Interleukin-2 Suggested as Basis for Celiac Disease Diagnostic Test
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 19 Aug 2019
A study designed to link changes in cytokine release following ingestion of gluten by individuals suffering from celiac disease found that interleukin-2 (IL-2) was the earliest and most prominent cytokine.Posted on 19 Aug 2019
Investigators at the biotechnology company ImmusanT (Cambridge, MA, USA), the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute (Melbourne, Australia), and collaborators in the United States and Norway were searching for biomarkers that could be used in a simple blood test for diagnosis of celiac disease.
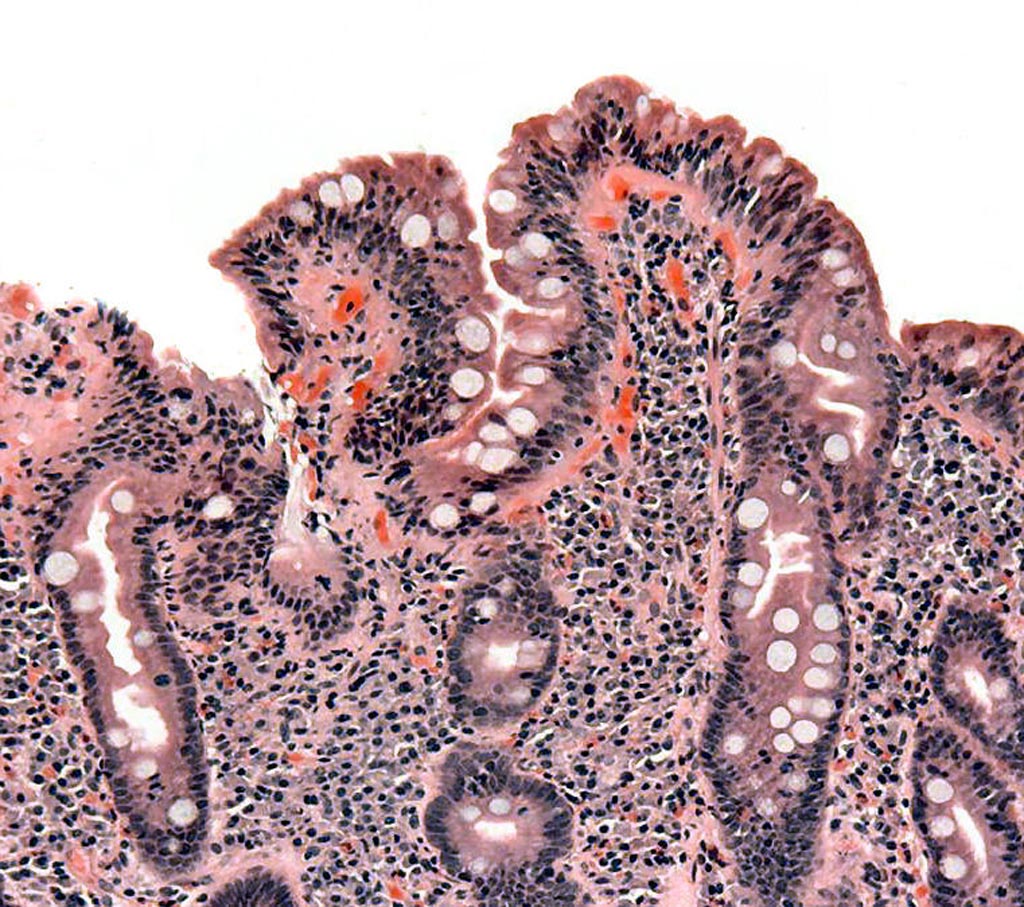
Image: A biopsy of small bowel showing celiac disease manifested by blunting of villi, crypt hypertrophy, and lymphocyte infiltration of crypts (Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons).
Currently, diagnosis of celiac disease is typically made by a combination of blood antibody tests and intestinal biopsies, augmented by specific genetic testing. This approach is complicated by the fact that frequently the autoantibodies in the blood are negative, and many individuals have only minor intestinal changes with normal villi. Some celiac sufferers may have severe symptoms and be investigated for years before a diagnosis is achieved. Increasingly, diagnosis of celiac disease is being made in asymptomatic individuals, as a result of screening. Evidence regarding the effects of screening, however, has not been sufficient to determine its usefulness.
For the current study, the investigators injected celiac patients with gluten peptides, which induced gastrointestinal symptoms, particularly nausea and vomiting. In the second phase of the study, the patients consumed a diet including gluten.
Results revealed that peptide injection elevated at least 15 plasma cytokines, with IL-2, IL-8, and IL-10 being most prominent (fold-change increase at four hours of 272, 11, and 1.2, respectively). IL-2 and IL-8 were the only cytokines elevated at two hours, preceding onset of symptoms. After gluten ingestion, IL-2 was the earliest and most prominent cytokine (15-fold change at four hours).
Senior author Dr. Robert P. Anderson, chief scientific officer of ImmusanT, said, "For the first time we have described the inflammatory reaction that patients with celiac disease experience in the immediate hours after they are exposed to gluten. The unpleasant symptoms associated with the disease are linked to an increase in inflammatory molecules in the bloodstream, such as interleukin-2 (IL-2), produced by T-cells of the immune system. This response is similar to what happens when an infection is present, however for people with celiac disease, gluten is the trigger. This information underpins a potential new approach to diagnosis that addresses the emerging medical need to identify patients without celiac disease who may be better served by other treatments for their chronic symptoms."
Contributing author Dr. Jason Tye-Din, head of celiac research at the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute, said, "For the many people following a gluten-free diet without a formal diagnosis of celiac disease, all that might be required is a blood test before, and four hours after, a small meal of gluten. This would be a dramatic improvement on the current approach, which requires people to actively consume gluten for at least several weeks before undergoing an invasive procedure to sample the small intestine."
The study was published in the August 7, 2019, online edition of the journal Science Advances.
Related Links:
ImmusanT
Walter and Eliza Hall Institute








 (3) (1).png)



