YKL-40 Associated with Severity in Patients with Necrotizing Soft-Tissue Infection
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 28 Oct 2021
Necrotizing soft-tissue infection (NSTI) is a rare, severe and fast-progressing bacterial infection. NSTI can be caused by a myriad of aerobic, anaerobic and facultative anaerobic bacteria, but predominantly by Group A Streptococcus in monomicrobial infections.Posted on 28 Oct 2021
YKL-40, also called chitinase-3-like-1 protein, may be an attractive prognostic biomarker in NSTI. YKL-40 is an acute phase protein secreted by several of immune cells, including macrophages, neutrophils and endothelial cells. Proteomic analysis has indicated YKL-40 as a promising biomarker in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock.
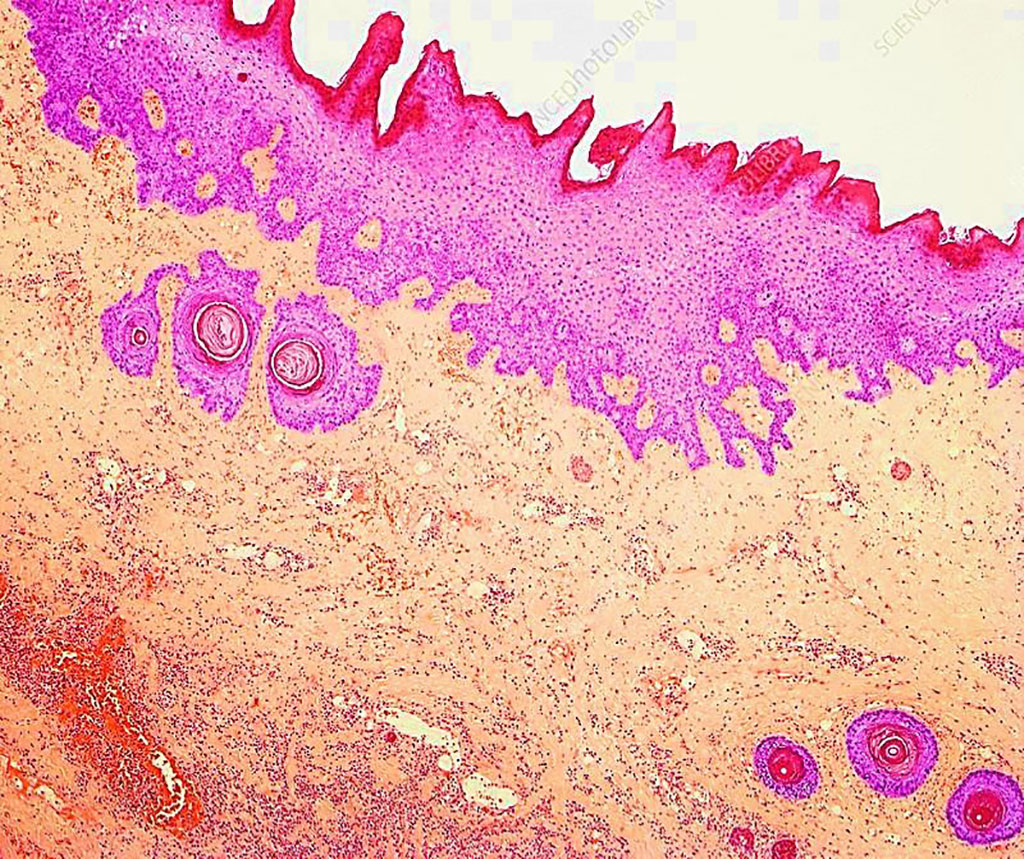
Image: Histopathological features of necrotizing fasciitis; light micrograph of a section of infected skin showing an extensive acute inflammatory reaction with associated intravascular thrombosis and necrosis (Photo courtesy of Dr. Steve Gschmeissner/Science Photo Library)
Clinical Scientists at the Copenhagen University Hospital (Copenhagen, Denmark) investigated the association between plasma YKL-40 and 30-day mortality in patients with NSTI, and assessed its value as a marker of disease severity. They determined plasma YKL-40 levels in 161 patients with NSTI and 65 age-sex matched controls upon admission and at day 1, 2 and 3.
Patient had blood samples collected into ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) sample tubes upon admission (baseline), and at the following three days (all between 8 AM and 12 AM). Plasma YKL-40 was quantified in duplicates by commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent (ELISA) technique (Quidel, San Diego, CA, USA) at each of the four time points. The minimal detectable limit for YKL-40 was 10 ng/mL.
The investigators reported that baseline plasma YKL-40 was 1,191 ng/mL in patients with NSTI compared with 40 ng/mL in controls. YKL-40 was found to be significantly higher in patients with septic shock (1,942 versus 720 ng/mL), and in patients receiving renal-replacement therapy (2,382 versus 1,041 ng/mL). YKL-40 correlated with Simplified Acute Physiology Score II. Baseline YKL-40 above 1,840 ng/mL was associated with increased risk of 30-day mortality in age-sex-comorbidity adjusted analysis (OR 3.77), but after further adjustment for Simplified Acute Physiology Score II no association was found between YKL-40 and early mortality.
Plasma YKL-40 was significantly higher in patients with NSTI compared to controls at admission, and at day 1 and 2. Plasma YKL-40 at admission was significantly higher among 45 patients infected with mono or polymicrobial Group A Streptococcus in blood and/or tissue (2,338 ng/mL) compared to 104 other types of NSTI (1,246 ng/mL). However, this was not observed at day 1, 2 and 3. No microbial findings were observed in 12 patients.
The authors concluded that high plasma YKL-40 levels were associated with disease severity and risk of death in patients with NSTI. However, YKL-40 is not an independent predictor for 30-day mortality. The study was published on October 9, 2021 in the journal BMC Infectious Diseases.
Related Links:
Copenhagen University Hospital
Quidel














