Laser Light Method Uses AI-Assisted Imaging to Identify Bacteria in Fluids
Posted on 07 Mar 2023
The commonly used traditional culturing techniques often require several hours or even days for completion. Now, a revolutionary approach promises to deliver faster, more precise, and cost-effective microbial assays of almost any fluid one wishes to test for microbes in an instant.
Scientists at Stanford University (Stanford, CA, USA) have created an innovative adaptation of the technology in an old inkjet printer and combined it with AI-assisted imaging to develop a faster, cheaper way to spot bacteria in blood, wastewater, and more. The method involves shining a laser on a drop of blood, mucus, or wastewater, and then using the light reflecting back to positively identify bacteria in the sample. The new test can be carried out within minutes and offers hope for improved and rapid detection of infections, more effective utilization of antibiotics, safer food products, enhanced environmental surveillance, and speedier drug development processes.
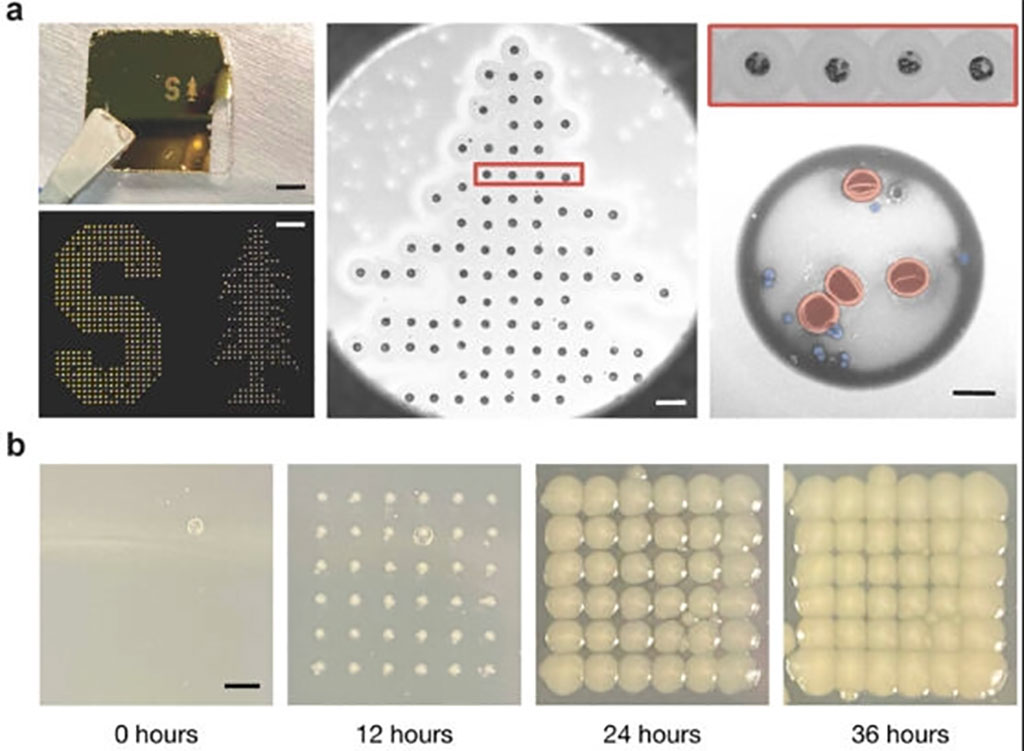
The novelty of this discovery lies not in the fact that bacteria possess unique spectral fingerprints, which has been established for years, but rather in how the research team has managed to extract these spectra amidst the blinding array of light emanating from every sample. A single milliliter of blood can contain billions of cells, merely a tiny fraction of which may be microbes. Therefore, the challenge was to identify a way to exclusively distinguish and amplify the light emanating just from the bacteria. The team pursued different scientific approaches, blending a decades-old computing technology - the inkjet printer - with two of the most advanced technologies of our times - artificial intelligence and nanoparticles.
The researchers found a solution to the difficulties of handling biological samples by modifying the printer to use acoustic pulses in order to put samples to paper. This method results in each printed blood dot being just two trillionths of a liter in volume, making them incredibly small - over a billion times smaller than a raindrop. Due to their tiny size, these droplets may contain just a few dozen cells. To enhance the bacteria detection process, the researchers infused the samples with gold nanorods, which act like antennas that draw laser light towards any present bacteria and amplify the signal to 1500 times its original strength. With appropriate isolation and amplification, the bacterial spectra clearly stand out for identification. The researchers also utilized machine learning to analyze the spectra of each printed dot and identify any telltale signatures of bacteria in the sample.
“We can find out not just that bacteria are present, but specifically which bacteria are in the sample – E. coli, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Salmonella, anthrax, and more,” said Jennifer Dionne, an associate professor of materials science and engineering and, by courtesy, of radiology at Stanford University. “Every microbe has its own unique optical fingerprint. It’s like the genetic and proteomic code scribbled in light.”
Related Links:
Stanford University














