Genetic Biomarkers Determine Risk of Developing Endometriosis
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 07 Feb 2018
Endometriosis is one of the most common women's health disorders, causing up to 10% of reproductive-age women to experience painful periods and potential infertility. Diagnosis can elude patients for decades, in part because exploratory surgery is considered the ultimate diagnostic method.Posted on 07 Feb 2018
Endometriosis is a condition in which the layer of tissue that normally covers the inside of the uterus grows outside of it. Most often this is on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and tissue around the uterus and ovaries; however, in rare cases it may also occur in other parts of the body.
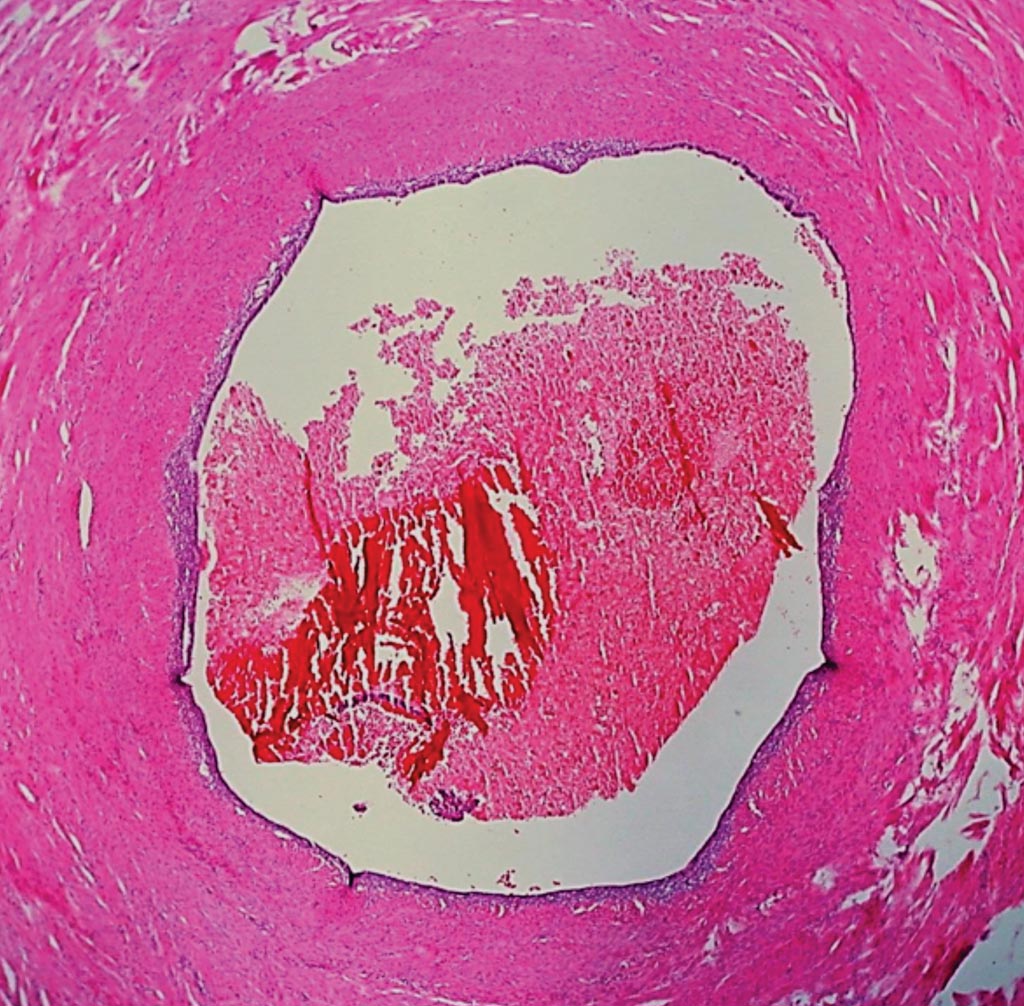
Image: Histopathology of Endometriosis of the Fallopian Tube (Luminal Pattern). In this pattern, the normal complex, folded tubal mucosa is replaced by flat columnar epithelium with a tin underpinning of specialized endometrial stroma. There are also blood cells in the lumen Photo courtesy of Dr. Ed Uthman).
Predictive Technology (Salt Lake City, UT, USA), a biotech holding corporation, is commercializing an assay that uses genetic biomarkers to determine whether a woman is at risk of developing endometriosis as well as to diagnose the disease and personalize treatment guidance. The assay uses both blood or saliva samples and employs polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to detect a set of biomarkers that the firm purports to be both diagnostic and prognostic of endometriosis. The assay was originally developed by Juneau Biosciences (Salt Lake City, UT, USA).
An earlier genome-wide association study (GWAS) study had shown a relationship with some single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), while an article published last year described a panel of four genes associated with endometriosis that are potential regulators of mesothelial barrier integrity, suggesting a mechanism for the disease. The Predictive Technology test will enable the firm to predict how well patients are going to respond to different therapies, similar to a pharmacogenomics test.
Specifically, the company will use data analytics to gauge the interaction between the individual and the type of disease to guide treatment more appropriately, both its own therapeutic as well as other treatments like hormonal birth control, GnRH agonists such as Lupron, or possibly a GnRH antagonist from AbbVie called Elagolix that is currently before the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA, Silver Springs, MD, USA).
Bradley Robinson, CEO of Predictive Technology, said, “The prognostic aspect of the company's test could lead to future development of a "screen your teen" product, which could be used to uncover risk of endometriosis prior to puberty, well before damage and scarring of the disease causes symptoms of painful periods and potential infertility.”
Related Links:
Predictive Technology
Juneau Biosciences














