Genome Wide Sequencing Study Reveals Why Some Cystic Fibrosis Patients Develop Fewer Lung Infections
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 23 Dec 2019
Results published in a recent paper provided an explanation at the molecular level as to why some cystic fibrosis patients have a reduced tendency to contract chronic lung infections. Posted on 23 Dec 2019
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. It is caused by the presence of mutations in both copies of the gene for the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) protein, which is involved in production of sweat, digestive fluids, and mucus. Those with a single working copy are carriers and otherwise mostly normal.
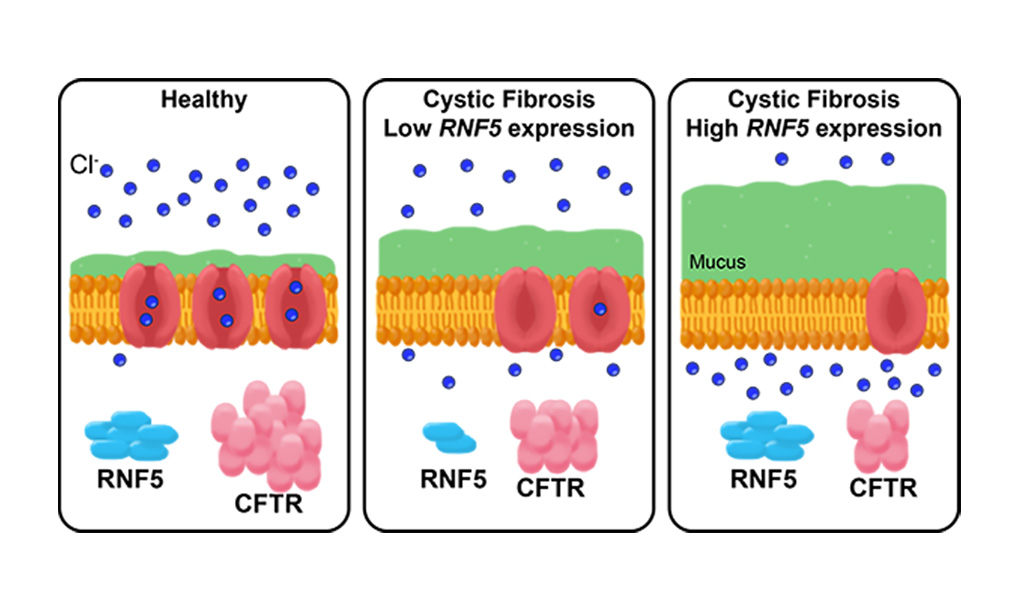
Image: In healthy people, the CFTR protein is embedded in the membrane of most cells, where it forms a channel for chlorine ions. In people with cystic fibrosis, an inherited mutation in the CFTR gene means their channels do not work as well and cells produce more mucus. The RNF5 protein inhibits CFTR, so people with cystic fibrosis who have genetic variations that decrease RNF5 expression have CFTR channels that function a little better, and thus are not as prone to infections as people with high RNF5 expression (Photo courtesy of University of California, San Diego)
Mutations of the CFTR gene affecting chloride ion channel function lead to dysregulation of epithelial fluid transport in the lung, pancreas, and other organs, resulting in cystic fibrosis. When CFTR is not functional, secretions which are usually thin, instead become thick. In the lungs, this thicker mucus can promote bacterial growth, making lung infections a serious and chronic problem for many people with CF. Interestingly, some CF patients do not experience lung infections as early or as frequently as others.
Investigators at the University of California, San Diego (USA) now think they can explain the delayed development of lung infections by some CF patients. These investigators were in the process of studying the associations between genetic variation, gene expression, and disease within the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) region of genes. The MHC is a set of genes that code for cell surface proteins essential for the acquired immune system to recognize foreign molecules in vertebrates, which in turn determines histocompatibility. The main function of MHC molecules is to bind to antigens derived from pathogens and display them on the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T-cells.
In conducting this study, the investigators used whole genome sequencing (WGS) of 419 individuals with CF to create a comprehensive map of regulatory variation in the MHC region. Building on this regulatory map, they explored GWAS signals for 4083 traits, detecting co-localization for 180 disease loci with eQTLs. Expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) are genomic loci that explain all or a fraction of variation in expression levels of mRNAs. An expression trait is a trait regarding the amount of an mRNA transcript or a protein, which are usually the product of a single gene with a specific chromosomal location. This distinguishes the expression from most classical complex traits, which are not the product of the expression of a single gene.
GWS results revealed a specific MHC region that was associated with decreased expression of the RNF5 gene. Previous studies had shown that inhibition of RNF5 in some CF patients resulted in rescue of mutant cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator function.
“We have known there is an association between MHC genes and bacterial colonization in patients with cystic fibrosis, but no one knew why,” said senior author Dr. Kelly A. Frazer, professor of pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. “We assumed it was due to MHC’s involvement in the immune system. But now we know that is likely not the only mechanism - different expression levels of RNF5 may also play an important role. The cystic fibrosis field is trying to figure out what are the modifiers across the genome that increase or decrease the probability that an individual patient will respond to these expensive drugs. RNF5 may be one of these modifier genes.”
The study was published in the December 10, 2019, online edition of the journal eLife.
Related Links:
University of California, San Diego














