Six Biomarkers Predict Severity of COVID-19
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 08 Sep 2020
Coronavirus disease 2019 patients admitted to the ICU have high mortality. The host response to coronavirus disease 2019 has only been partially elucidated, and prognostic biomarkers have not been identified.Posted on 08 Sep 2020
COVID-19 primarily affects lungs and in the most severe cases results in acute respiratory distress syndrome associated with or without multiple organ dysfunction. A “cytokine storm” may determine the severity of COVID-19, which is the excessive or uncontrolled release of cytokines in response to a pathologic event, such as a viral infection.
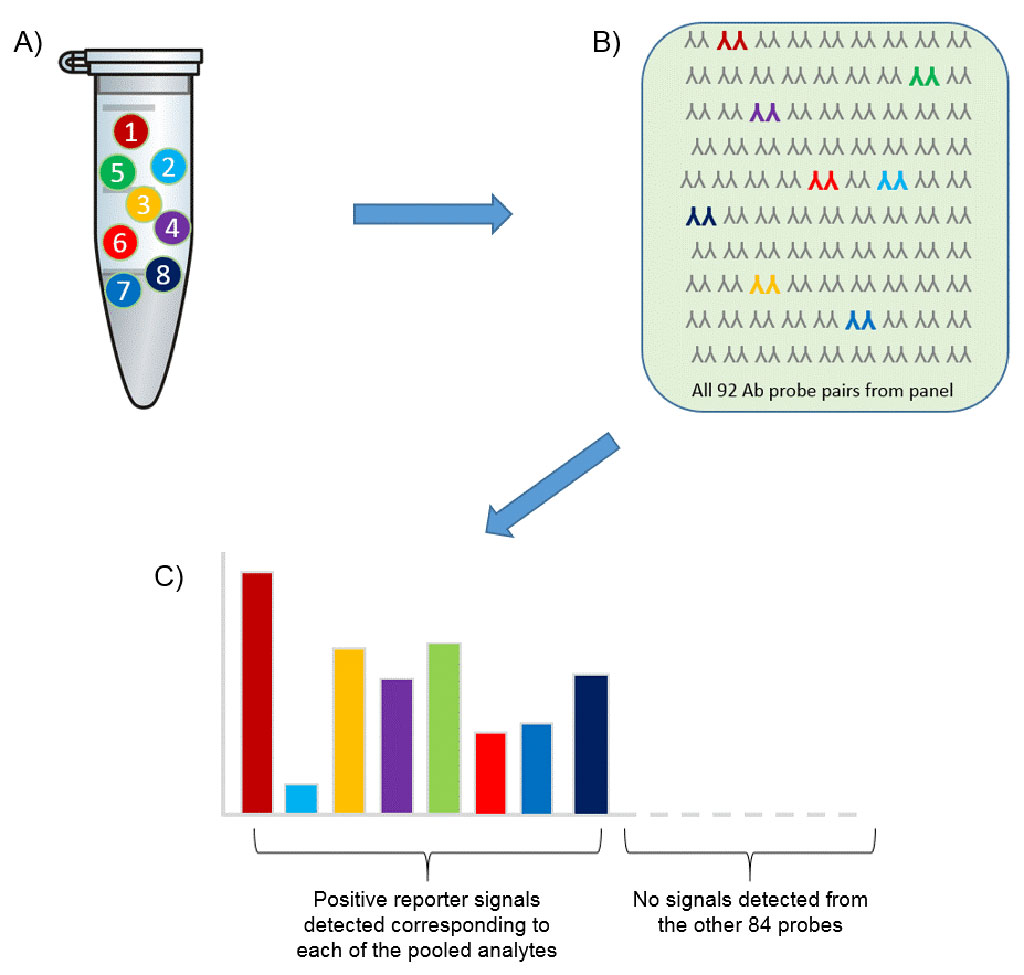
Image: Schematic diagram of the immunoassay based on proximity extension assay (PEA) technology (Photo courtesy of Olink Proteomics).
Scientists from various institutions collaborating with the Lawson Health Research Institute (London, ON, Canada) enrolled consecutive patients who were admitted to their level-3 academic ICUs at London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC, London, ON, Canada) and were suspected of having COVID-19 based on standard hospital screening procedures. Blood sampling began on ICU admission for up to three days in COVID-19 negative patients or up to seven days in COVID-19 positive patients (with one additional blood draw on day 10).
The team measured 1,161 plasma proteins from the blood of 30 participants: 10 COVID-19 patients and 10 patients with other infections admitted to LHSC's ICU, as well as 10 healthy control participants. A total of 1,161 plasma proteins were measured using an immunoassay based on proximity extension assay (PEA) technology (Olink Proteomics, Uppsala, Sweden). The team identified six molecules of importance (CLM-1, IL12RB1, CD83, FAM3B, IGFR1R and OPTC). They found that these molecules were elevated in COVID-19 patients who would become even more severely ill. They found that when measured on a COVID-19 patient's first day of ICU admission, the molecules could be used to predict which patients will survive following standard ICU treatment.
Douglas D. Fraser, MD, PhD, a Critical Care Physician and lead study author, said, “When a patient is admitted to ICU, we normally wait to see if they are going to get worse before we consider any risky interventions. To improve outcomes, we not only need new therapies but also a way to predict prognosis or which patients are going to get worse.”
The authors conclude that they have described a unique proteome in COVID-19 positive ICU patients, with identification of six novel proteins that appear to be accurate outcome biomarkers for future studies. Given the high morbidity and mortality associated with COVID-19 critical illness, their exploratory data may be invaluable for guiding resource mobilization and/or goals of care discussion, but only after validation in larger COVID-19 positive cohorts. Furthermore, patient stratification is critically important for future COVID-19 interventional trials. The study was published in the September, 2020 issue of the journal Critical Care Explorations.
Related Links:
Lawson Health Research Institute
London Health Sciences Centre
Olink Proteomics














