Blood Test Detects Early Colorectal Adenomas
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 08 Feb 2021
Colonoscopies are the gold standard for screening but have low compliance rates due to the invasiveness of the procedure. Stool-based tests have poor compliance and low sensitivity for advanced adenomas (AA), at about 24% to 42%. Posted on 08 Feb 2021
Many of the 50,000 annual colorectal cancer (CRC) deaths can be attributed to 1/3 eligible Americans not following screening guidelines or approximately 1/2 of the population not adherent to the follow-up post-polypectomy guidelines. The new understanding of the natural history and shared etiology of adenomas and CRC inform integration of clinically relevant biomarkers.
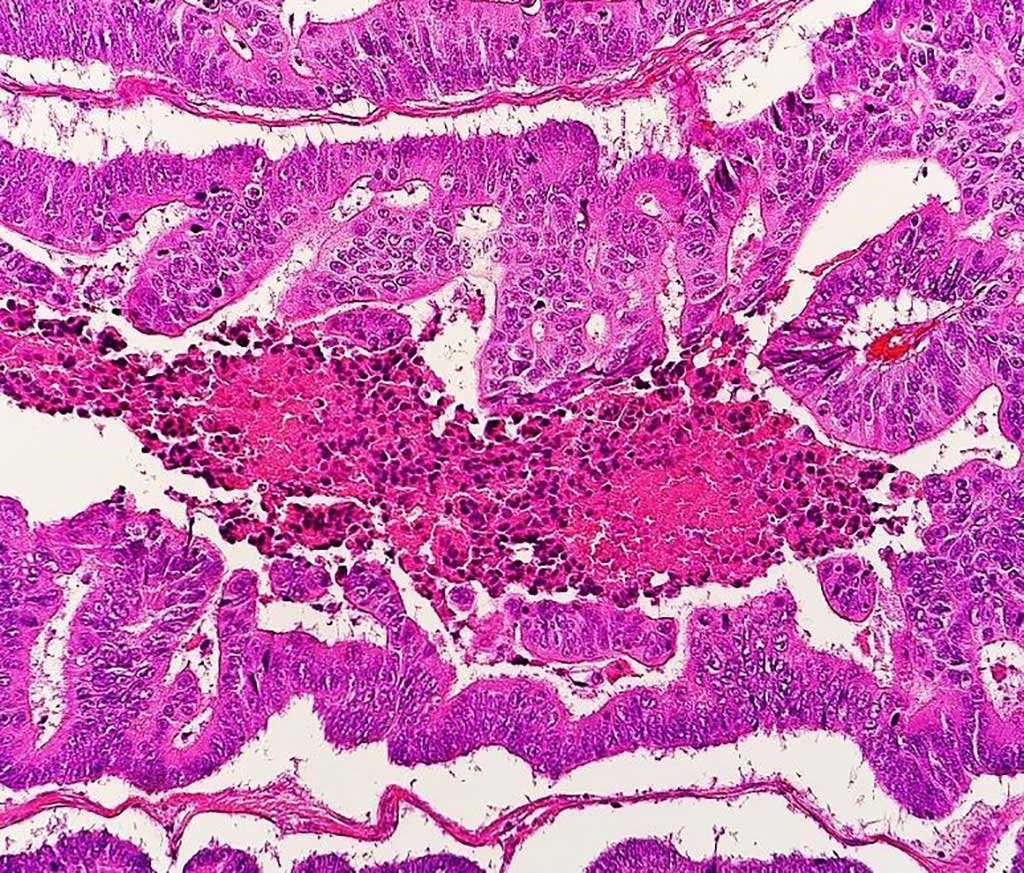
Image: Photomicrograph of a moderately differentiated colorectal carcinoma with dirty necrosis (Photo courtesy of Mikael Häggström, MD).
Medical Scientists at the Stanford University Medical Center (Stanford, CA, USA) and their colleagues conducted a prospective, blinded study of 458 individuals who had their blood drawn prior to undergoing colonoscopy and who had no prior history of colorectal cancer. Of them, 239 individuals underwent screening colonoscopy and 219 underwent surveillance colonoscopy. Most of the individuals (86%) were asymptomatic, whereas 14% had symptoms or a positive fecal immunochemical test.
The team developed the FirstSight blood test (CellMax Life, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) to detect adenoma-carcinoma pathways in blood samples based on the presence of circulating gastrointestinal epithelial cells and somatic mutations of cell-free tumor DNA. The test analyzes two biomarkers: circulating gastrointestinal epithelial cells and somatic mutations of cell-free DNA. The probability of advanced neoplasia was obtained by ordinal/nominal logistic regression methods together with SEER-incidence rate and prior history of AA on a training set of 346 subjects. A cutpoint was selected to obtain a test specificity (non-neoplastic finding or negative colonoscopy) of 90% resulting in a sensitivity of 100% and 80.0% for detection of CRC and advanced neoplasia (AN = CRC+AA), respectively, on the training subjects.
The investigators reported that the area under the ROC curve is 0.91. Validation using the fixed cutpoint and 112 test subjects achieved 91.4% specificity and 100% and 75.0% sensitivity for CRC and AN. Shai Friedland, MD, a Professor of Gastroenterology and his colleagues concluded that “This blood test has high sensitivity for colorectal advanced neoplasia while retaining high specificity. The quantitative nature of the score has the potential to enable prognostic stratification of patients for screening or post-polypectomy surveillance colonoscopy.” The study was presented at the Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium (virtual meeting); held January 15-17, 2021.
Related Links:
Stanford University Medical Center
CellMax Life