Effective Prognostic Marker Identified for Ovarian Cancer
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 21 Aug 2014
High-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HG- SOC) is the most prevalent of epithelial ovarian cancers and remains poorly understood due to a lack of biomarkers identified for clinical use, for diagnosis, or for prognosis of patient survival rates.Posted on 21 Aug 2014
The application of bioinformatics analysis on cancer genomics data has enabled the identification genes whose mutation status could be used for prognosis and development of personalized treatment for HG-SOC, which is the most lethal ovarian cancers, with only 30% patients surviving more than five years after diagnosis.
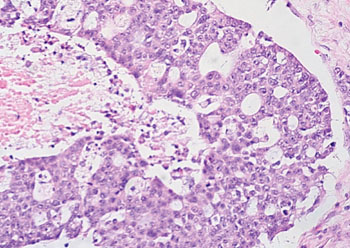
Image: Histopathology of high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (Photo courtesy of Dr. Ed Uthman, MD).
Scientists at the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR; Singapore) analyzed data from 334 HG-SOC patients logged in the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA; Bethesda, MD, USA). The sequences were generated based on either Illumina (San Diego, CA, USA) or ABI SOLID sequencing technologies (Applied Biosystems; Carlsbad, CA, USA).
The team identified the gene, Checkpoint Kinase 2 (CHEK2), as an effective prognostic marker of patient survival. HG-SOC patients with mutations in this gene succumbed to the disease within five years of diagnosis, possibly because CHEK2 mutations were associated with poor response to existing cancer therapies. Mortality after diagnosis currently remains high, as patients receive similar treatment options of chemotherapy and radiotherapy despite the diverse nature of tumor cells within tumors and across different tumor samples. With these findings, personalized medicine for ovarian cancer could be developed, with targeted treatment that would be optimized for subgroups of patients.
Sir David Philip Lane, FRS, FRSE FRCPath, the chief scientist at A*STAR, said, “These findings show how the various research institutes at A*STAR offer their expertise in developing new approaches to examine different aspects of the same disease that have not been successfully studied before, such as ovarian cancer. The diverse capabilities and knowledge of our scientists allows us to investigate diseases holistically, from diagnosis to treatment.” The study was published on July 15, 2014, in the journal Cell Cycle.
Related Links:
Agency for Science, Technology and Research
The Cancer Genome Atlas
Illumina