Metastatic Gastric Cancer Outcomes Informed by Single-Cell Transcriptome Profiles
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 21 Jan 2021
Peritoneal Carcinomatosis (PC) is a late stage manifestation of several gastrointestinal malignancies including appendiceal, colorectal, and gastric cancer. In PC, tumors metastasize to and deposit on the peritoneal surface and often leave patients with only palliative treatment options.Posted on 21 Jan 2021
Single cell sequencing examines the sequence information from individual cells with optimized next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies, providing a higher resolution of cellular differences and a better understanding of the function of an individual cell in the context of its microenvironment.
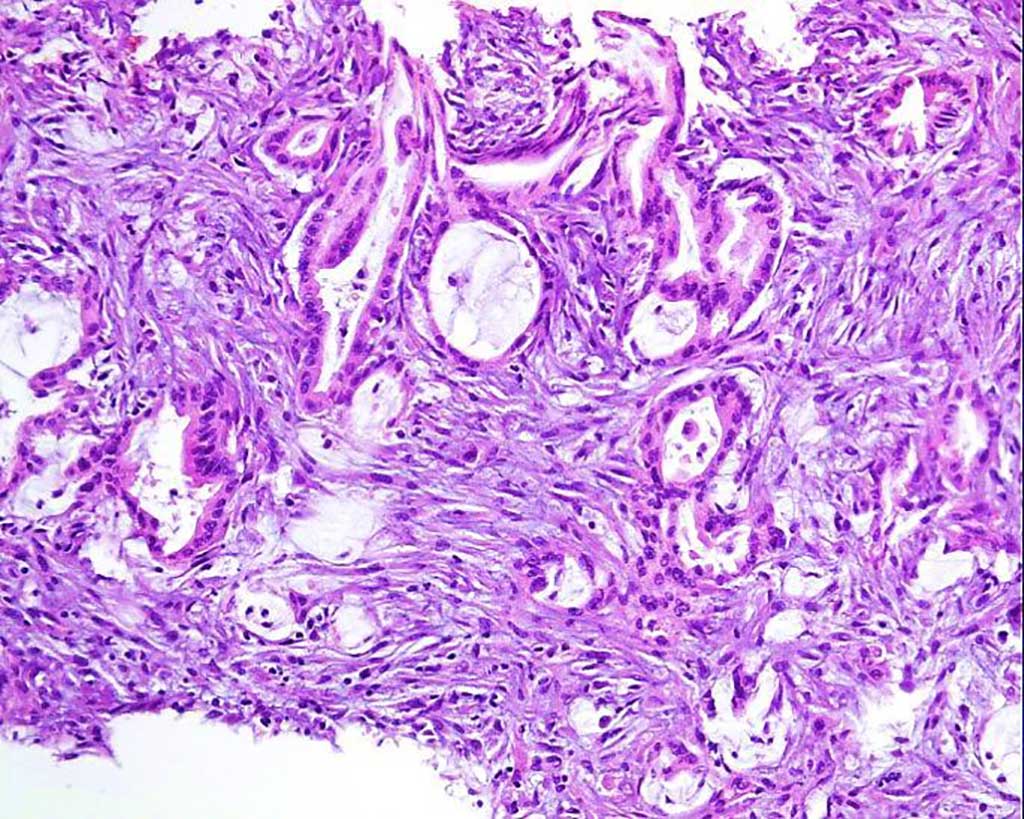
Image: Photomicrograph of omental nodules indicated an adenocarcinoma infiltrating the adipose and fibrous tissues (Photo courtesy of Beijing Shijitan Hospital).
Molecular Biologists at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center (Houston, TX, USA) performed single-cell transcriptome profiling of (PC) from 15 patients with gastric adenocarcinoma (GAC), constructed a map of 45,048 PC cells, profiled the transcriptome states of tumor cell populations, incisively explored Intra-Tumoral Heterogeneity (ITH) of malignant PC cells and identified significant correlates with patient survival.
The scientists subsequently validated that prognostic signature, which appeared to divide the tumors into groups with "gastric-dominant" or "gastrointestinal-mixed" groups, using data for another 1,336 gastric adenocarcinoma cases considered for the Cancer Genome Atlas project and three other large cohorts. The investigators uncovered the diversity in tumor cell lineage/state compositions in PC specimens and defined it as a key contributor to ITH. Single-cell analysis of ITH classified PC specimens into two subtypes that were prognostically independent of clinical variables, and a 12-gene prognostic signature was derived and validated in multiple large-scale GAC cohorts.
Linghua Wang, MD, PhD, an Assistant Professor in Genomic Medicine and co-senior author of the study, said, “The intriguing aspect is that, by classifying tumor cells based on lineage compositions, we noted two groups of patients. The more gastric-like peritoneal carcinomatosis cells had an aggressive phenotype and were associated with shorter survival. However, the more intestine-like peritoneal carcinomatosis cells were less aggressive, and patients had longer survival.”
The authors concluded that the prognostic signature appears fundamental to GAC carcinogenesis and progression and could be practical for patient stratification. The study was published on January 4, 2021 in the journal Nature Medicine.
Related Links:
University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center














