Proteomic Analysis of Urinary Extracellular Vesicles for the Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 30 Apr 2020
A new method for diagnosis of prostate cancer relies on advanced proteomics-based analysis of extracellular vesicles isolated from urine samples.Posted on 30 Apr 2020
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are cell-derived vesicles that are present in many and perhaps all biological fluids, including blood, urine, and cultured medium of cell cultures. The vesicles, which contain RNA, proteins, lipids, and metabolites that are reflective of the cell type of origin, are either released from the cell when multivesicular bodies (MVBs) fuse with the plasma membrane, or they are released directly from the plasma membrane.
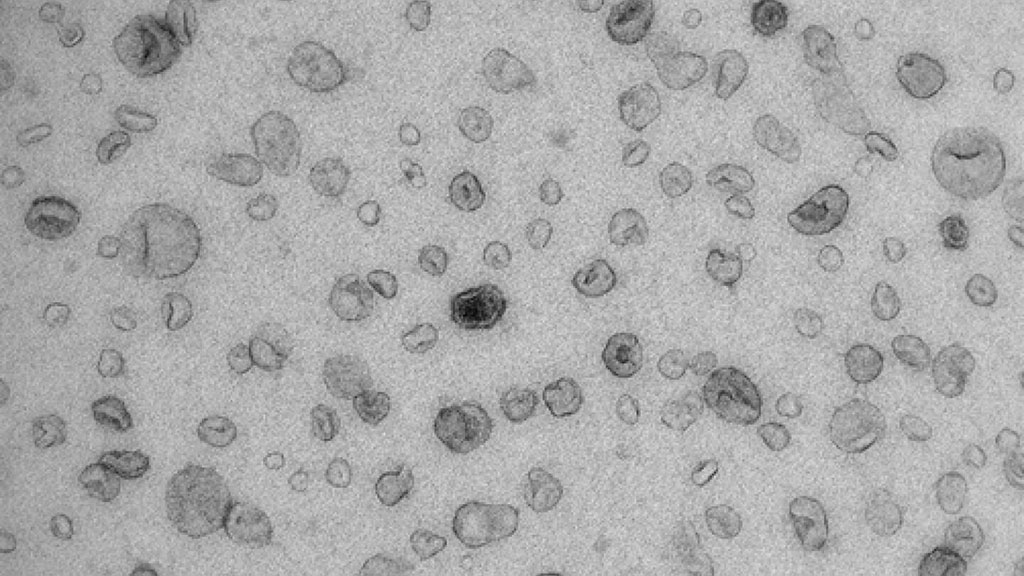
Image: Electron microscope image of urinary extracellular vesicles (EVs) (Photo courtesy of Pekka Rappu, University of Turku).
EVs are increasingly being recognized as important vehicles of communication between cells and as promising diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in cancer. Despite the huge clinical potential, the wide variety of methods for separating EVs from biofluids, which provide material of highly variable purity, and the lack of knowledge regarding methodological reproducibility have impeded the entry of EVs into the clinical arena.
In an effort to increase the usefulness of EVs, investigators at Ghent University (Belgium) and colleagues at the University of Turku (Finland) used mass spectrometry-based proteomics to analyze EVs that had been separated and purified from urine by a novel procedure. This density-based fractionation of urine samples obtained from men with benign and malignant prostate disease by bottom-up Optiprep (the iodine-containing non-ionic radiocontrast agent iodixanol) density gradient centrifugation separated EVs and soluble proteins with high specificity and repeatability.
The investigators reported that differential quantitative proteomic analysis of EV-enriched and protein-enriched urine fractions identified unique and biologically and clinically relevant proteomes in urinary EVs. In addition, by profiling matched prostate cancer tissue-derived EVs and urinary EVs, they demonstrated that the urinary EV proteome was a reflection of that of EVs derived from the tissue of origin.
“Detecting and examining these vesicles in urine has an enormous potential for developing new tests for early detection of urological cancers. However, research related to this is still in its infancy,” said first author Bert Dhondt, a researcher in the laboratory for experimental cancer research at Ghent University. “In the future, the results of the study can aid patients with urological cancers through faster diagnosis and timely treatment.”
The proteomic analysis of EVs in the urine of prostate cancer patients was described in the March 11, 2020, online edition of Journal of Extracellular Vesicles.
Related Links:
Ghent University
University of Turku













