MicroRNA Pair Serves as Biomarkers for Rapid Sepsis Diagnosis
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 17 Jul 2018
Two microRNAs that could be the basis of a test to help physicians classify patients into those with organ failure who are at high risk of sepsis and death and those patients with milder infections have been identified.Posted on 17 Jul 2018
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) and short interfering RNAs (siRNA) comprise a class of about 20 nucleotides-long RNA fragments that block gene expression by attaching to molecules of messenger RNA in a fashion that prevents them from transmitting the protein synthesizing instructions they had received from the DNA. MiRNAs resemble siRNAs of the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway, except miRNAs derive from regions of RNA transcripts that fold back on themselves to form short hairpins, whereas siRNAs derive from longer regions of double-stranded RNA. With their capacity to fine-tune protein expression via sequence-specific interactions, miRNAs help regulate cell maintenance and differentiation.
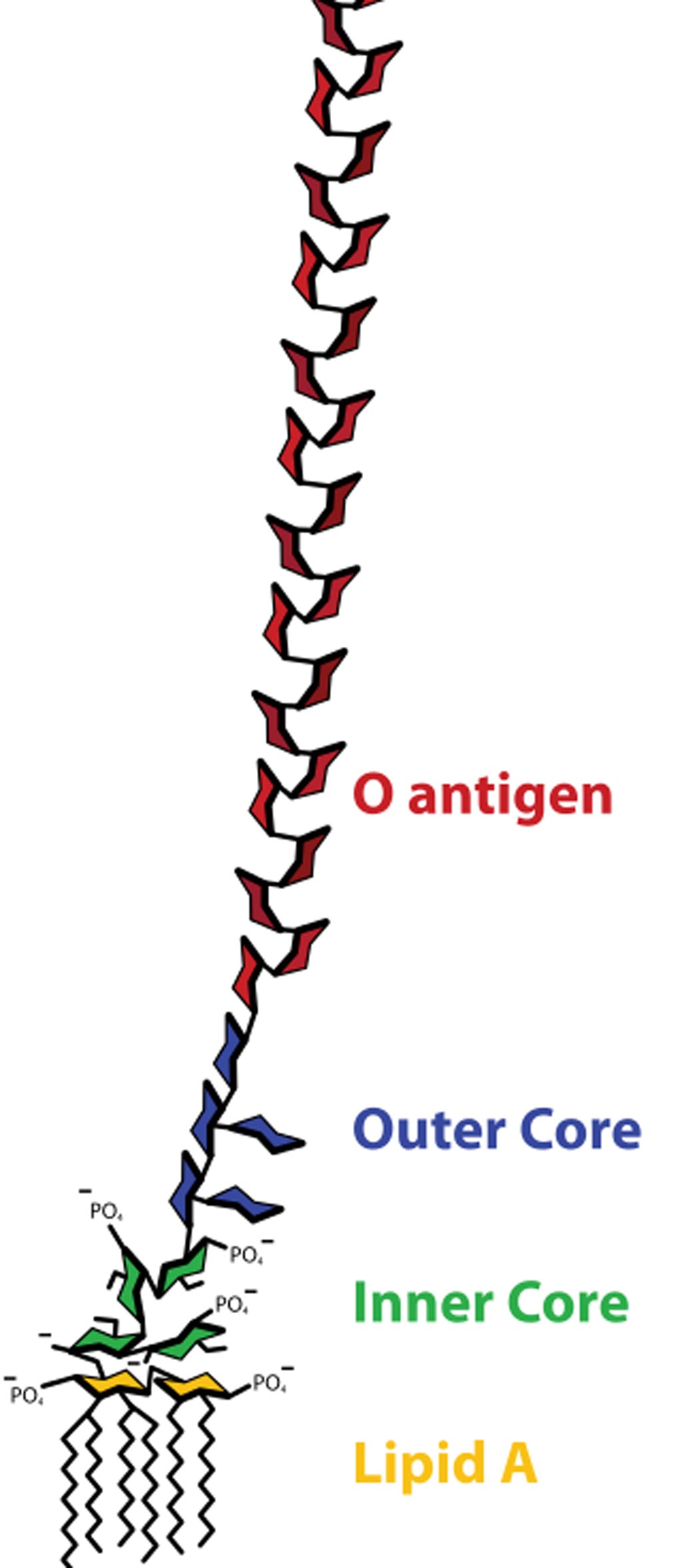
Image: The structure of a lipopolysaccharide (Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons).
Sepsis is a dysregulated systemic immune response to disseminated infection that has a high mortality rate. In some patients, sepsis results in a period of immunosuppression (known as immunoparalysis) characterized by reduced inflammatory cytokine output, increased secondary infection, and an increased risk of organ failure and mortality.
Prolonged exposure to microbial products such as lipopolysaccharide can induce a form of innate immune memory, known as lipopolysaccharide tolerance, which blunts subsequent responses to unrelated pathogens. Lipopolysaccharide tolerance recapitulates several key features of sepsis-associated immunosuppression and can be used as a model for studying this phenomenon.
In this regard, investigators at the Columbia University Irving Medical Center (New York, NY, USA) performed a screen for tolerance-associated microRNAs and identified miR-221 and miR-222 as regulators of the functional reprogramming of macrophages during the formation of lipopolysaccharide tolerance. Prolonged stimulation with lipopolysaccharide in mice led to increased expression of miR-221 and miR-222.
While clinical trials will be needed to validate the usefulness of testing patients for these microRNAs as a quick guide to prognosis and treatment, a small study revealed that among 30 hospitalized patients, those with evidence of organ failure exhibited higher levels of miR-221 and miR-222 in their blood samples. In septic patients, those with elevated miR-221 and miR-222 also exhibited evidence of immunosuppression.
“The best treatment for sepsis starts with rapid detection. Our results suggest that specific molecules called microRNAs may be potential biomarkers of poor prognosis, indicating the need for more aggressive treatment options,” said senior author Dr.Sankar Ghosh, professor of microbiology and immunology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center.
Related Links:
Columbia University Irving Medical Center