Genetic Test May Improve Post-Stent Treatment Outcome
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 17 Apr 2018
A test for specific genetic mutations successfully informed blood-thinner treatment selection following stent placement to open clogged blood vessels, leading to significantly fewer complications.Posted on 17 Apr 2018
Genetic testing identified patients with specific mutations that render the widely used blood thinner clopidogrel ineffective. Patients with the genetic mutations who received alternative medications were much less likely to die or have a heart attack, stroke or other complications than patients with the mutations who received clopidogrel.
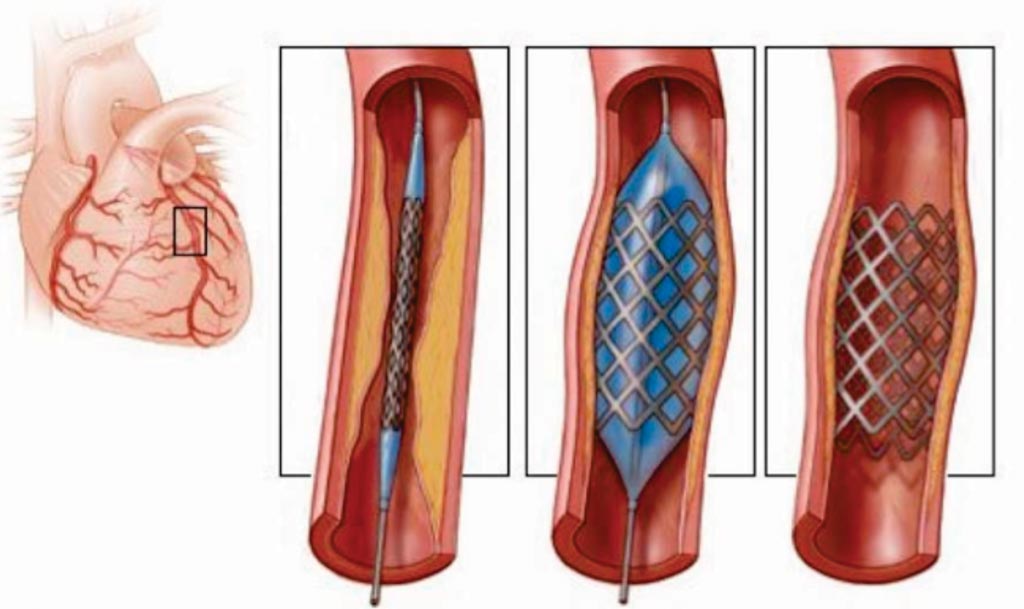
Image: A diagram of various stents used in angioplasty (Photo courtesy of Open Biomedical Initiative).
Medical scientists at University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill (NC, USA) included 1,193 patients in a study at the University of North Carolina Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory who received stent placement between July 1, 2012, and June 30, 2014. Their average age was 63 years and more than two-thirds were male. Most were white, 21% were black, and 1% was Asian. Patients identified as high risk, due to decreased blood flow to the heart, received the genetic testing and the follow up was 12 months.
The scientists used the polymerase chain reaction-based TaqMan allelic discrimination assays, The team found genetic testing for cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily C member 19 (CYP2C19) mutations could be used to guide blood-thinner treatment after stent placement. Furthermore, patients with the mutations who received one of two clopidogrel alternatives compared to clopidogrel were more than three times less likely to die or have a heart attack, stroke or other major complications 12 months after treatment. Specifically, major complications occurred among 27 % of clopidogrel patients with the genetic mutations, compared to 8% of patients with the mutations who received the alternative medications.
George Andrew Stouffer, III, MD, FAHA, chief of cardiology and co-director of the McAllister Heart Institute at UNC, said, “We are using CYP2C19 genetic testing on a daily basis at our institution to help decide in a timely manner which drug to prescribe.” The study was published on April 3, 2018, in the journal Circulation: Genomic and Precision Medicine.
Related Links:
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill