Lateral Flow Test Detects Bacteria Causing Gingivitis and Cardiovascular Diseases
Posted on 20 Oct 2023
Gingivitis, the initial stage of gum disease, is caused by bacteria that can make their way into the bloodstream and result in cardiovascular disease as well as other serious health conditions. A newly designed device now provides an early warning system for tooth decay that may result from conditions like gingivitis and periodontitis.
In order to develop the gingivitis test, engineers at the University of Cincinnati (Cincinnati, OH, USA) faced the challenge of creating a device capable of identifying the specific bacteria responsible for gingivitis. The researchers, who have been exploring biosensing for various applications, are focusing on saliva for point-of-care (POC) tests. Saliva is an ideal substance for testing since it's easy to collect and plentiful. However, saliva is also a complex mixture containing elements like proteins, peptides, DNA, and other compounds, each potentially signaling different health conditions, which makes isolating a particular biomarker for analysis difficult.
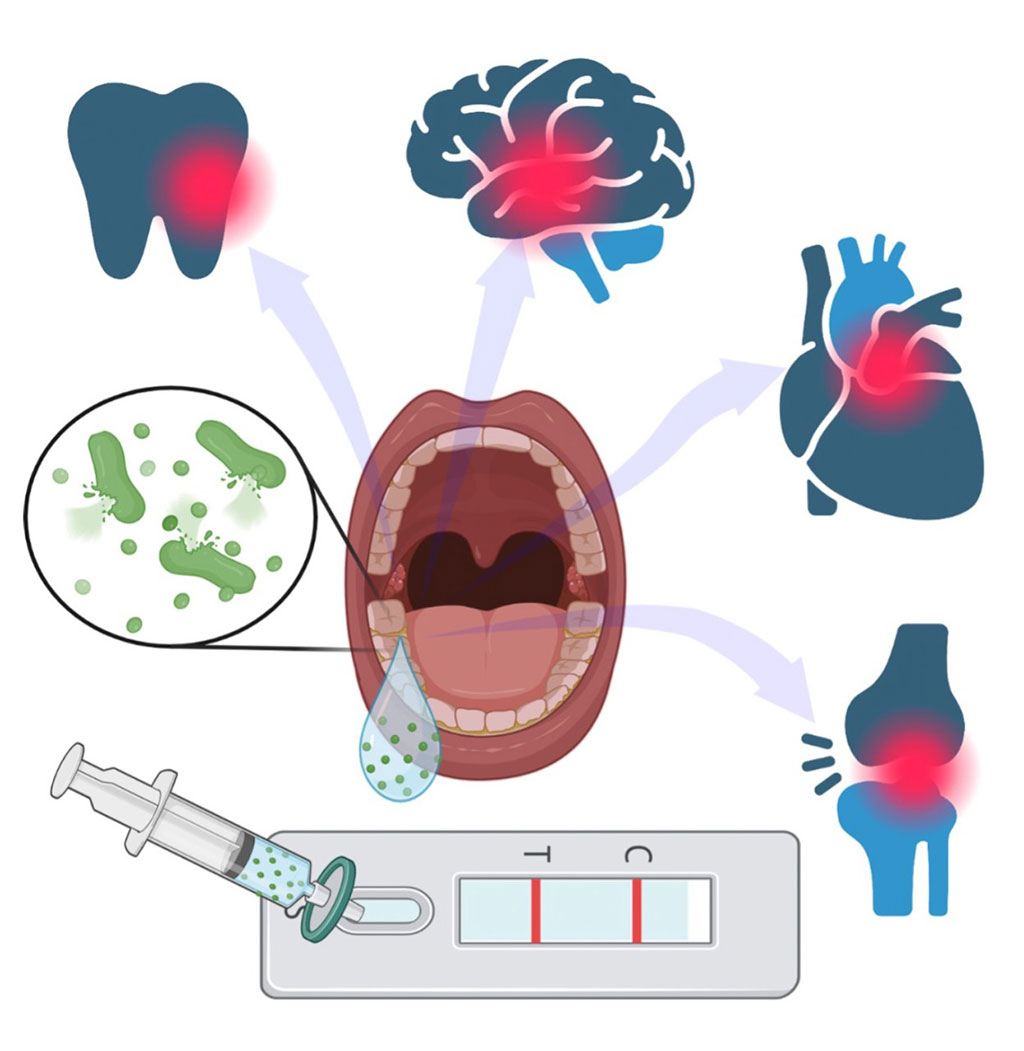
To resolve this issue, researchers pretreated the sample using potato starch to remove a protein called amylase that could interfere with the test results. Their point-of-care lateral flow assay (LFA) device uses antibodies that react to the endotoxins found in the bacteria. The team will undertake further development to improve assay sensitivity using saliva samples and explore its ability to detect multiple lipopolysaccharides (LPS) molecules related to diseases for more accurate diagnostics of patients' health. Finally, because the sensitivity of the current antibody-based detection is significantly affected by the performance of the conjugate antibody, the researchers will work on developing aptamer-based sandwich lateral flow assay for improved flexibility and performance.
“It’s been quite the challenge to get to the point where we can detect this toxin created by the bacteria responsible for gingivitis,” said Andrew Steckl, an Ohio Eminent Scholar and distinguished research professor in UC’s College of Engineering and Applied Science. “There are good reasons to use saliva. It’s relatively plentiful and easy to obtain through noninvasive methods. And saliva has a lot of important elements that can act as indicators of your health.”
Related Links:
University of Cincinnati














