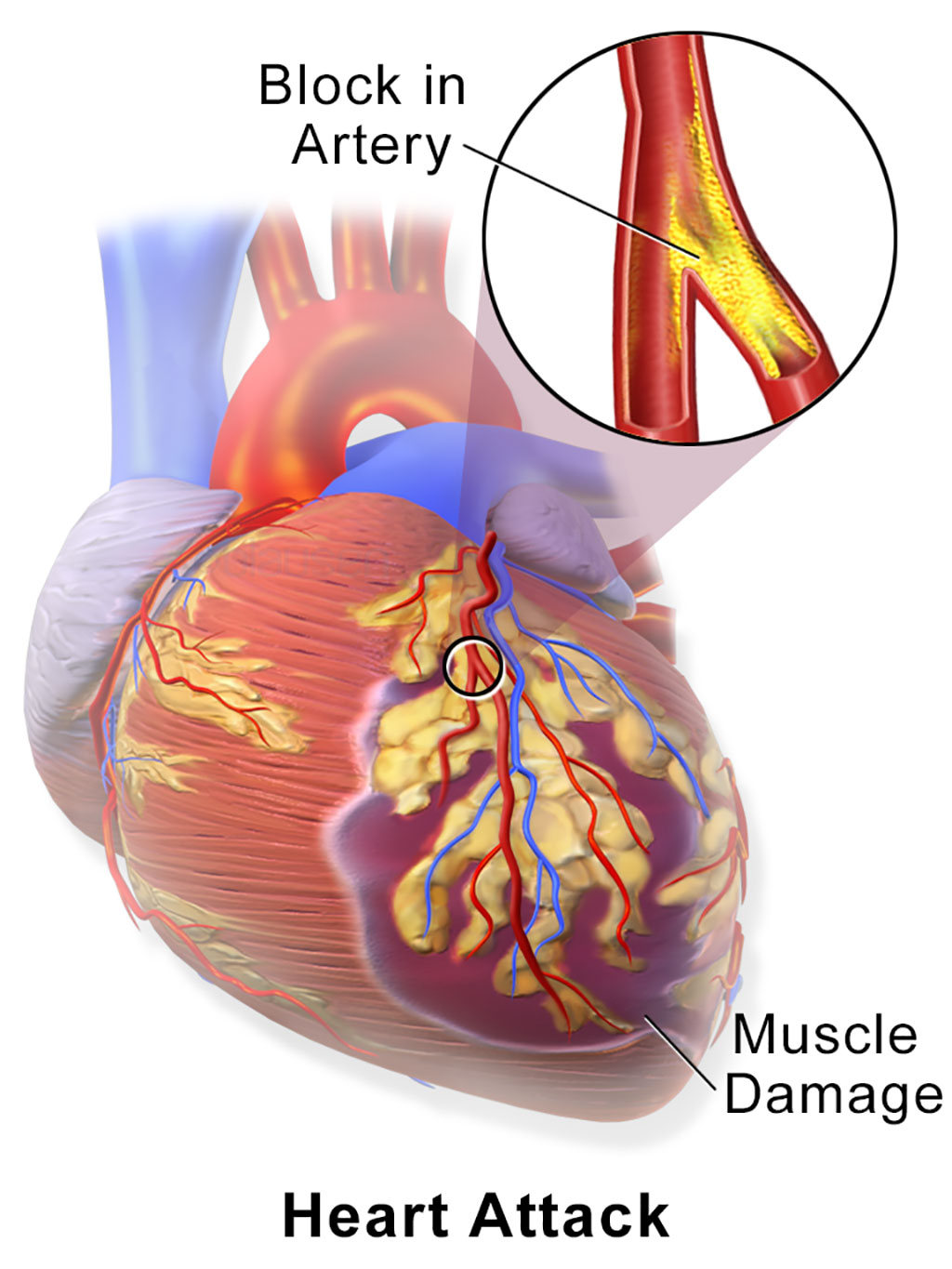
Image: A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to a part of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle (Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons)
To this end, they analyzed plasma metabolites in MI and non-MI chest pain cases to identify markers for diagnosis of MI based on metabolomics. Non-MI cardiac chest pain cases included unstable angina (UA), myocarditis, and valvular heart diseases. A total of 230 volunteers were recruited, consisting of 146 chest pain patients admitted with suspected MI (85 MIs and 61 non-MI chest pain cases) and 84 control individuals. Blood samples from all suspected MI cases were collected not longer than six hours after the onset of chest pain. Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry were applied to identify and quantify the plasma metabolites.
Results revealed that metabolites belonging to pyrimidine, methionine, and arginine metabolism were elevated in MI plasma samples. Specifically, deoxyuridine (dU), homoserine, and methionine were identified as potential markers for distinguishing MI cases from other cardiac chest pain cases after the onset of chest pains. Individuals with high plasma abundance of dU, homoserine, or methionine were also found to have increased risk of MI.
"We analyzed circulating metabolites in blood plasma samples from cardiac chest pain patients, including heart attack cases and other cardiac chest pain cases, to identify potential markers for heart attack diagnosis and early warning," said contributing author Dr. Xiangqing Kong, a senior researcher at Nanjing Medical University. "Such markers could be helpful in confirming heart attack in a timely manner when angiography is unavailable."
The identification of metabolites useful for early diagnosis of MI was described in the April 23, 2021, online edition of the journal Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.
Related Links:
Nanjing Medical University














